IBDP Physics- A.2 Forces and momentum- IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
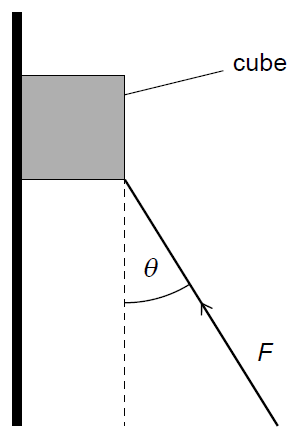
(B) \(\frac{(F \sin \theta – mg)}{m}\)
(C) \(\frac{(F \cos \theta – g)}{m}\)
(D) \(\frac{(F \sin \theta – g)}{m}\)
▶️ Answer/Explanation
1. Analyze forces in the vertical direction:
- Upward force: The vertical component of the applied force \(F\). Since \(\theta\) is measured from the vertical, this component is \(F \cos \theta\).
- Downward force: The weight of the cube, \(mg\).
2. Apply Newton’s second law:
\(\Sigma F_y = ma\)
\(F \cos \theta – mg = ma\)
3. Solve for the acceleration \(a\):
\(a = \frac{F \cos \theta – mg}{m}\)
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
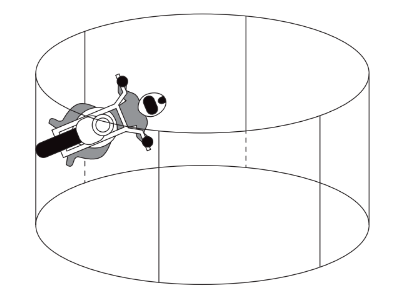
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The forces acting on the cyclist are: the weight acting vertically downward, the normal reaction from the wall acting horizontally towards the centre of the cylinder, and the frictional force acting vertically upward to balance the weight.
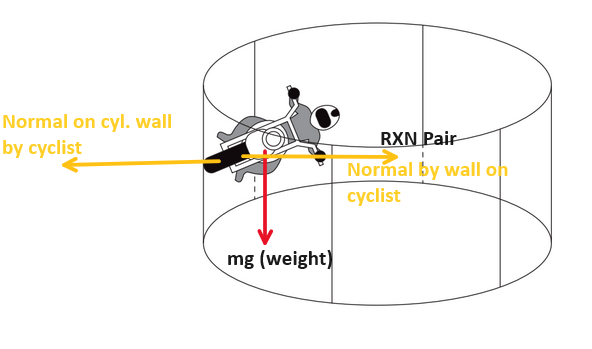
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
What is correct about the collision of the tennis ball with the ground?
(B) Elastic because the kinetic energy of the system is conserved
(C) Inelastic because momentum of the system is not conserved
(D) Inelastic because the kinetic energy of the system is not conserved
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In an elastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system is conserved. Here, the ball rebounds to a lower height, so it leaves the collision with less kinetic energy than it had just before impact.
Some kinetic energy is transformed into other forms of energy during the collision (for example, internal energy/heat and sound), so kinetic energy is not conserved.
✅ Answer: (D)
