Question
(a) (i) Fig. 1.1 is a branching key used to identify different species of bacteria.
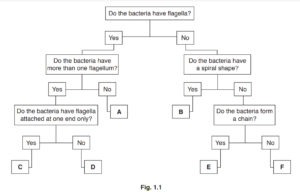
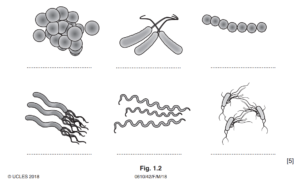
Fig. 1.2 shows six different species of bacteria.
Use the key to identify the six different species of bacteria.
Write the letters on the lines in Fig. 1.2.
(ii) State the name of the kingdom that bacteria belong to. [1]
(b) State one similarity between the structure of bacteria and the structure of viruses. [1]
(c) Fig. 1.3 is a photomicrograph of Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera.
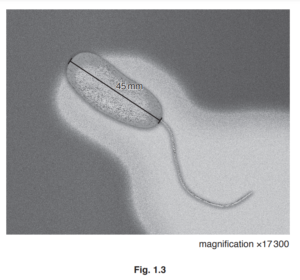
(i) Write the formula that would be used to calculate the actual length of the bacterium (not
including the flagellum) in Fig. 1.3.
(ii) The actual length of the bacterium shown in Fig. 1.3 is 0.0026mm.
Convert this value to micrometres (µm).
Space for working. µm [1]
(d) (i) Describe and explain the effects of cholera bacteria on the gut.
(ii) Suggest one treatment for cholera. [1]
[Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
1 (a) (i) each row in this order:
F A E
C B D
1 (a) (ii) prokaryote ; 1
1 (b) presence of genetic material / DNA / RNA ;
presence of protein ;
1 (c) (i) (actual length of bacterium) = size / length, of the image ÷ magnification ; 1
1 (c) (ii) 2.6 (∝m);
1(d)(i) 1 produces a toxin ;
2 bacteria / toxin, attach to the wall of the, small / large, intestine ;
3 correct ref to chloride ions ;
4 secretion / loss, chloride ions, into the, small intestine ;
5 causing a water potential gradient / water potential of the intestinal lumen is
lowered ;
6 causing osmotic movement of water into the gut / water flows from, the cells /
blood, into the, lumen / gut ;
7 loss of salts from the blood ;
8 causing, diarrhoea / dehydration ;
1 (d) (ii) oral rehydration (therapy / salts / treatment / solution) ;
in-take of water, sugar and, salt / ions ;
antibiotics ;
Question
All living organisms are placed into groups according to their features.
Myriapods are one of the main groups of arthropods.
(a) State two features of myriapods that can be used to distinguish them from other arthropods.
1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
Fig. 1.1 shows that there are four main groups of arthropods.
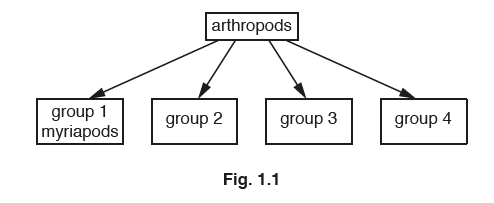
(b) State the names of two of the other groups of arthropods in Fig. 1.1.
1 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
2 ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[2]
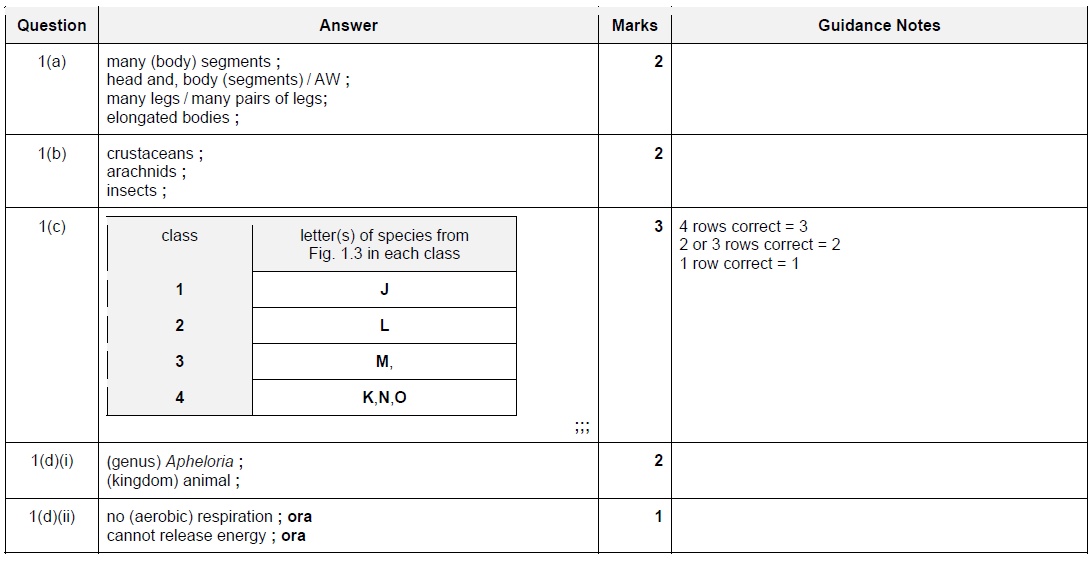
(c) Myriapods can be classified into four classes, 1, 2, 3 and 4.
Fig. 1.2 is a dichotomous key that can be used to distinguish the four classes of myriapods.
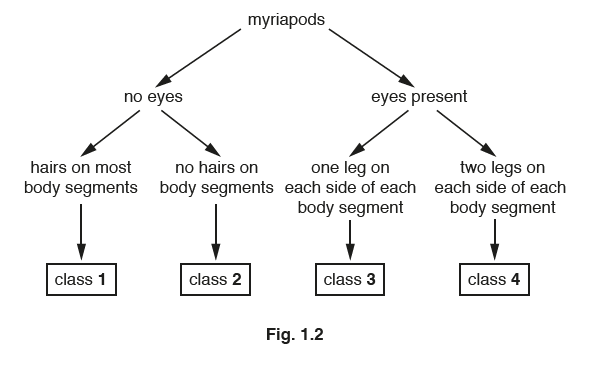
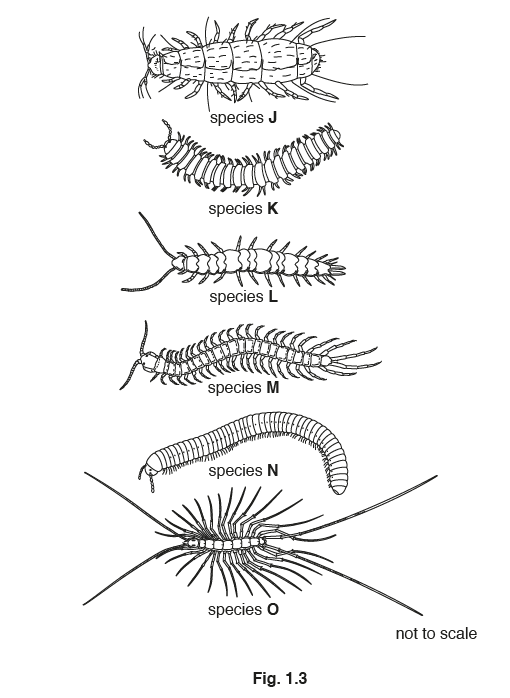
Complete Table 1.1 by using the key in Fig. 1.2 to classify the six myriapods in Fig. 1.3 into
the four classes.
(d) Fig. 1.4 is a photograph of the myriapod, Apheloria virginiensis.
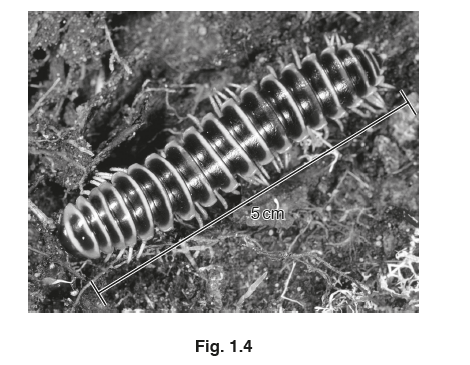
(i) State the genus name and kingdom name for the myriapod shown in Fig. 1.4.
genus ………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
kingdom ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2]
(ii) A. virginiensis releases the poison cyanide when it is attacked by predators.
Cyanide stops enzymes in the mitochondria from functioning.
Suggest why cells die if the mitochondria do not function.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. [1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
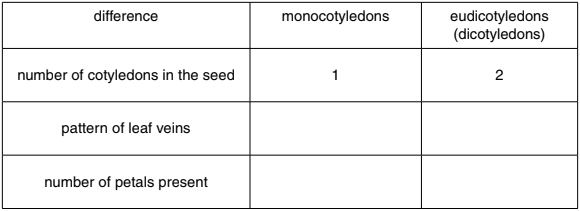
Flowering plants can be divided into two groups: monocotyledons and eudicotyledons (dicotyledons).
Complete Table 1.1 to state the differences between these two types of flowering plants. An example has been done for you.
Table 1.1
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Fig. 1.1 shows five different mammals.
They are not drawn to the same scale.
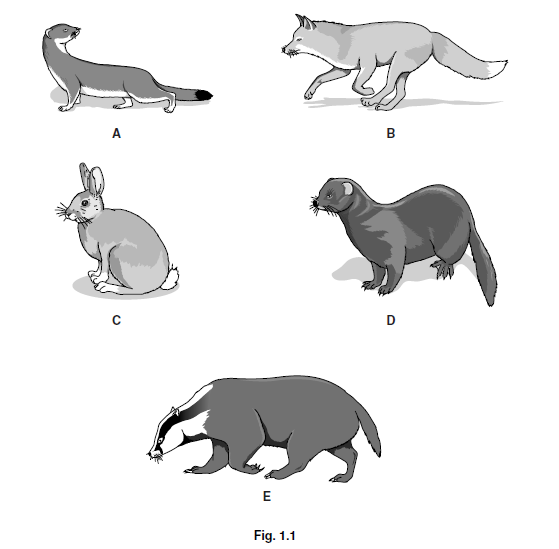
Use the key to identify the mammals shown in Fig. 1.1.
Complete Table 1.1 by writing the names of the five mammals.

[4]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:

QUESTIONS:
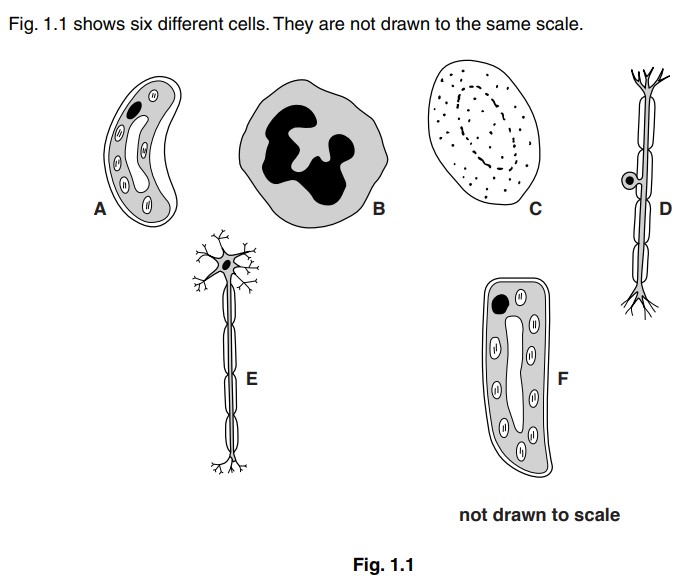
(a) Table 1.1 shows a key which can be used to identify these cells.
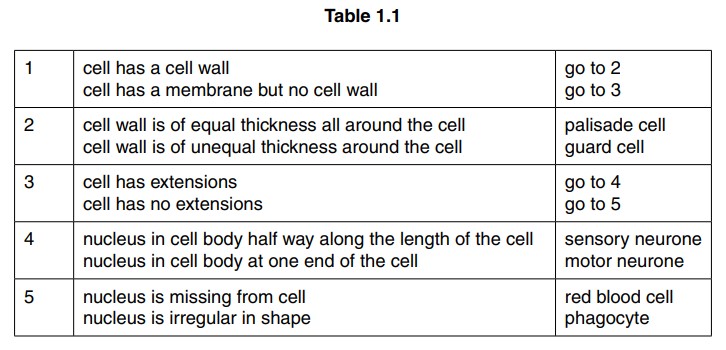
Use this key to identify cells A, B, C, D and E. Cell F has been done for you.
(b) (i) State the main function of a palisade cell.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(ii) Suggest and explain two ways in which the structure of a palisade cell is adapted to this function.
adaptation 1 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
explanation …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
adaptation 2 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
explanation …………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
1 (a) 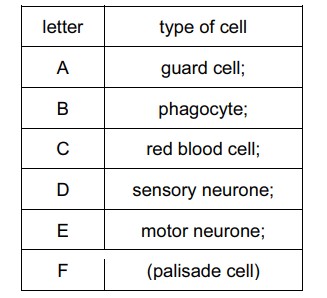
(b) (i) photosynthesis / make carbohydrate/ glucose/ sugar;
(ii) contains (many) chloroplasts;
to absorb energy / light;
long and thin/ elongated;
so many can fit into a small area (of the leaf);
chloroplasts close to edge of cell/ thin cytoplasmic layer;
so that more light/ energy can be absorbed;
