IBDP Chemistry -Structure 2.4 From models to materials - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 2 -FA 2025
Question
\[ \text{Fe}^{3+}(aq) + 2\text{S}_2\text{O}_3^{2-}(aq) \rightarrow \text{Fe}(\text{S}_2\text{O}_3)_2^-(aq) \]
(i) Solid \(\text{CoCl}_2\) is added as a catalyst. Explain how the presence of the catalyst increases the rate of reaction.
(ii) The reaction proceeds until the violet colour disappears. During this process, the thiosulfate ion, \(\text{S}_2\text{O}_3^{2-}\), is oxidized to \(\text{SO}_2\), while \(\text{Fe}^{3+}\) is reduced to \(\text{Fe}^{2+}\). Deduce the oxidation half-equation and the overall redox equation for this second stage of the reaction.
(i) Describe each of these two types of bonding.
(ii) Deduce a Lewis (electron-dot) formula for the nitrate ion.
(iii) State the molecular shape of the nitrate ion.
Most-appropriate topic codes (Chemistry):
• TOPIC R2.1: Electron transfer reactions — part (a-ii)
• TOPIC S2.1: Ionic bonding — part (b-i)
• TOPIC S2.2: Covalent bonding — parts (b-i), (b-ii)
• TOPIC S2.4: From shape to function — part (b-iii)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
(i) The catalyst provides an alternative pathway with a lower activation energy (\(E_a\)), allowing more particles to react upon collision.
(ii)
• Oxidation: \(\text{S}_2\text{O}_3^{2-} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow 2\text{SO}_2 + 2\text{H}^+ + 4\text{e}^-\)
• Overall: \(\text{S}_2\text{O}_3^{2-} + 4\text{Fe}^{3+} + \text{H}_2\text{O} \rightarrow 2\text{SO}_2 + 4\text{Fe}^{2+} + 2\text{H}^+\)
(b)
(i)
• Ionic: Electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions (cations and anions).
• Covalent: Electrostatic attraction between shared pairs of electrons and the nuclei of bonded atoms.
(ii) Nitrogen double-bonded to one oxygen atom and single-bonded to two others, enclosed in square brackets with an overall \(1-\) charge (resonance structures apply). 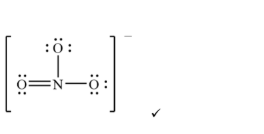
(iii) Trigonal planar.
