Question
The diagram shows a simple reflex arc.
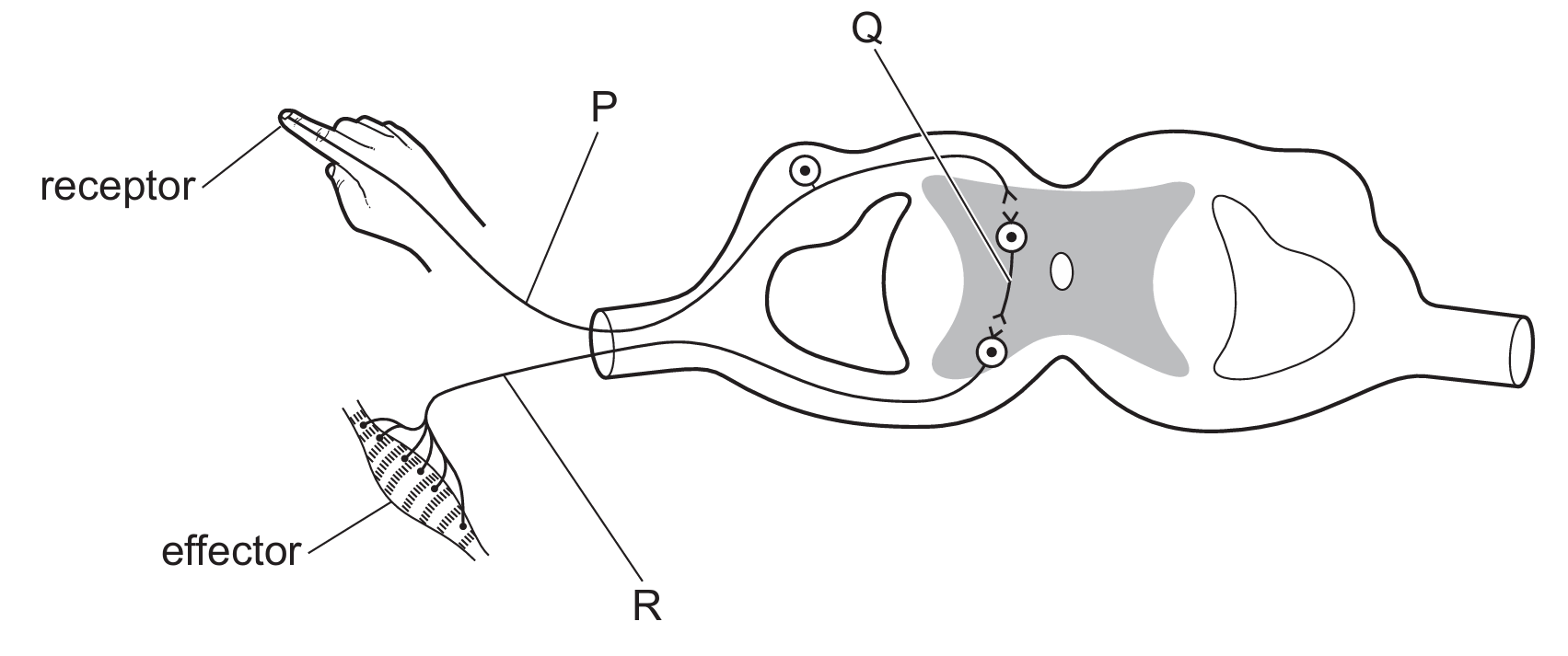
What are the names of the structures labelled $P$, $Q$ and $R$?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
In a reflex arc, the impulse travels from the receptor to the effector in a specific sequence. Structure $P$ is the sensory neurone, which carries the electrical impulse from the receptor to the central nervous system. Structure $Q$ is the relay neurone, located entirely within the spinal cord, connecting the sensory and motor neurones. Finally, structure $R$ is the motor neurone, which transmits the signal to the effector (the muscle) to trigger a response. This sequence ensures a rapid, involuntary reaction to a stimulus. Matches row $D$.
✅ Answer: (D)
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
The diagram shows a synapse.
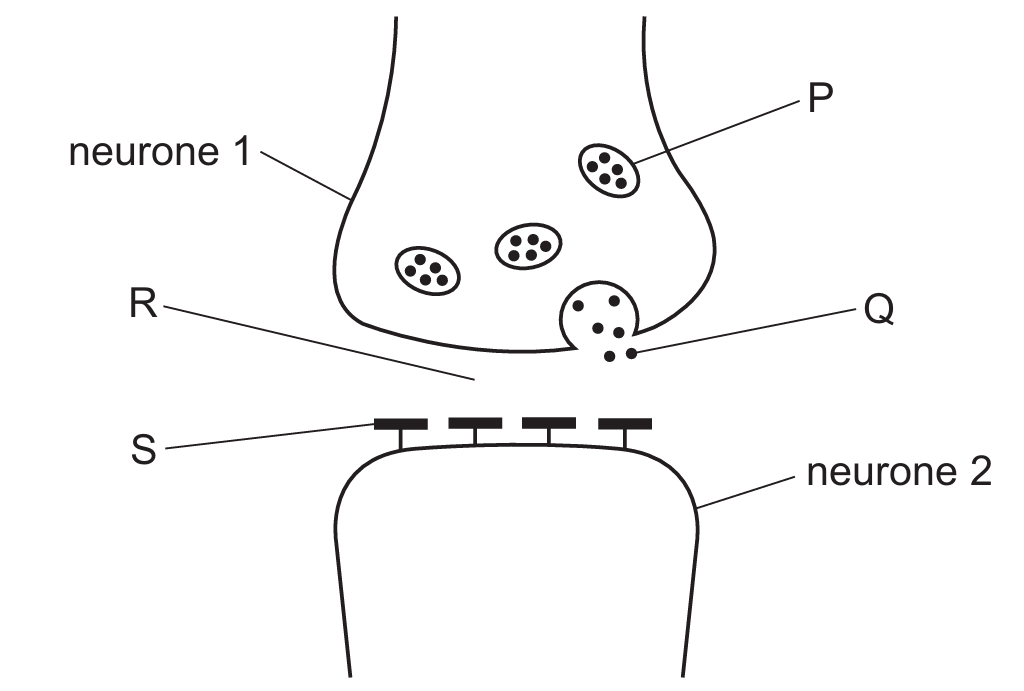
What are the labelled parts?
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The diagram illustrates the junction between two neurones, known as a synapse. Label P identifies the vesicles, which store chemical messengers within the pre-synaptic neurone. Label Q refers to the neurotransmitter molecules being released into the space. Label R is the synaptic gap (or cleft), the physical space across which the chemicals diffuse. Finally, label S points to the receptors on the post-synaptic membrane that bind with the neurotransmitter to trigger an impulse in neurone $2$. Matching these identifications leads to option C.
✅ Answer: (C)
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
Events that occur at a synapse are listed.
They are not in the correct order.
$1$ An impulse is stimulated in the next neurone.
$2$ An impulse stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules from vesicles into the synaptic gap.
$3$ Neurotransmitter molecules bind with receptor proteins on the next neurone.
$4$ The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the gap.
$2$ An impulse stimulates the release of neurotransmitter molecules from vesicles into the synaptic gap.
$3$ Neurotransmitter molecules bind with receptor proteins on the next neurone.
$4$ The neurotransmitter molecules diffuse across the gap.
What is the actual sequence of events?
(A) $2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 1 \rightarrow 3$
(B) $2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 1$
(C) $4 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 1 \rightarrow 3$
(D) $4 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 1$
(B) $2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 1$
(C) $4 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 1 \rightarrow 3$
(D) $4 \rightarrow 2 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 1$
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The process begins when an electrical impulse reaches the presynaptic terminal, triggering the release of neurotransmitters from vesicles ($2$). These chemical messengers then travel by diffusion across the narrow synaptic gap ($4$). Once they reach the postsynaptic membrane, the molecules bind to specific receptor proteins ($3$). This binding causes a change in the membrane potential, which ultimately stimulates a new electrical impulse in the next neurone ($1$). Following this logical flow, the correct sequence is $2 \rightarrow 4 \rightarrow 3 \rightarrow 1$.
✅ Answer: (B)
✅ Answer: (B)
