IBDP Chemistry - Reactivity 3.1 Proton transfer reactions- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A - FA 2025
Question
(B) \(1.5\) cm\(^3\) s\(^{-1}\)
(C) \(1.0\) cm\(^3\) s\(^{-1}\)
(D) \(0.5\) cm\(^3\) s\(^{-1}\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
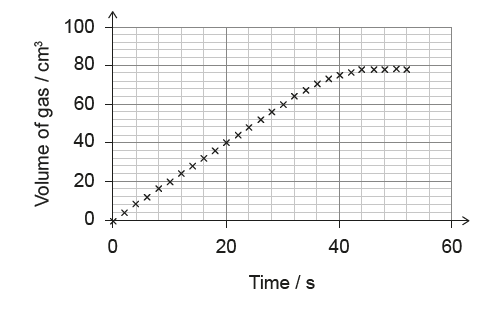
1. Define Average Rate:
\(\text{Average Rate} = \frac{\Delta \text{Volume}}{\Delta \text{Time}}\)
2. Read Graph Points:
- At \(t = 0\) s, \(V = 0\) cm\(^3\).
- At \(t = 20\) s, read the y-value. The graph passes through exactly \(40\) cm\(^3\) (check the grid lines: 20, 40, 60). Yes, at \(t=20\), \(V=40\).
3. Calculate Rate:
Rate = \(\frac{40 – 0}{20 – 0} = \frac{40}{20} = 2.0\) cm\(^3\) s\(^{-1}\).
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
Which combination describes a strong Brønsted–Lowry acid?
| Proton donor | Conjugate base | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | good | strong |
| B. | good | weak |
| C. | poor | strong |
| D. | poor | weak |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Therefore, the correct combination is:
✅ Answer: B — good proton donor, weak conjugate base.
Question
(B) \(2\text{HCl}(\text{aq}) + \text{ZnO}(\text{s}) \rightarrow \text{ZnCl}_{2}(\text{aq}) + \text{H}_{2}\text{O}(\ell)\)
(C) \(4\text{NH}_{3}(\text{g}) + 5\text{O}_{2}(\text{g}) \rightarrow 4\text{NO}(\text{g}) + 6\text{H}_{2}\text{O}(\ell)\)
(D) \(\text{C}_{2}\text{H}_{4}(\text{g}) + \text{H}_{2}(\text{g}) \rightarrow \text{C}_{2}\text{H}_{6}(\text{g})\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Recall Brønsted–Lowry neutralization:
A Brønsted–Lowry acid is a proton (\(\text{H}^{+}\)) donor and a Brønsted–Lowry base is a proton acceptor.
Neutralization occurs when an acid reacts with a base to form a salt and water.
2. Check each option:
(A) \(2\text{HCl}(\text{aq}) + \text{Zn}(\text{s})\): acid reacting with a metal → redox reaction producing \(\text{H}_{2}(\text{g})\), not neutralization.
(B) \(2\text{HCl}(\text{aq}) + \text{ZnO}(\text{s})\): \(\text{HCl}\) (acid) reacts with basic oxide \(\text{ZnO}\) (base) to give the salt \(\text{ZnCl}_{2}(\text{aq})\) and water \(\text{H}_{2}\text{O}(\ell)\) → this is acid–base neutralization.
(C) \(4\text{NH}_{3}(\text{g}) + 5\text{O}_{2}(\text{g})\): combustion/oxidation reaction, not neutralization.
(D) \(\text{C}_{2}\text{H}_{4}(\text{g}) + \text{H}_{2}(\text{g})\): hydrogenation (addition) reaction, not acid–base.
3. Select the correct reaction:
Only option (B) shows an acid reacting with a base to form a salt and water.
✅ Answer: (B)
