IBDP Physics SL Paper 1B- Data-Based Question- New Syllabus
Question
Volume = (10.6 ± 0.2) cm³
Mass = (10.82 ± 0.01) g
(ii) Express your final answers in kg m⁻³ with appropriate precision.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Read the volume at the bottom of the meniscus, with the cylinder placed on a horizontal surface and the viewer’s eyes level with the reading.
\(\boxed{\text{Read at bottom of meniscus with eye level to measurement}}\)
(b)(i)
\[ \rho = \frac{m}{V} = \frac{10.82}{10.6} \approx 1.02 \text{ g cm}^{-3} \] Uncertainty: \[ \frac{\Delta \rho}{\rho} = \frac{\Delta V}{V} + \frac{\Delta m}{m} = \frac{0.2}{10.6} + \frac{0.01}{10.82} \approx 0.0198 \] \[ \Delta \rho = 1.02 \times 0.0198 \approx 0.02 \text{ g cm}^{-3} \] \(\boxed{1.02 \pm 0.02 \text{ g cm}^{-3}}\)
(b)(ii)
Convert to kg m⁻³: \(1.02 \text{ g cm}^{-3} = 1020 \text{ kg m}^{-3}\), \(\Delta \rho = 20 \text{ kg m}^{-3}\).
\(\boxed{1020 \pm 20 \text{ kg m}^{-3}}\)
(c)
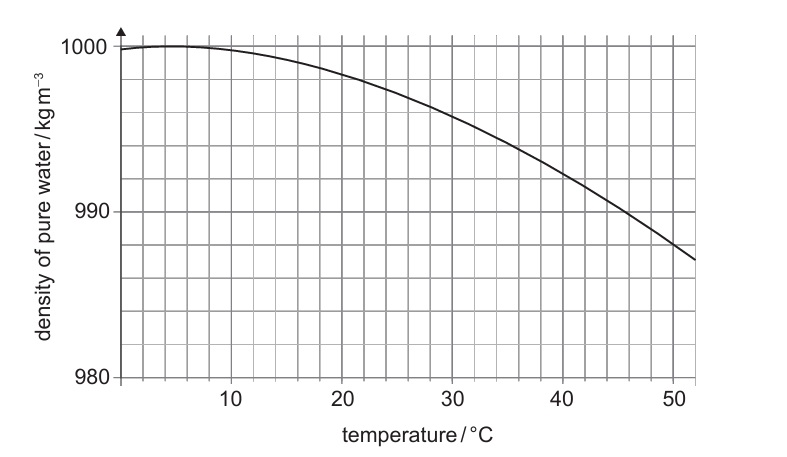
From the graph, pure water at 35°C has a density of ≈ 994 kg m⁻³. The measured density \(1020 \pm 20 \text{ kg m}^{-3}\) does not overlap with this value, so the sample is not pure.
\(\boxed{\text{Measured density outside range of pure water at 35°C → not pure.}}\)