Question
This reflex action was caused by a person touching a spiky cactus plant.
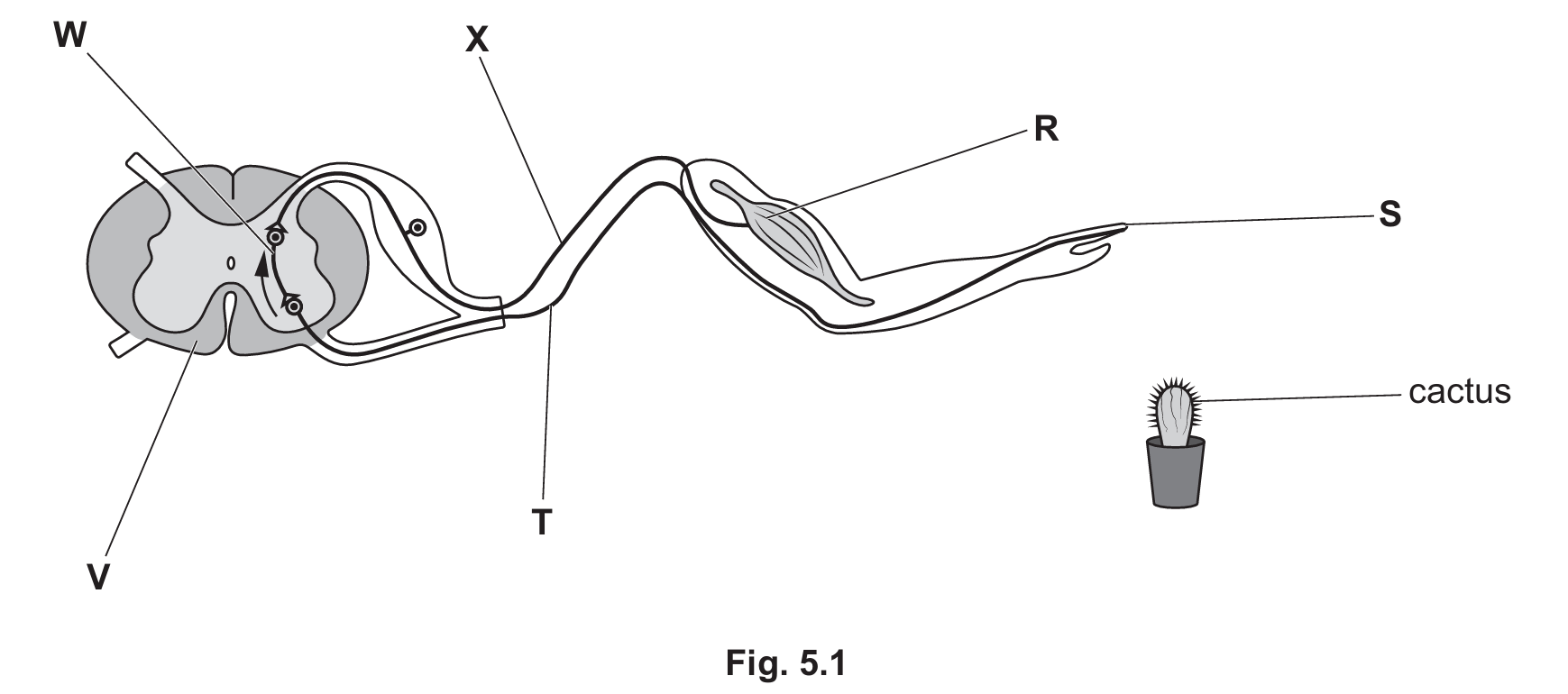
(ii) Write the correct letters from Fig. $5.1$ in the gaps to complete the statements about the reflex arc.
A painful stimulus such as a cactus spine is detected by ……………………………………. in the skin.
An impulse passes along ……………………………………. until it reaches the spinal cord.
The impulse is passed to ……………………………………. and then passes out of the spinal cord in ……………………………………. .
The impulse causes ……………………………………. to produce a response.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Answer: Coordination / regulation (of body functions).
The nervous system is responsible for detecting stimuli, processing information, and coordinating the body’s response to ensure survival and proper functioning.
(b) (i)
Answer: Any two from: S, T, X.
Explanation: The nervous system is divided into the Central Nervous System (CNS), which consists of the brain and spinal cord, and the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), which consists of nerves outside of the brain and spinal cord.
- In Fig $5.1$, the large central structure is the spinal cord (CNS).
- S represents the sensory receptor/nerve endings in the skin.
- T represents the sensory neurone running from the skin to the spinal cord.
- X represents the motor neurone running from the spinal cord to the muscle.
These structures ($S, T, X$) lie outside the spinal cord and are therefore part of the PNS.
(b) (ii)
Answer:
1. Detected by S.
2. Passes along T.
3. Passed to W … passes out in X.
4. Causes R.
Explanation of the Reflex Arc Path:
- Stimulus detection (S): The painful stimulus (cactus) is detected by the receptor cells in the skin, labeled S.
- Sensory Neurone (T): The electrical impulse travels away from the receptor toward the Central Nervous System via the sensory neurone, labeled T.
- Relay Neurone (W): Inside the grey matter of the spinal cord, the impulse is transferred across a synapse to the relay neurone (interneurone), labeled W. Note that relay neurones connect sensory and motor neurones within the CNS.
- Motor Neurone (X): The impulse is then transferred to the motor neurone, labeled X, which carries the signal out of the spinal cord toward the effector.
- Response (R): The impulse reaches the effector muscle, labeled R, causing it to contract and pull the hand away.
(b) (iii)
Answer: Synapse.
Explanation: A synapse is the small gap or junction between two neurones (e.g., between the sensory neurone $T$ and the relay neurone $W$) where chemicals called neurotransmitters serve to transmit the electrical signal from one cell to the next.
