Question
(a) Fig. 3.1 shows the percentage of water in different structures of the human body.
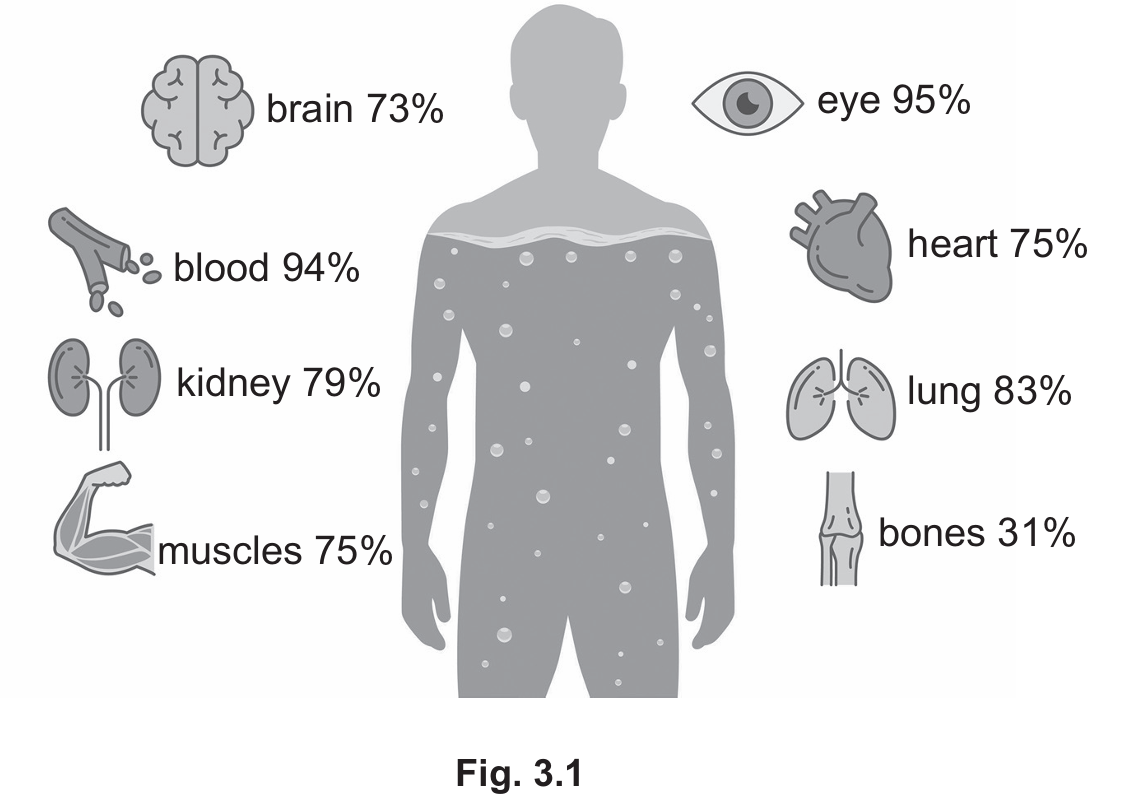
(i) The mean mass of a human eye is $28\,\text{g}$.
Using information from Fig. 3.1, calculate the mass of water in a human eye.
Give your answer to two significant figures.
(ii) Describe the importance of water in the human body.
(b) Cholera is a disease caused by a pathogen in contaminated water.
Fig. 3.2 is a diagram of the cholera pathogen.
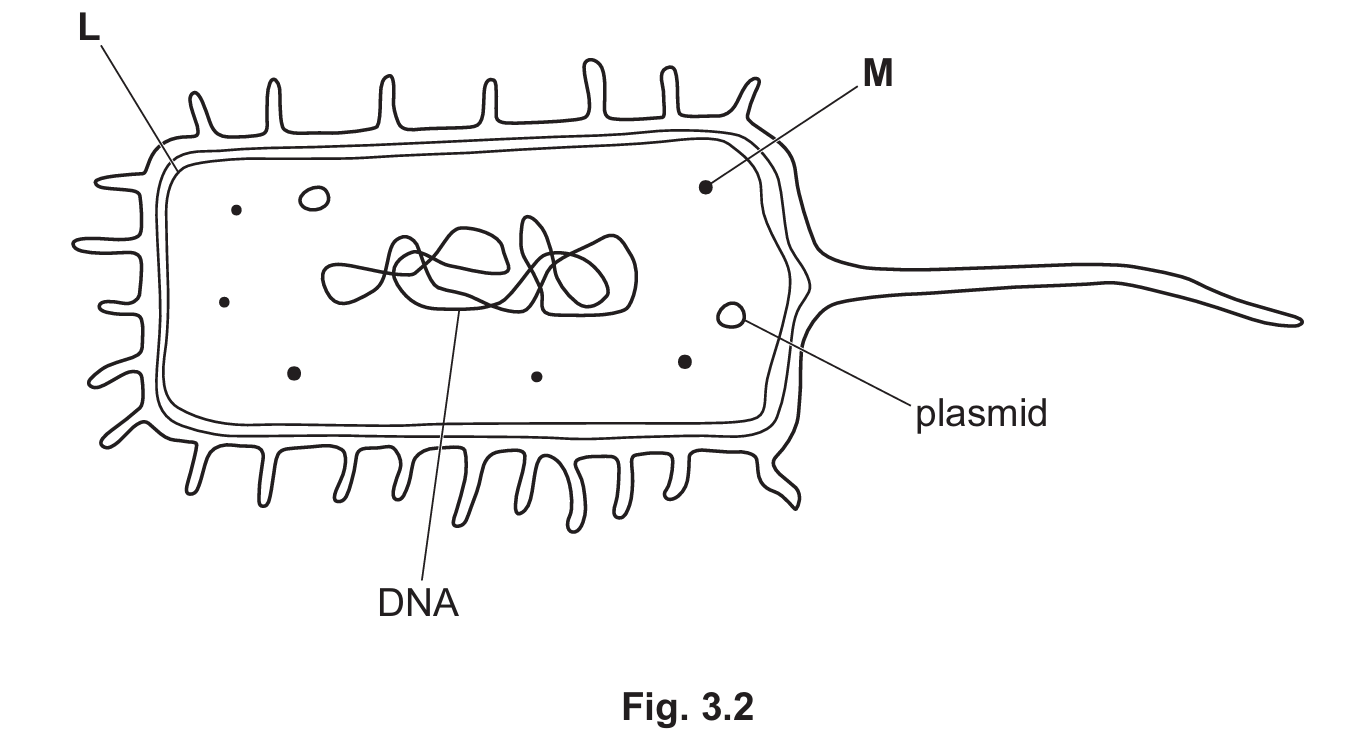
(i) State the name of structures L and M shown in Fig. 3.2.
(ii) Identify two features shown in Fig. 3.2 that are typical of prokaryotes.
(iii) State the type of pathogen that causes cholera.
(iv) The scientific name for the pathogen that causes cholera is Vibrio cholerae.
State the genus name for this pathogen.
(v) Explain how the cholera pathogen causes dehydration of the human body.
(vi) Complete the sentences about the use of plasmids in genetic modification.
During genetic modification, human DNA and plasmid DNA are cut with a restriction enzyme. This creates ………………. which are joined together using an enzyme called …………….. . The modified plasmid containing the human gene is called a ……………… plasmid.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
According to Fig 3.1, the eye is composed of $95\%$ water.
Mass of water = $28\,\text{g} \times 0.95 = 26.6\,\text{g}$.
Rounding to two significant figures, the answer is $27\,\text{g}$.
(a)(ii)
Water acts as a critical solvent in the body, allowing substances to dissolve for transport (e.g., in blood plasma) and for metabolic reactions (e.g., digestion/hydrolysis). It is also vital for excretion (urine) and temperature regulation (sweating).
(b)(i)
L: Cell membrane (the inner line beneath the cell wall).
M: Ribosome (the small dots in the cytoplasm).
(b)(ii)
Typical prokaryotic features visible in the diagram include:
1. Circular DNA (the looped genetic material, not enclosed in a nucleus).
2. Plasmids (small circular rings of DNA).
3. Cell wall (the outer layer; note: prokaryotes do not have a nucleus).
(b)(iii)
The type of pathogen is a bacterium.
(b)(iv)
The scientific name is Vibrio cholerae. The genus name is the first part: Vibrio.
(b)(v)
The cholera bacterium produces a toxin that causes the secretion of chloride ions ($\text{Cl}^-$) into the small intestine. This accumulation of ions lowers the water potential in the gut lumen. Consequently, water moves out of the cells and blood into the gut by osmosis, leading to watery diarrhoea and dehydration.
(b)(vi)
During genetic modification:
1. Restriction enzymes create sticky ends.
2. These are joined together using an enzyme called DNA ligase (or simply ligase).
3. The modified plasmid is called a recombinant plasmid.
