Question
Sensory neurones conduct impulses from
the brain and spinal cord to muscles.
one sense organ to another sense organ.
sense organs to the brain and spinal cord.
sense organs to muscles.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Sensory neurons, also known as afferent neurons, are responsible for transmitting sensory information from various sense organs (such as the eyes, ears, skin, nose, and tongue) to the central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord. This transmission of impulses allows us to perceive and interpret different sensory stimuli like light, sound, touch, taste, and smell.
Question
The diagram shows a section through human skin.
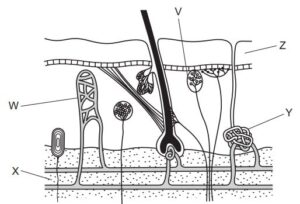
Which row matches the labelled part to its function?
| insulation | sensing temperature | sweat production |
A | Y | W | Z |
B | Y | V | X |
C | X | W | Z |
D | X | V | Y |
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
In a section through human skin, the functions you mentioned are related to different layers and components of the skin. Here’s how each function is associated with specific parts of the skin:
1. Insulation (Thermoregulation): The function of insulation to regulate body temperature is primarily associated with the subcutaneous tissue (also known as the hypodermis or adipose tissue layer). This layer is located beneath the dermis and is composed of fat cells that provide thermal insulation by trapping heat and preventing its loss from the body. Insulation helps to maintain a relatively stable body temperature in various environmental conditions.
2. Sensing Temperature (Thermosensation): Sensing temperature is a function carried out by specialized nerve endings located within the dermis and epidermis layers of the skin. These nerve endings, known as thermoreceptors, detect changes in temperature and send signals to the brain to initiate appropriate responses. Cold receptors (thermoreceptors sensitive to lower temperatures) and warm receptors (thermoreceptors sensitive to higher temperatures) enable the body to sense changes in temperature and adjust its physiological processes accordingly.
3. Sweat Production (Sudoriferous Glands): Sweat production is primarily associated with sweat glands, which are located in the dermis layer of the skin. There are two main types of sweat glands: eccrine glands and apocrine glands. Eccrine sweat glands are responsible for producing most of the sweat in response to heat, physical activity, or stress. Sweat plays a crucial role in cooling the body through evaporative cooling. Apocrine glands, located mainly in areas with hair follicles (e.g., armpits and groin), produce a different type of sweat that can be influenced by emotional and hormonal factors.
Question
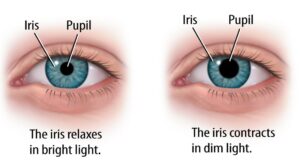
Which structure controls the amount of light entering the eye?
A cornea
B iris
C lens
D retina
▶️Answer/Explanation
The structure that controls the amount of light entering the eye is:
B. iris
The iris is the colored part of the eye and it contains muscles that can contract or dilate to adjust the size of the pupil, which is the opening that allows light to enter the eye. This contraction and dilation of the iris help regulate the amount of light that reaches the retina at the back of the eye.
Question
Some structures in the eye are listed.
1 cornea
2 iris
3 lens
4 retina
Which structures contain light receptors?
A 1, 2 and 3 B 2, 3 and 4 C 2 and 4 only D 4 only
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
The structure in the eye that contains light receptors is the retina. The retina contains specialized cells called photoreceptors, specifically rods and cones, which are responsible for detecting light and transmitting visual signals to the brain. The other structures listed, such as the cornea, iris, and lens, play important roles in the overall functioning of the eye, but they do not contain light receptors themselves.
Question
Which type of cell is found in sense organs?
A ciliated
B effector
C receptor
D palisade
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
The type of cell that is found in sense organs and is responsible for detecting various stimuli is referred to as a “receptor” cell. Receptor cells are specialized to respond to specific types of stimuli, such as light, sound, touch, taste, or smell. They play a crucial role in transmitting sensory information to the nervous system, allowing us to perceive and interpret the world around us. Therefore, the correct answer is:
C. Receptor
