Question
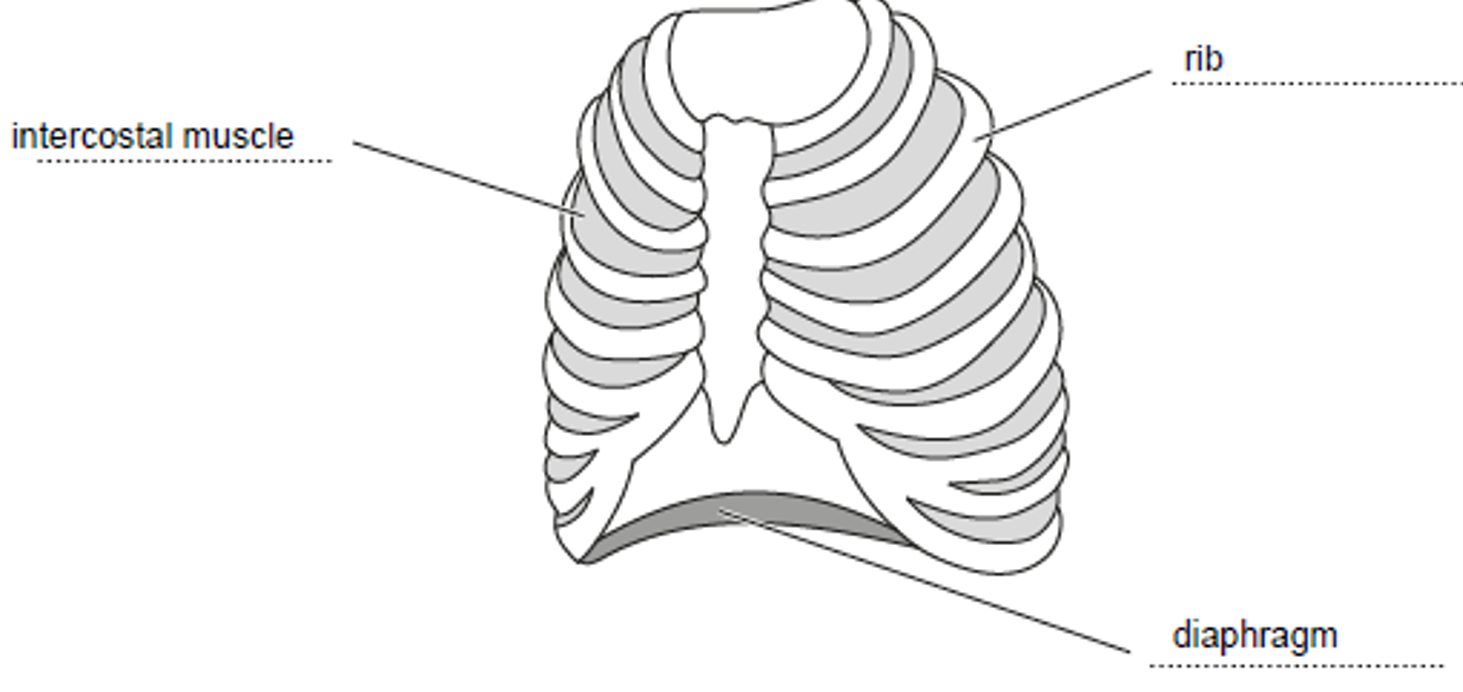
(a) Fig. 5.1 is a diagram of some of the muscles and bones found in the human gas exchange system.
Complete Fig. 5.1 by labelling the structures in the spaces provided. 
(b) During breathing, air moves into and out of the alveoli.
(i) Circle the name of the part of the breathing system that is connected to the alveoli.
(ii) State the name of the organ that contains the alveoli.
(c) Fig. 5.2 shows one alveolus and capillary.
(i) Circle the arrow on Fig. 5.2 that shows the net direction of movement of carbon dioxide. 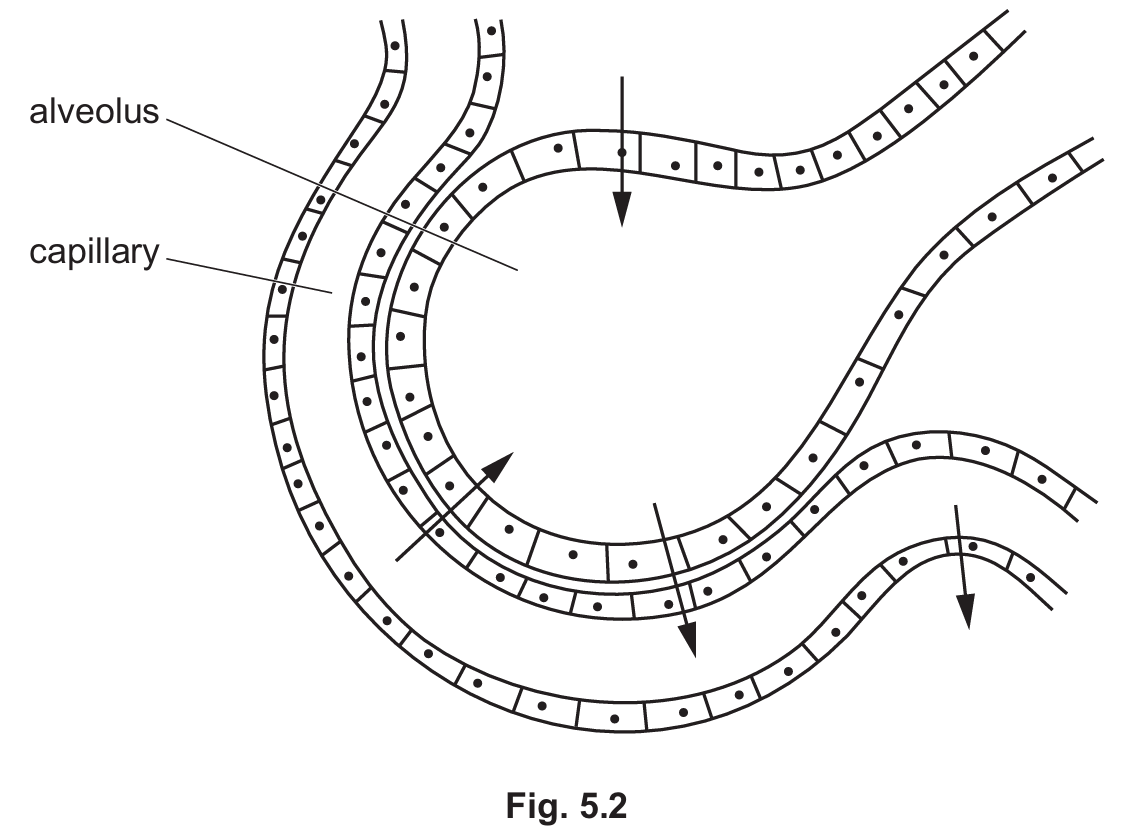
(ii) The alveoli are adapted for efficient gas exchange.
Describe the features of alveoli that enable efficient gas exchange.
(d) (i) State the word equation for aerobic respiration.
(ii) State the name of the cell structure where aerobic respiration takes place.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
The correctly labelled structures are:
- Top-right label: Intercostal muscle(s)
- Left label: Rib
- Bottom label: Diaphragm
(b)
(i) The correct term to circle is bronchioles.
Explanation: The trachea divides into bronchi, which divide into bronchioles, which finally connect to the alveoli.
(ii) Lungs.
(c)
(i) The arrow pointing from the blood capillary into the alveolus (the upward/inward pointing arrow) should be circled.
Explanation: Carbon dioxide is a waste product that diffuses from the high concentration in the deoxygenated blood to the lower concentration in the alveolar air space to be exhaled.
(ii) The features include (any three):
- Large surface area: Millions of alveoli provide a vast area for diffusion.
- Thin walls: The walls are one cell thick, providing a short diffusion distance.
- Good blood supply: A dense capillary network maintains the concentration gradient.
- Moist lining: Allows gases to dissolve before diffusing.
(d)
(i) \(\text{glucose} + \text{oxygen} \longrightarrow \text{carbon dioxide} + \text{water}\)
(ii) Mitochondria (or mitochondrion).
