Question
(a) Alveoli are the gas exchange surface in humans.
State three features of alveoli that make them an effective gas exchange surface.
State three features of alveoli that make them an effective gas exchange surface.
(b) Fig. 2.1 is a diagram of the human breathing system.
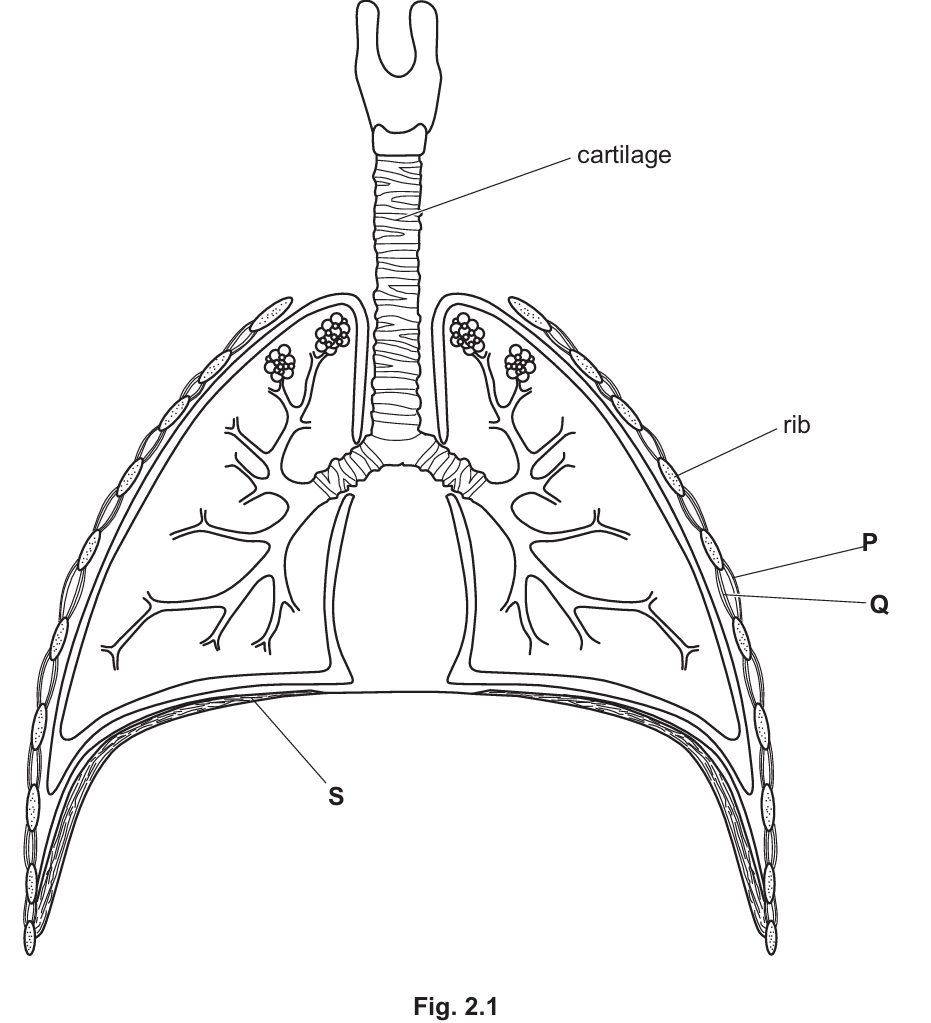

(i) Three muscles involved in inspiration are labelled P, Q and S in Fig. 2.1.
Identify the letters in Fig. 2.1 that label the muscles which contract during inspiration.
Identify the letters in Fig. 2.1 that label the muscles which contract during inspiration.
(ii) State the function of cartilage in the breathing system.
(c) (i) State the balanced chemical equation for aerobic respiration.
(ii) During physical activity breathing changes.
Explain the mechanism that links the increase in physical activity to the changes in breathing.
Explain the mechanism that links the increase in physical activity to the changes in breathing.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Detailed solution
(a)
Any three of the following features:
- Large surface area (provided by the millions of alveoli) allows for faster diffusion of gases.
- Thin walls (one cell thick) or thin surface ensures a short diffusion distance for oxygen and carbon dioxide.
- Good blood supply (dense network of capillaries) maintains a steep concentration gradient for diffusion.
- Good ventilation maintains the concentration gradients of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
(b) (i)
P and S
Explanation: Inspiration (breathing in) requires the volume of the thorax to increase. This is achieved by the contraction of the diaphragm (S), which flattens, and the external intercostal muscles (P), which pull the ribs upwards and outwards. The internal intercostal muscles (Q) relax during inspiration.
(b) (ii)
It keeps the trachea / bronchi / airway open OR prevents the collapse of the trachea / bronchi / airway during pressure changes (specifically when air pressure drops during inhalation).
(c) (i)
The balanced chemical equation is: $$C_{6}H_{12}O_{6} + 6O_{2} \rightarrow 6CO_{2} + 6H_{2}O$$
(c) (ii)
The mechanism involves the detection of blood chemistry changes by the brain:
- Physical activity leads to an increase in respiration in muscle cells, producing more carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)).
- This causes an increased concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood (lowering the pH).
- This increase is detected by the brain (specifically the medulla).
- The brain sends increased nerve impulses to the muscles involved in breathing (diaphragm and intercostals).
- This causes an increase in the rate and depth of breathing to expel the excess carbon dioxide and take in more oxygen.
- (Optional) Adrenaline may also be released, which further stimulates increased breathing and heart rate.
