IBDP Physics- C.2 Wave model- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
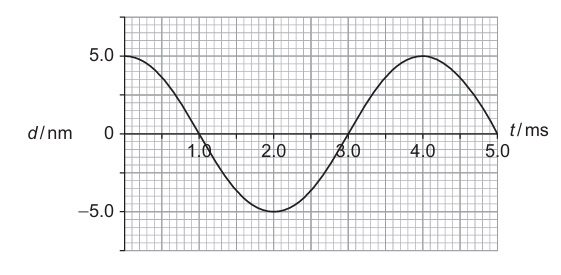
(B) 250 Hz, 5.0 nm
(C) \(4.0 \times 10^{-3}\) Hz, 10.0 nm
(D) 250 Hz, 10.0 nm
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Determine Amplitude:
The maximum displacement from the equilibrium position (\(d = 0\)) is 5.0 nm.
2. Determine Period (T):
The graph shows one complete cycle from \(t = 0\) to \(t = 4.0\) ms.
\(T = 4.0 \text{ ms} = 4.0 \times 10^{-3} \text{ s}\).
3. Calculate Frequency (f):
\(f = \frac{1}{T} = \frac{1}{4.0 \times 10^{-3}} = 250 \text{ Hz}\).
4. Match Options:
Frequency = 250 Hz, Amplitude = 5.0 nm.
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
It is a …
(B) longitudinal wave
(C) standing wave
(D) travelling wave
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Polarization refers to the restriction of the direction of oscillation of a wave. Only transverse waves have oscillations that are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation and can therefore be polarized.
Longitudinal waves oscillate parallel to the direction of propagation and cannot be polarized. Whether a wave is standing or travelling does not determine whether it can be polarized.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which point is at the centre of a compression?

(B) B
(C) C
(D) D
▶️ Answer/Explanation
For a longitudinal wave, a compression occurs where neighbouring particles are closest together.
This corresponds to a region where the displacement changes from positive to negative with distance (the curve has a steep negative slope), meaning particles on either side have moved towards the same region.
From the graph, point A is at the centre of a compression.
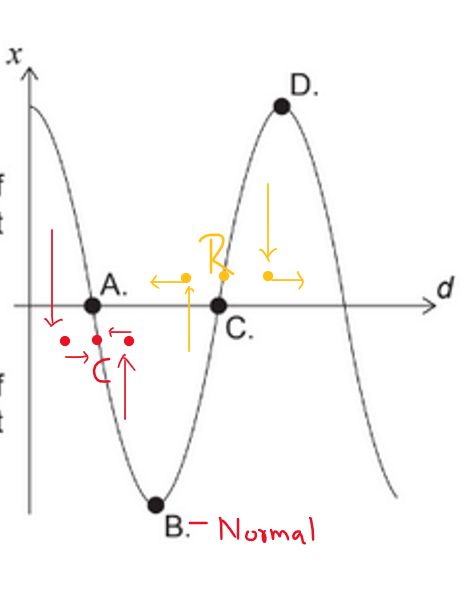
So:
A — compression
B — normal pressure point
C — rarefaction
D — normal pressure point
✅ Answer: (A)
