Nuclear properties and the radioactive decay law IB DP Physics Study Notes - 2025 Syllabus
Nuclear properties and the radioactive decay law IB DP Physics Study Notes
Nuclear properties and the radioactive decay law IB DP Physics Study Notes at IITian Academy focus on specific topic and type of questions asked in actual exam. Study Notes focus on IB Physics syllabus with Students should understand
the existence of the strong nuclear force, a short-range, attractive force between nucleons
the activity, count rate and half-life in radioactive decay
the changes in activity and count rate during radioactive decay using integer values of half-life
the effect of background radiation on count rate.
Standard level and higher level: 7 hours
Additional higher level: 5 hours
- IB DP Physics 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Physics 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 1
- IB DP Physics 2025 SL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
- IB DP Physics 2025 HL- IB Style Practice Questions with Answer-Topic Wise-Paper 2
Nuclear reactions

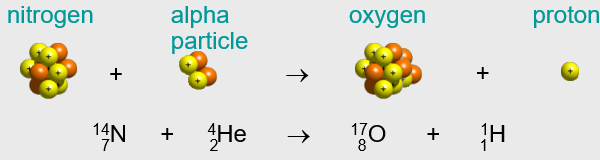
- The first induced nuclear reaction was accomplished by none other than Australian physicist Ernest Rutherford, the same guy who bombarded atoms with alpha particles and discovered the nuclear structure of the atom.
- From his experience with alpha emitters, Rutherford thought that alpha particles might just be energetic enough to breach the nuclear boundary.

- In fact, he did just that in the following nuclear reaction:

FYI
- The nuclear reaction above is an example of an artificial (induced) transmutation – where one element is transmuted into another through artificial means. It is alchemy!
- Here is another induced transmutation that has been successfully accomplished:



FYI

- At last man’s striving in the studies of alchemy have come to fruition! Recall what a driving force this was in chemistry and physics…
- Particle accelerators are required.
- But don’t go home asking mom for one so you can make your own bootleg gold.
- Both accelerators and energy costs far outweigh the return in gold!
Example:
Carbon-14 undergoes β⁻ decay. Write and balance the nuclear equation showing this transformation.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The decay equation is:
\( \ce{^{14}_6C -> ^{14}_7N + \beta^- + \bar{\nu}_e} \)
- Conservation of nucleon number: 14 = 14
- Conservation of charge: 6 = 7 + (-1)
- Include the antineutrino \( \bar{\nu}_e \) in β⁻ decay
The unified atomic mass unit
- In the world of nuclear reactions, we have to keep very precise track of the mass of the nuclei if we are to determine the energy of a reaction.
- To this end, we define the unified atomic mass unit (u) using a neutral carbon-12 atom as our standard of precisely 12.000000 u.

Example:
How many atomic mass units (u) are there in 25.32 g of a substance?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Convert grams to kg: \( 25.32 \, \text{g} = 0.02532 \, \text{kg} \)
Use the relation: \( 1 \, \text{u} = 1.661 \times 10^{-27} \, \text{kg} \)
Now divide:
\( \frac{0.02532}{1.661 \times 10^{-27}} = \boxed{1.524 \times 10^{25} \, \text{u}} \)