Question
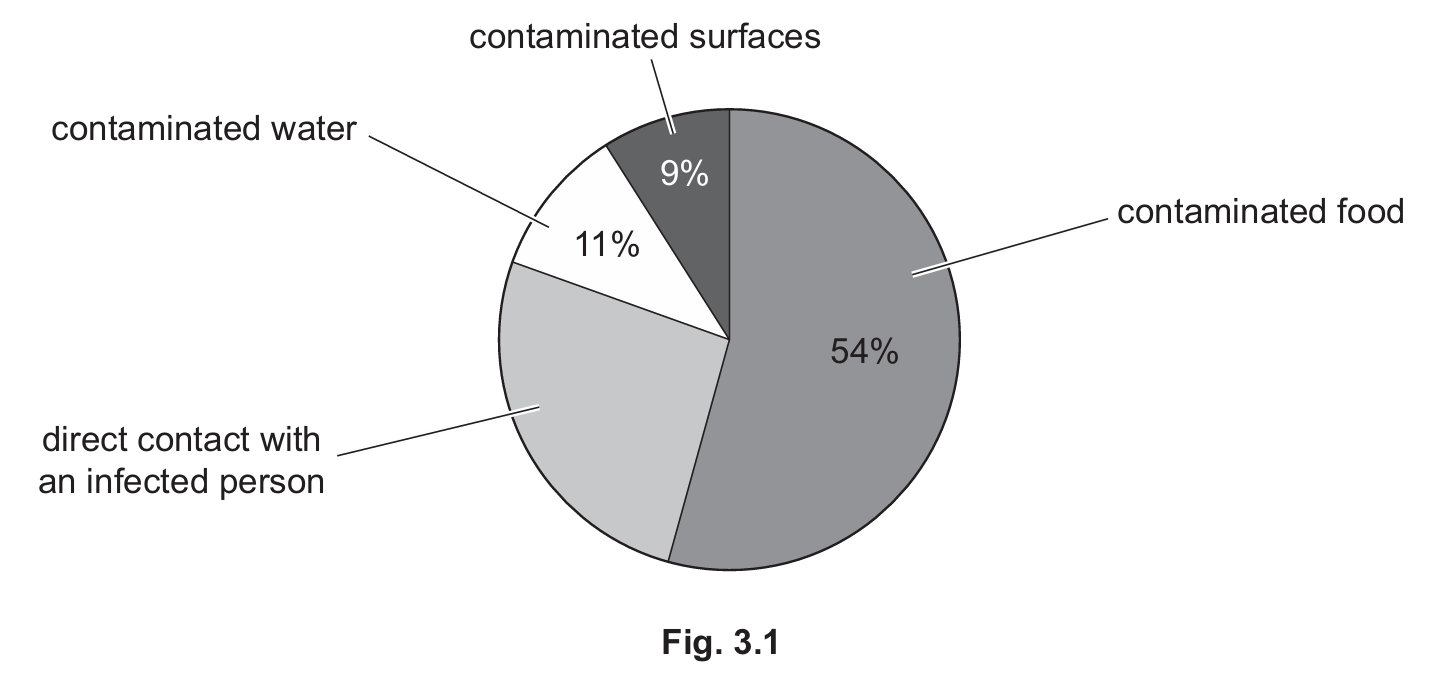
(ii) In one area, $300$ people caught norovirus. Using Fig. 3.1, calculate how many of the $300$ people caught the virus from contaminated water.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Defence via Gastric Juice
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid ($\text{HCl}$). This creates an acidic environment (low pH) which kills pathogens (such as bacteria) that are ingested with food. This acts as a chemical barrier preventing infection.
(b) Data Analysis from Fig. 3.1
(i) To find the percentage for direct contact, subtract the other modes of transmission from $100\%$:
$$100\% – (54\% + 11\% + 9\%) = 100\% – 74\% = \mathbf{26\%}$$
(ii) The chart states that $11\%$ of cases are from contaminated water. To calculate the number of people out of 300:
$$\frac{11}{100} \times 300 = 0.11 \times 300 = \mathbf{33} \text{ people}$$
(c) Preventing Indirect Transmission
Indirect transmission occurs via contaminated surfaces, food, or water. Preventive measures include:
- Hygienic food preparation: Ensuring food is cooked thoroughly and stored correctly.
- Clean water supply: Boiling or treating water (chlorination) to kill pathogens.
- Personal hygiene: Washing hands thoroughly after using the toilet and before handling food.
- Waste disposal: Proper treatment of sewage to prevent water source contamination.
(d) Respiratory Defences
Body defences that prevent viruses in the air from reaching the lungs include:
- Mucus: Produced by goblet cells in the trachea and bronchi; it traps airborne particles and pathogens.
- Cilia: Hair-like structures on the lining of the airways that beat to sweep mucus (containing trapped pathogens) away from the lungs towards the throat to be swallowed.
- Nose hairs: Trap larger dust particles and pathogens entering the nose.
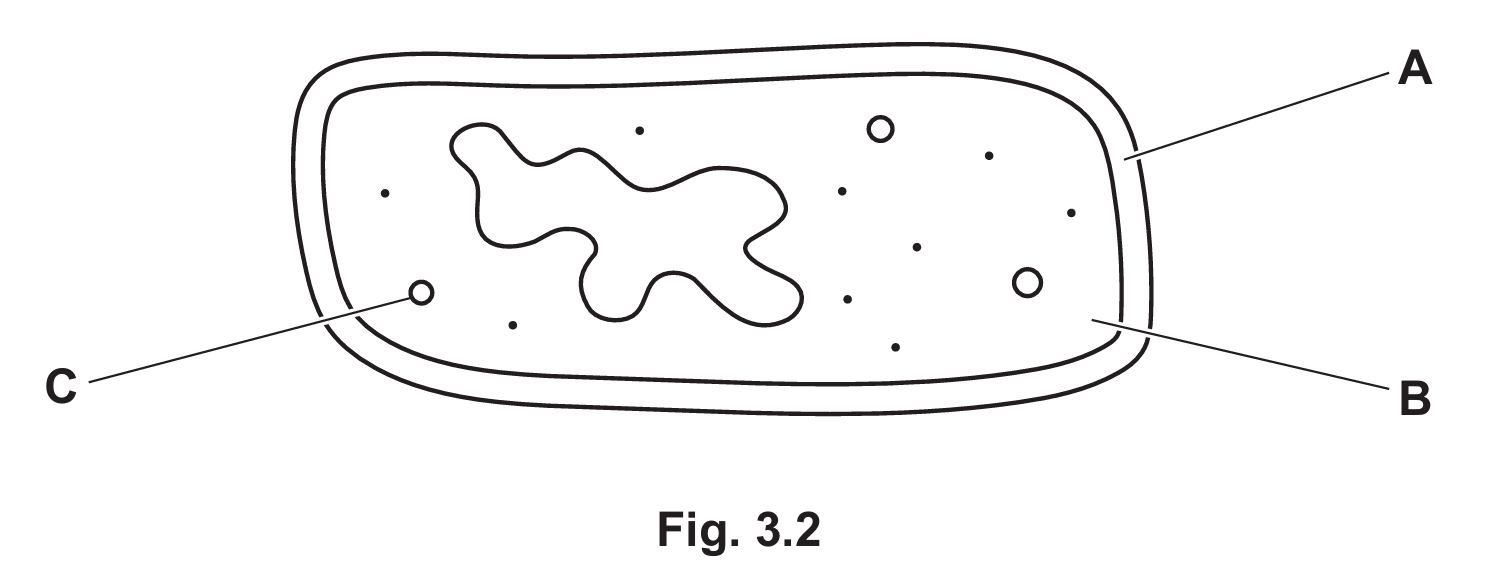
(e) Bacterium Structure
Based on the standard structure of a bacterial cell:
- A: Cell Wall (Provides structural support and protection).
- B: Cytoplasm (Site of metabolic reactions).
- C: Plasmid (Small circular loop of DNA).
