Question
The kidney is an organ in the excretory system.
(a) Describe what is meant by the term excretion.
(b) State the name of the substance excreted by the lungs.
(c) Fig. 4.1 shows a simplified diagram of a cross-section of a kidney.
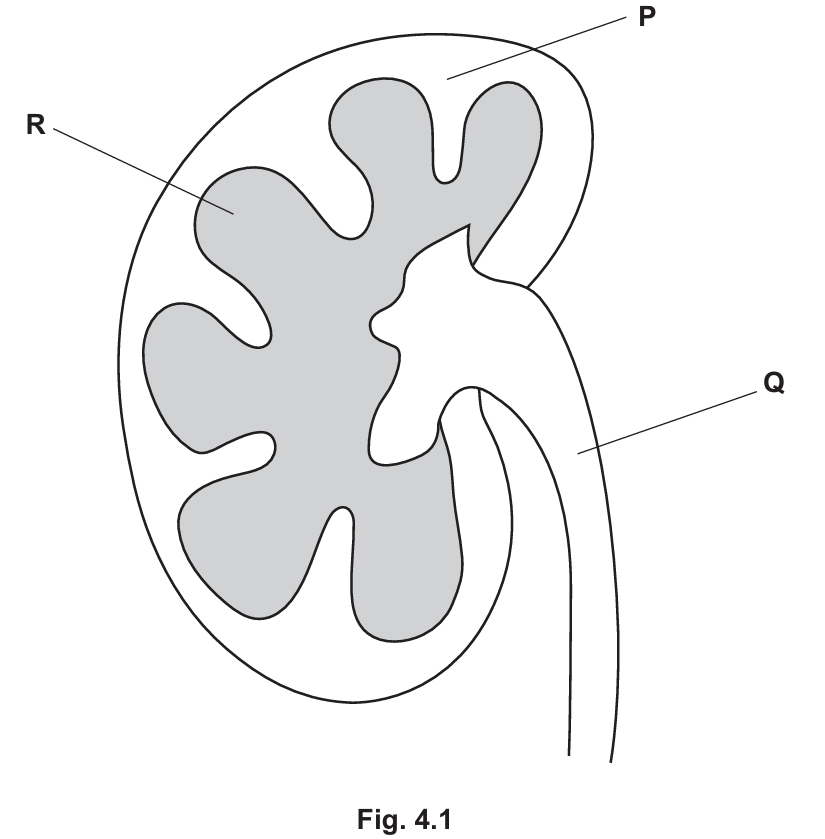
State the names of the parts labelled P, Q and R in Fig. 4.1.
(d) Fig. 4.2 shows the structure of a kidney nephron.
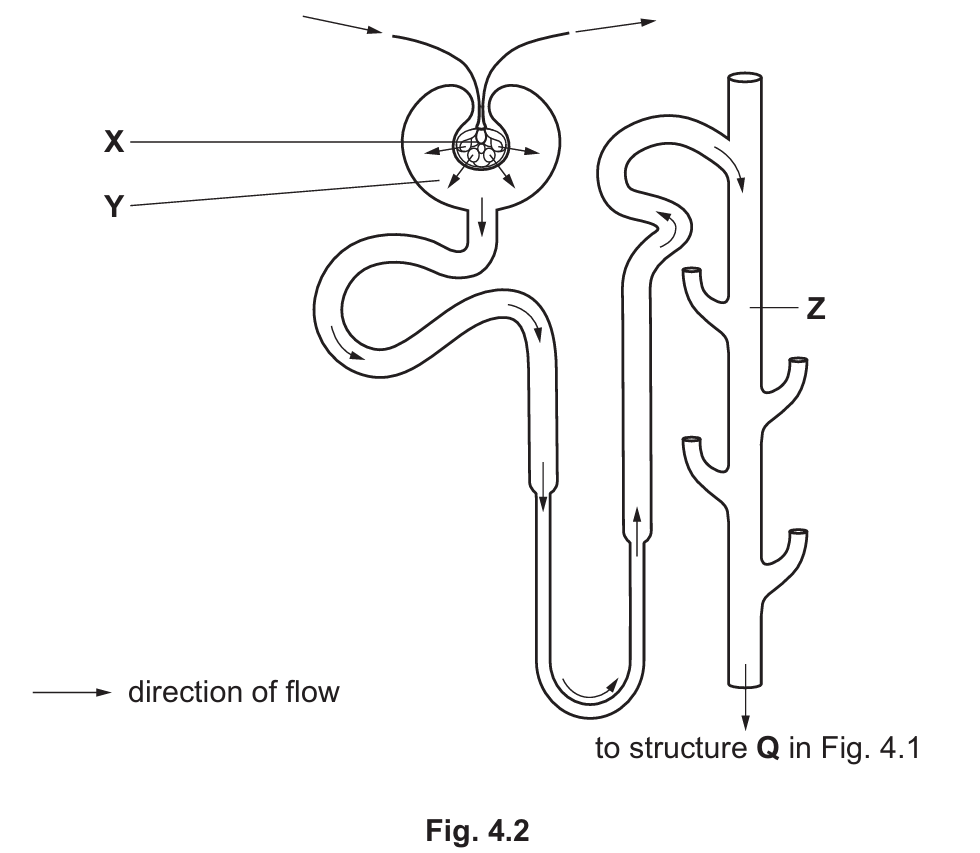
Describe and explain the difference in the composition of the fluids in structures X, Y and Z in Fig. 4.2.
(e) The liver is also involved in excretion.
Describe two ways that amino acids are processed in the liver.
Describe two ways that amino acids are processed in the liver.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
(a)
Excretion is the removal of waste products of metabolism (chemical reactions in cells including respiration), toxic materials, and substances in excess of requirements from organisms.
(b)
Carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)).
(c)
- P: Cortex
- Q: Ureter
- R: Medulla
(d)
The composition of fluids changes as it moves through the nephron due to filtration and reabsorption:
- Difference (X vs Y): Structure X (blood in glomerulus) contains blood cells and large proteins, whereas Structure Y (filtrate in Bowman’s capsule) contains glucose, water, urea, and ions, but no large proteins or blood cells.
- Explanation: This is due to ultrafiltration. The basement membrane acts as a filter, allowing small molecules to pass from X to Y but preventing large molecules (proteins/cells) from passing through.
- Difference (Y vs Z): Structure Y contains glucose, but Structure Z (urine in collecting duct) contains no glucose.
- Explanation: All glucose is selectively reabsorbed back into the blood capillaries in the proximal convoluted tubule.
- Difference (Concentration): Structure Z contains a higher concentration of urea and waste ions compared to Y.
- Explanation: As the filtrate moves through the nephron (Loop of Henle and collecting duct), water is reabsorbed into the blood to conserve it, leaving the waste products more concentrated in the urine.
(e)
The liver processes amino acids in the following ways:
- Deamination: The nitrogen-containing part (amine group) of excess amino acids is removed to form urea, which is then excreted by the kidneys.
- Assimilation / Protein Synthesis: Amino acids are built up (synthesized) into new proteins required by the body, such as plasma proteins (e.g., fibrinogen) or enzymes.
