Question
The diagram shows part of the gas exchange system in humans.
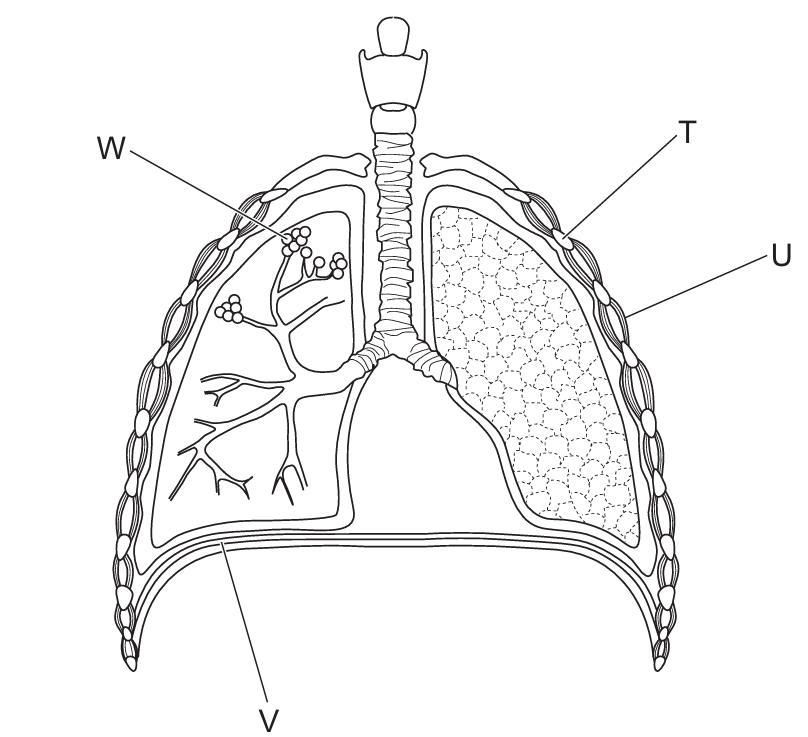
Which row identifies the structures in the diagram?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
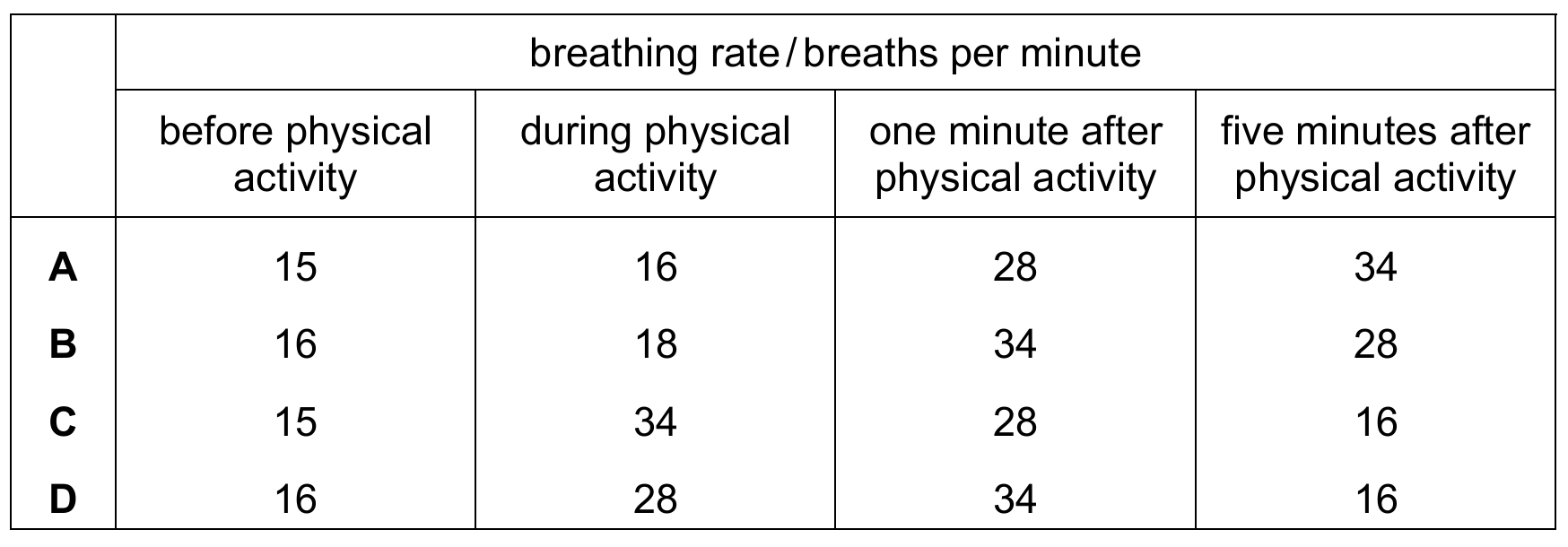
During physical activity, breathing rate increases significantly to supply more oxygen to muscles and remove carbon dioxide. Row C correctly illustrates this peak during exercise ($15 \rightarrow 34$). Immediately after activity stops, the rate begins to decrease ($34 \rightarrow 28$) as the body starts to recover. Within five minutes, the breathing rate should return to near-resting levels ($16$). Row D is incorrect because the rate cannot continue to rise after exercise stops, while Rows A and B show insufficient increases for physical exertion.
Question
B glucose
C lactic acid
D water
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is A.
Explanation:
In yeast, anaerobic respiration is also known as alcoholic fermentation. During this process, glucose is broken down in the absence of oxygen to produce ethanol (a type of alcohol) and carbon dioxide. Unlike aerobic respiration, water is not produced, and unlike anaerobic respiration in muscles, lactic acid is not formed. This process is essential in brewing and baking, where the ethanol and $CO_2$ are the desired primary products.
