IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 2 for 2025 Exams
IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 2- April/May 2025 Exam
IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 2: Prepare for the IB exams with subject-specific Prediction questions, model answers. All topics covered.
Prepared by IB teachers: Access our IB DP Biology HL Prediction Paper 2 with model answer. Students: Practice with exam-style papers for IB DP Biology HL Exam
Question 1: Squirrel Defense Mechanisms
California ground squirrels (Otospermophilus beecheyi) chew moulted rattlesnake skins and lick their fur to acquire rattlesnake scent as a defense mechanism. An experiment tested rattlesnake responses to different scents.
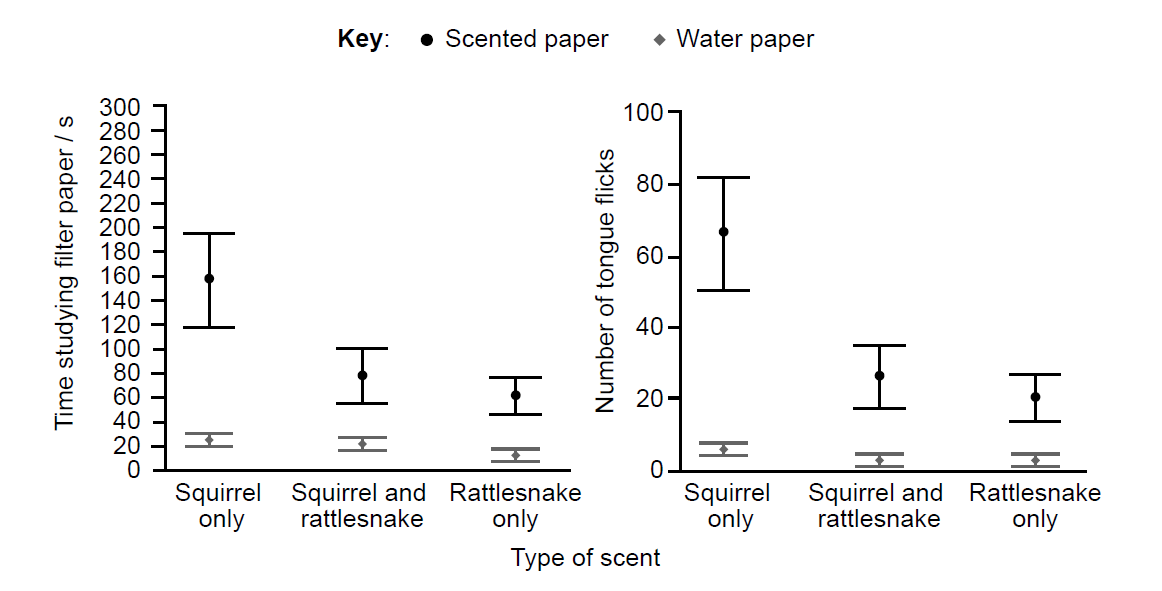
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: 80s (accept 75s–85s)
Explanation: From the graph, the difference between pure squirrel scent (≈20s) and mixed scent (≈100s) is approximately 80 seconds.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer:
- Snakes spend minimal time studying control filter paper (water).
- Filter paper itself isn’t attractive to snakes.
Explanation: The control establishes baseline behavior, showing snakes aren’t responding to the paper itself but to specific scents.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: To ensure snakes respond to scent rather than position preference.
Explanation: Eliminates potential bias from snakes developing a preference for one side of the chamber.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: Masks squirrel scent/suggests presence of rival snake.
Explanation: Snakes may avoid areas with other snakes’ scents to prevent conflict.
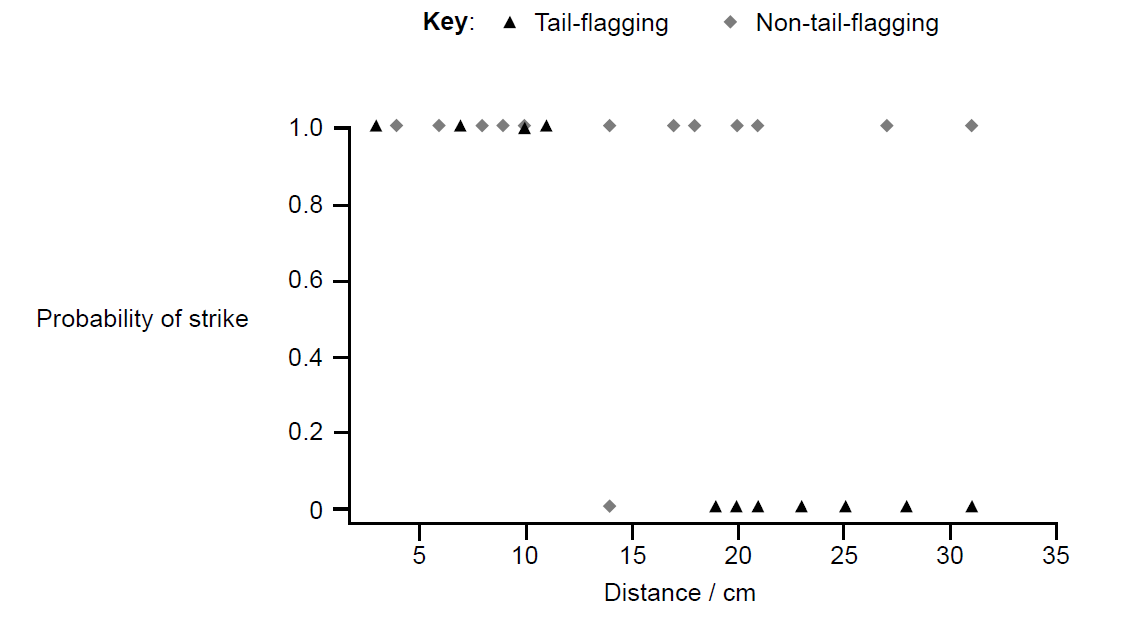
Key: ▲ Tail-flagging squirrels ◆ Non-tail-flagging squirrels
Source: Adapted from Barbour & Clark (2012)
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer:
- Both have high strike probability at short distances (<10 cm).
- Tail-flagging squirrels have lower strike probability at greater distances (e.g., 20 cm: ≈0.2 vs. 0.8 for non-tail-flagging).
Explanation: Tail-flagging deters attacks beyond close range, signaling alertness to the snake.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: 14 cm (accept 12–16 cm).
Explanation: The tail-flagging curve intersects the 0.5 probability line at ~14 cm on the x-axis.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: Tail-flagging signals alertness, making successful strikes unlikely.
Explanation: Snakes conserve energy by avoiding prey that is aware of their presence.
Grey squirrels (Sciurus carolinensis) were exposed to hawk sounds and bird chatter. Their vigilance was measured:
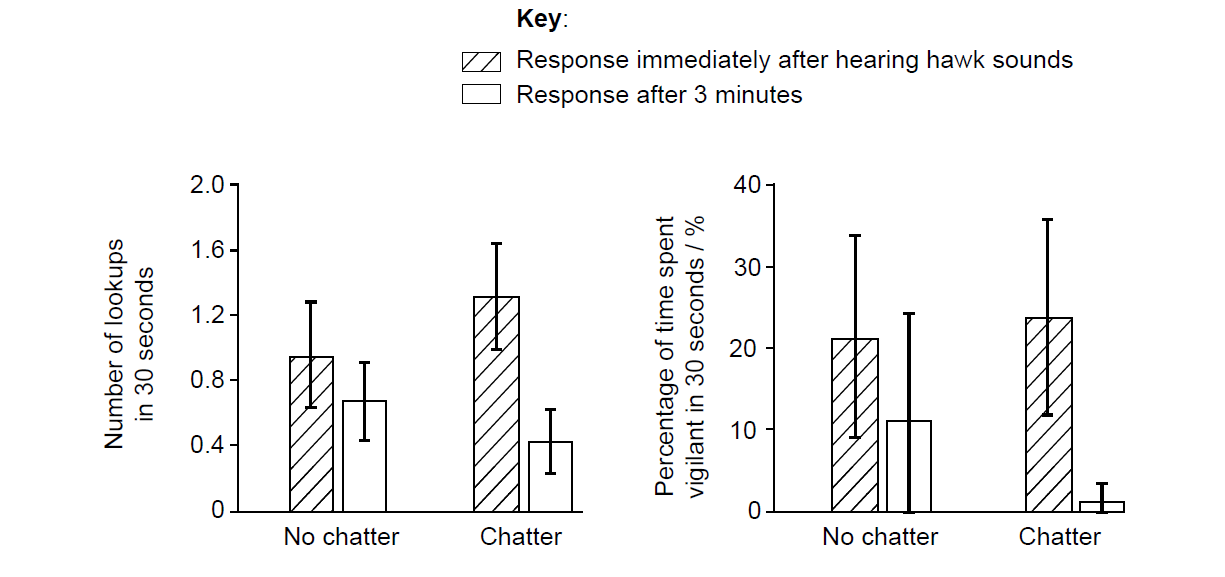
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer: With bird chatter AND 3 minutes after hawk sounds.
Explanation: Chatter signals safety, and time reduces perceived threat.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer:
- No significant difference immediately after hawk sounds (bars overlap).
- Chatter’s effect becomes apparent after 3 minutes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Correct answer:
- Chatter reduces vigilance over time (lower lookups and % vigilance after 3 minutes).
- Squirrels interpret chatter as an “all clear” signal.
- Immediate response to hawk sounds dominates initial behavior.
