Question
The table shows the breathing rate and the average total volume of air breathed by a student when exercising for $20$ minutes.
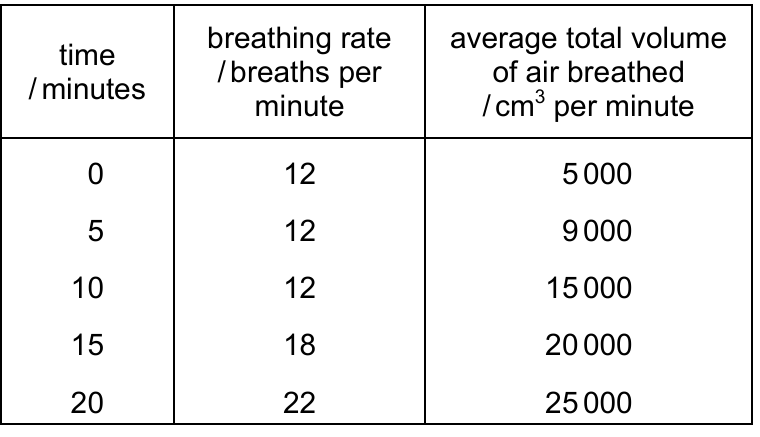
Which conclusion can be made from the data in the table about the effect of exercise on breathing?
(B) Between $0$ minutes and $10$ minutes, the depth of breathing increases.
(C) Between $10$ minutes and $20$ minutes, there is no change to the rate of breathing.
(D) Between $15$ minutes and $20$ minutes, the depth of breathing decreases.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
The plotted points, $1$ and $2$, on the graph show two different types of structure in the breathing system of a human.
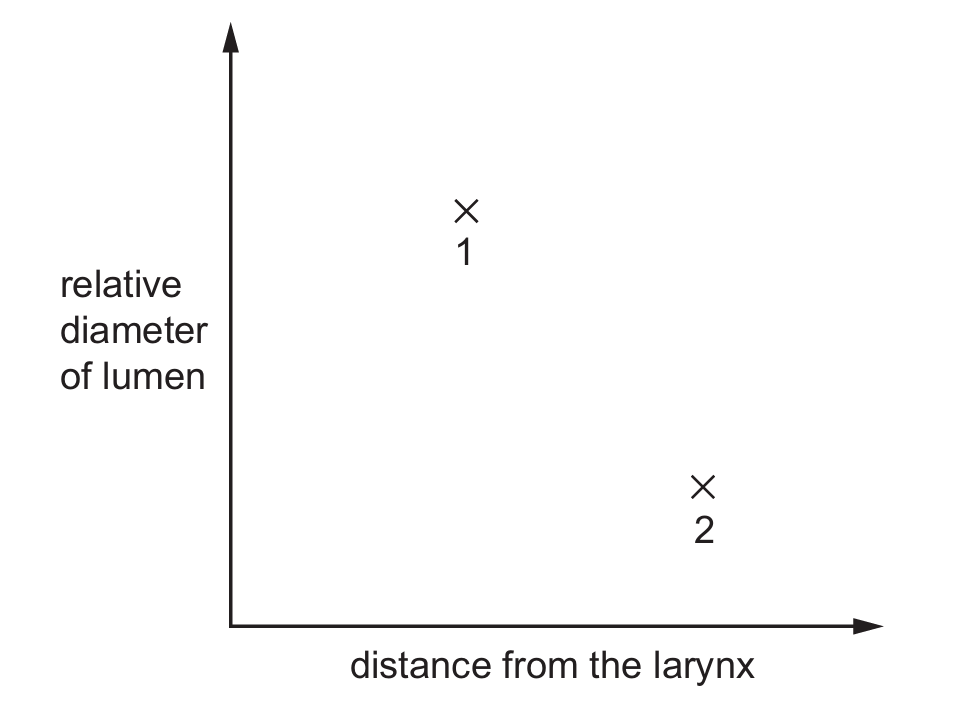
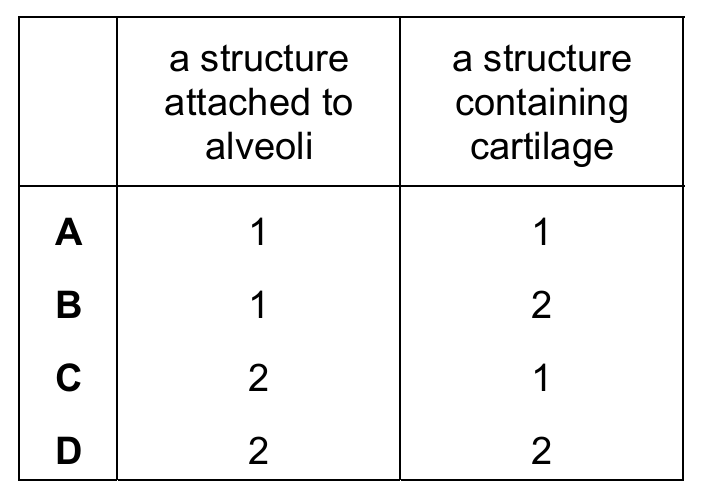
Which row identifies a structure attached to alveoli and a structure containing cartilage?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
What helps to keep the trachea open during breathing?
(B) cilia
(C) external intercostal muscles
(D) larynx
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The trachea, or windpipe, is supported by a series of $C$-shaped rings made of cartilage. This stiff yet flexible tissue provides structural support that prevents the airway from collapsing under the negative pressure created during inhalation. While the other options are part of the respiratory system, they serve different functions:
- Cilia are microscopic hairs that sweep mucus and debris out of the airways.
- External intercostal muscles assist in expanding the ribcage during breathing.
- The larynx is the voice box located at the top of the trachea.
Therefore, cartilage is specifically responsible for maintaining the patency of the tracheal tube.
✅ Answer: (A)
