Question
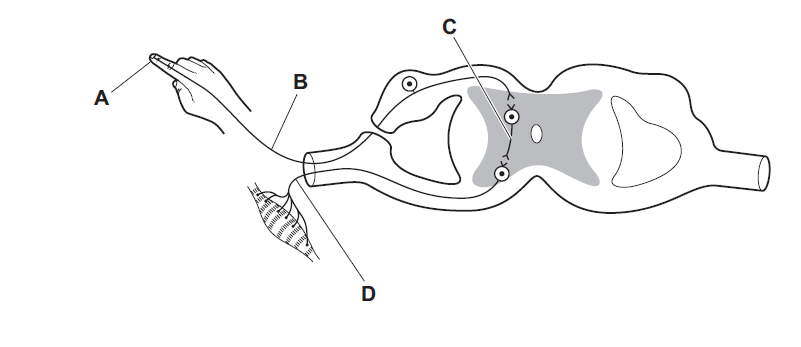
The diagram shows a simple reflex arc.
Which labelled part is the sensory neuron?
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The labelled part B is the sensory neuron. In a simple reflex arc, the sensory neuron is the component that carries information from the sensory receptors (such as those in the skin, muscles, or other sensory organs) to the central nervous system (typically the spinal cord). This sensory neuron is also known as the afferent neuron. This sensory neuron detects a stimulus in the environment or within the body and converts it into an electrical signal that can be transmitted to the nervous system for processing. The sensory neuron is the initial step in the reflex arc and plays a crucial role in relaying sensory information to the appropriate areas of the nervous system for a rapid and automatic response.
Question
A boy accidentally touches a very hot object and immediately takes his hand away.
In this reflex action, what is the effector?
A a heat receptor in his hand
B a motor neurone
C a muscle in his arm
D the spinal cord
▶️Answer/Explanation
In this reflex action, the effector is :
C. a muscle in his arm
When the boy accidentally touches a very hot object, the sensory receptors in his hand detect the heat and send a signal to the spinal cord. The spinal cord then sends a signal through motor neurons to the muscles in his arm, causing the muscles to contract and quickly move his hand away from the hot object. This type of reflex, known as a withdrawal reflex, is a protective mechanism that helps prevent tissue damage by removing the body part from a harmful stimulus.
Question
The diagram shows a simple reflex arc.
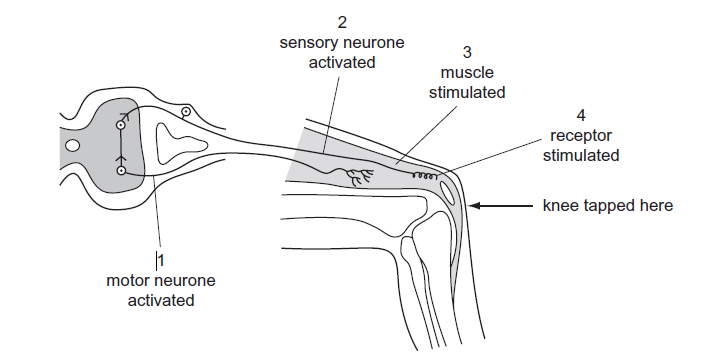
What is the correct order of events after the knee is tapped?
A 1 → 2 → 3 → 4
B 1 → 4 → 2 → 3
C 4 → 2 → 1 → 3
D 4 → 3 → 2 → 1
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Receptors stimulated: The initial event is the tapping of the knee, which stretches the muscle (quadriceps) in the thigh.
Sensory Neuron Activation: The activation of muscle spindles sends sensory nerve impulses through sensory neurons (afferent neurons) towards the spinal cord. These sensory neurons are responsible for transmitting the sensory information from the muscle spindles to the central nervous system.
- Motor Neuron Activation: The sensory neurons stimulate motor neurons (efferent neurons) in the spinal cord.
Muscle stimulated: : Activation of the motor neurons leads to the contraction of the appropriate muscle. In the case of the knee-jerk reflex, the muscle being contracted is the quadriceps muscle at the front of the thigh.
It’s important to note that in a simple reflex arc, the sensory information is processed and a response is generated at the level of the spinal cord, without involving higher brain centers. This allows for a rapid and automatic response to a specific stimulus.
Question
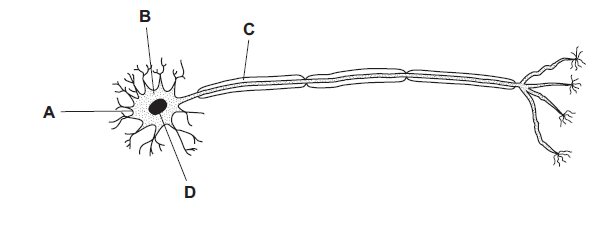
The diagram shows a motor (effector) neurone.
Which structure is also found in white blood cells, but not in red blood cells?
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
In diagram of a motor (effector) neuron, the structure that is found in white blood cells but not in red blood cells is the nucleus.
White blood cells, also known as leukocytes, are a type of blood cell that plays a crucial role in the immune system. They are responsible for defending the body against infections, pathogens, and foreign substances. One of the key characteristics of white blood cells is that they possess a nucleus, which contains the genetic material (DNA) of the cell. This nucleus allows white blood cells to carry out various immune functions, such as producing antibodies, recognizing and attacking pathogens, and coordinating immune responses.
On the other hand, red blood cells, also known as erythrocytes, are responsible for carrying oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and organs throughout the body. One of the distinctive features of red blood cells is that they lack a nucleus as well as other organelles like mitochondria. This absence of a nucleus in red blood cells provides them with more space to accommodate hemoglobin, the protein responsible for oxygen transport.
In summary, the presence of a nucleus in white blood cells enables them to carry out their immune functions, while red blood cells lack a nucleus to optimize their primary function of oxygen transportation.
Question
A man injures his arm in an accident. Afterwards, he can feel objects touching his hand, but he
cannot move his hand away from them.
What could cause this?
A Receptors in his hand are damaged.
B The nerve connection is cut only between the receptors in his hand and his central nervous
system.
C The nerve connection is cut only between his central nervous system and the effectors in his
arm.
D Both of these nerve connections are cut.
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is:
C. The nerve connection is cut only between his central nervous system and the effectors in his arm.
In this scenario, the man’s inability to move his hand away from objects after the injury suggests that the nerve connection between his central nervous system (which includes the brain and spinal cord) and the effectors (muscles responsible for movement) in his arm has been disrupted. The receptors in his hand (such as touch receptors) are still intact and functioning, as indicated by his ability to feel objects touching his hand. However, since the nerve pathway responsible for transmitting signals from his central nervous system to the muscles of his arm has been damaged, he is unable to move his hand away from objects despite feeling them.
