IBDP Chemistry - Structure 2.2 The covalent model- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A - FA 2025
Question
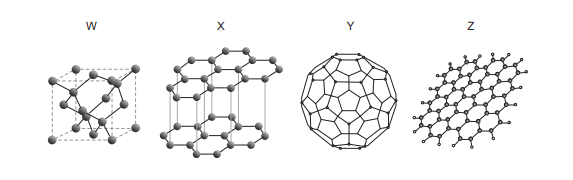
| Graphene | Fullerene | Graphite | Diamond | |
| A | Z | Y | X | W |
| B | W | Z | Y | X |
| C | X | W | Z | Y |
| D | Y | X | W | Z |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Identify each allotrope from its structure:
– \(W\): three-dimensional tetrahedral lattice of carbon atoms \(\Rightarrow\) diamond (\(\text{sp}^3\) hybridization).
– \(X\): stacked layers of hexagonal sheets with weak forces between layers \(\Rightarrow\) graphite (\(\text{sp}^2\) hybridization).
– \(Y\): roughly spherical cage of carbon atoms (e.g. \(\text{C}_{60}\)) \(\Rightarrow\) a fullerene.
– \(Z\): single extended hexagonal sheet of carbon atoms \(\Rightarrow\) graphene.
2. Match to the table:
Graphene \(\Rightarrow Z\)
Fullerene \(\Rightarrow Y\)
Graphite \(\Rightarrow X\)
Diamond \(\Rightarrow W\)
This pattern appears in row A.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
An incomplete octet means the central atom has fewer than \(8\) electrons in its valence shell in the Lewis structure.
For \(\text{H}_2\text{Se}\), \(\text{PH}_3\) and \(\text{OF}_2\), the central atoms (Se, P, and O) each have \(8\) electrons in their valence shell (bonding pairs plus lone pairs), so they obey the octet rule.
In \(\text{BF}_3\), boron is the central atom. It forms three single bonds with fluorine: \[ \text{B} – \text{F}_3 \] This gives boron only \(3 \times 2 = 6\) valence electrons around it, not \(8\), so boron has an incomplete octet.
Therefore, the molecule with a central atom that has an incomplete octet is \(\text{BF}_3\).
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In \(\text{SO}_2\), sulfur is the central atom. It is bonded to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons.
The electron domains around sulfur are therefore:
- Two bonding domains (the two \(\text{S–O}\) bonds).
- One non-bonding domain (one lone pair).
That gives a total of \(3\) electron domains around sulfur. According to VSEPR theory, \(3\) electron domains arrange themselves in a trigonal planar electron domain geometry.
(Note: the molecular shape of \(\text{SO}_2\) is bent, but the electron domain geometry is trigonal planar.)
✅ Answer: (D)
