IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 1A and 1B for 2025 Exams
IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 1A and 1B- April/May 2025 Exam
IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 1A and 1B: Prepare for the IB exams with subject-specific Prediction questions, model answers. All topics covered.
Prepared by IB teachers: Access our IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 1A and 1B with model answer. Students: Practice with exam-style papers for IB DP Biology HL Exam
Question 1
What allows the movement of water under tension in the xylem?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation: The cohesion of water molecules due to hydrogen bonding allows water to move under tension in the xylem.
Question 2
The diagram shows the elements present in two organic molecules, W and X. Which molecules could W and X be?
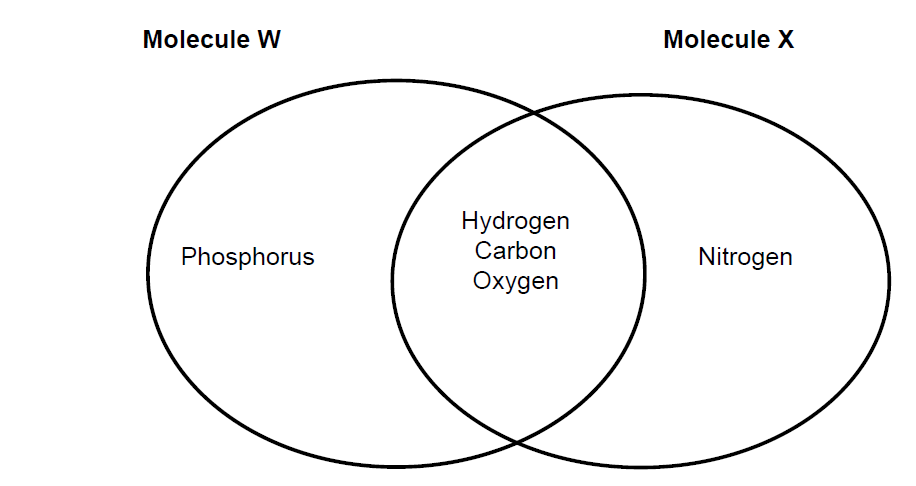
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation: Phospholipids contain phosphorus (P) and proteins contain nitrogen (N), matching the elements shown in the diagram.
Question 3
Which property of DNA explains how genetic information can be replicated accurately?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: A
Explanation: Complementary base pairing ensures that each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
Question 4
Which molecules are produced during the hydrolysis of a triglyceride molecule?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation: Hydrolysis of triglycerides breaks the ester bonds, releasing fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 5
The structure of monomers affects the structure and function of the polymers they form. Which row describes the structural features of polysaccharides made from alpha-glucose and beta-glucose?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Answer: B
Explanation: Starch (from alpha-glucose) is branched and helical, while cellulose (from beta-glucose) is unbranched and straight.
Question 6

What describes the structure of insulin?
Select the correct option:
A. Insulin is a fibrous protein, since the amino acids are arranged in a linear pattern.
B. Insulin consists of a single continuous polypeptide chain with one free amino terminal and one free acid terminal.
C. Insulin has three disulphide bridges giving it tertiary structure and two polypeptide chains giving it quaternary structure.
D. Insulin has primary and secondary structure only, as there is no evidence of a three-dimensional shape in the diagram.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Answer: C
Explanation:
Insulin is a globular protein hormone with a complex structure. Let’s analyze each option and the diagram:
- A. Incorrect: Fibrous proteins (e.g., collagen) have long, repetitive, linear structures designed for strength. Insulin is a globular protein with a compact, functional shape, not a fibrous one, despite the linear representation in the diagram.
- B. Incorrect: The diagram shows two distinct polypeptide chains (Chain A and Chain B) connected by disulphide bridges (Cys-Cys bonds), not a single continuous chain. Insulin has two chains: Chain A (21 amino acids) and Chain B (30 amino acids).
- C. Correct: The diagram indicates three disulphide bridges (Cys residues linked between chains and within Chain B), which stabilize the tertiary structure (3D folding of each chain). The presence of two polypeptide chains (A and B) interacting via these bridges indicates quaternary structure (multiple polypeptide subunits). This matches insulin’s known structure.
- D. Incorrect: The diagram shows disulphide bonds, which contribute to tertiary structure, and two chains, indicating quaternary structure. While the diagram is 2D, insulin’s biological function relies on its 3D shape, which is implied by these features.
Scientific Detail:
Insulin’s structure includes:
- Primary: Sequence of amino acids (shown in the diagram).
- Secondary: Local folding (e.g., alpha helices, not visible in the diagram but present in insulin).
- Tertiary: 3D folding stabilized by three disulphide bridges (two inter-chain: A7-B7, A20-B19; one intra-chain: A6-A11).
- Quaternary: Two chains (A and B) linked together.
Mark Allocation:
[1 mark for correct answer, 3 marks for understanding primary, tertiary, and quaternary structures and rejecting incorrect options.]
