Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) Completion of the sentence:
Sense organs are groups of receptor cells responding to specific stimuli such as light, sound, touch, temperature and chemicals.
(b) Description and Explanation:
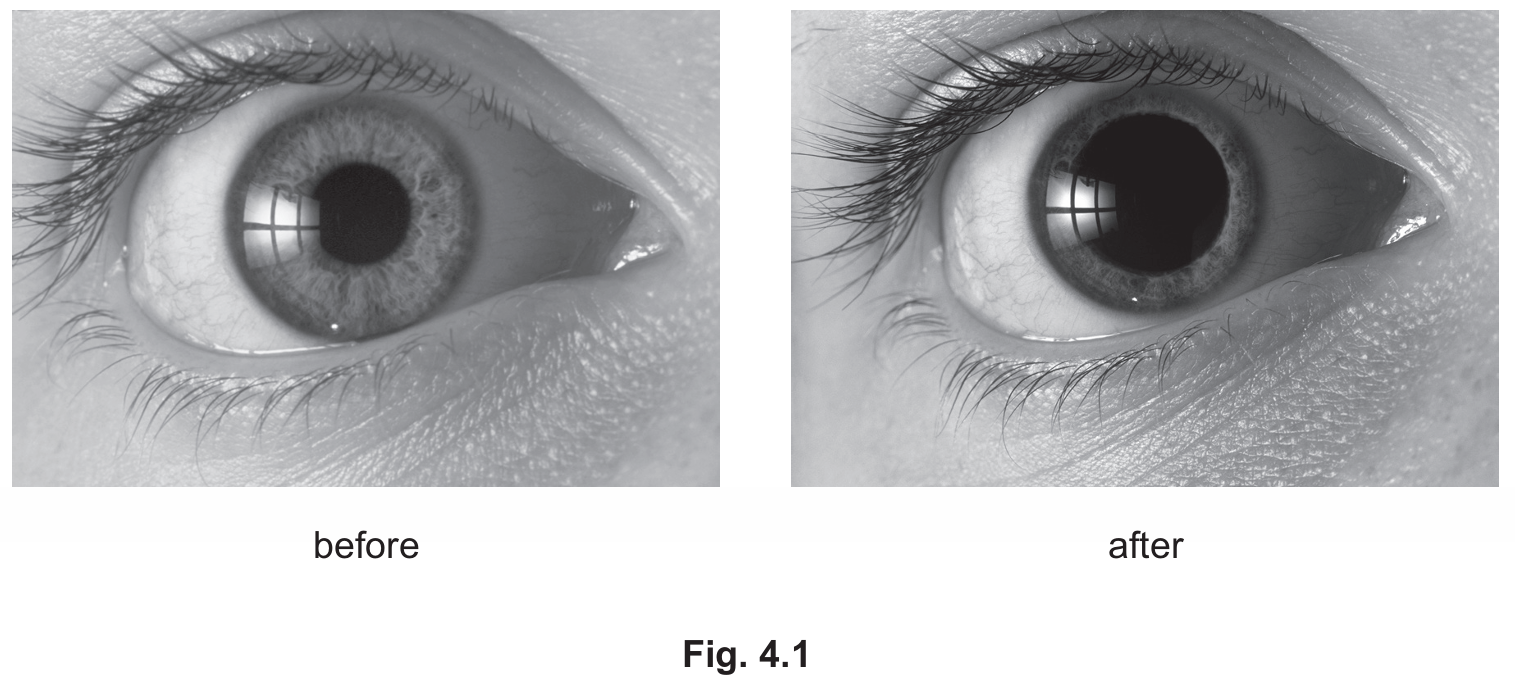
• Description: The pupil becomes larger (dilates) in the “after” diagram.
• Explanation: The light intensity in the environment decreased (became dimmer). The pupil dilated to allow more light to enter the eye to reach the retina.
(c)(i) Blind Spot Identification:
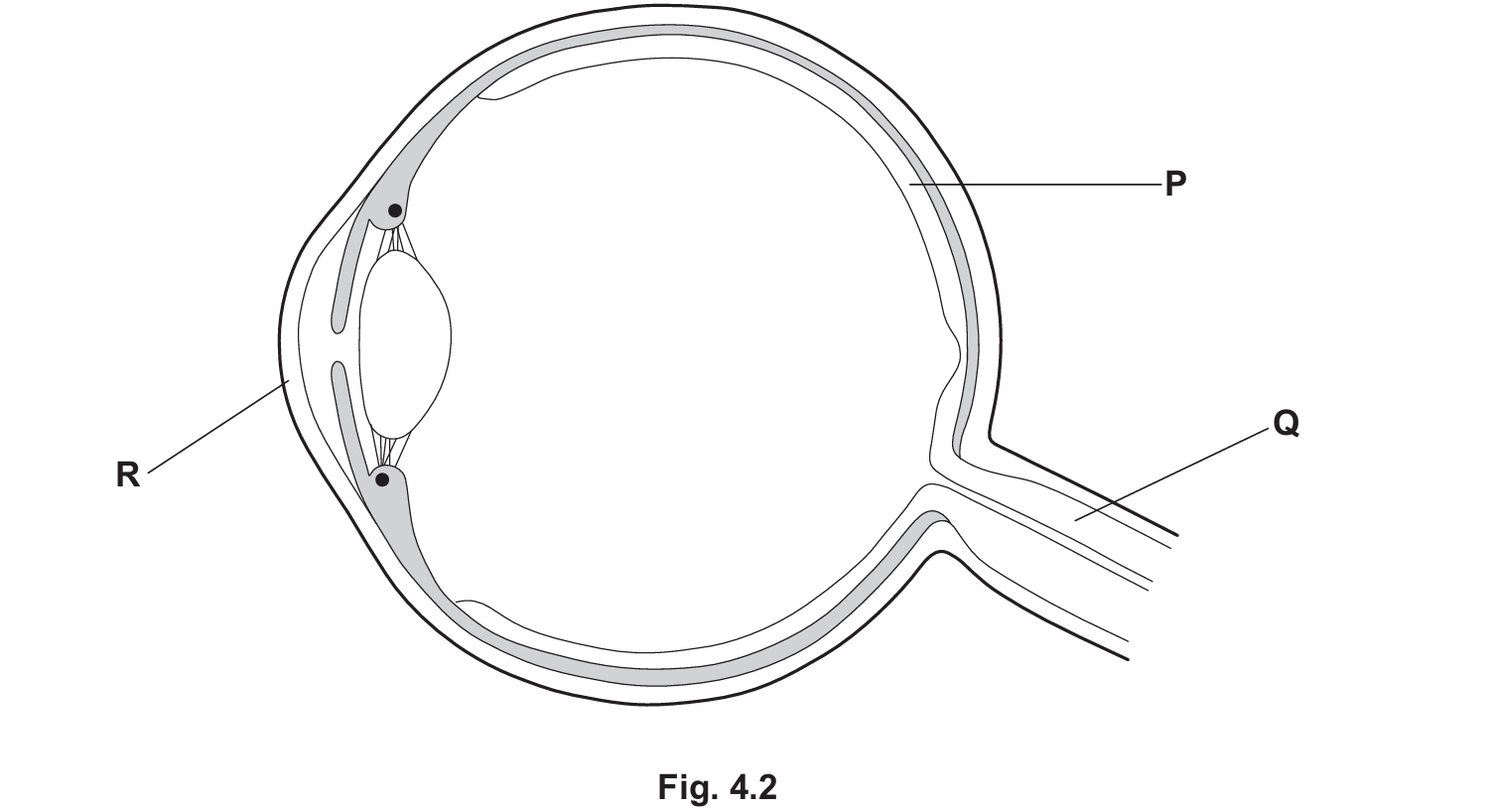
The X should be marked at the point where the optic nerve (Q) leaves the eye (the optic disc), where there are no receptor cells.
(c)(ii) Matching functions:
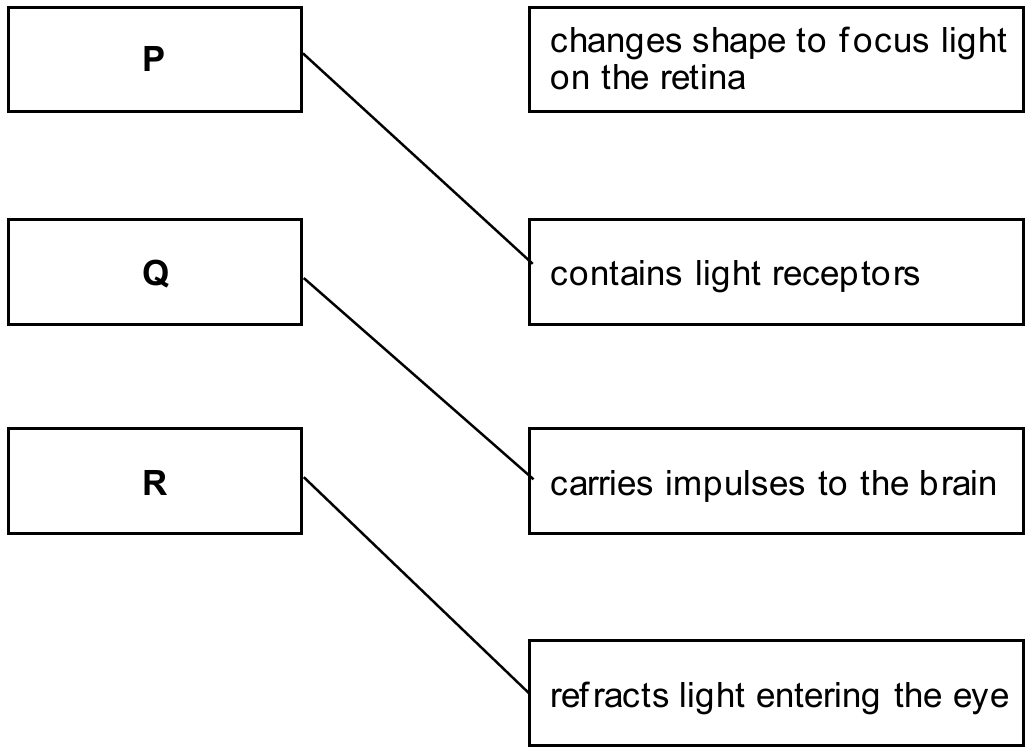
• P (Retina): contains light receptors.
• Q (Optic Nerve): carries impulses to the brain.
• R (Cornea): refracts light.
Part (a): Sense organs contain groups of specialized receptor cells that detect changes in the environment, known as stimuli. For example, the ear responds to sound, while the skin responds to touch and temperature.
Part (b): This image demonstrates the pupil reflex. In dim light, the pupil dilates (widens) to maximize light capture. Although the Core syllabus focuses on changes in diameter, the mechanism (Supplement) involves the contraction of radial muscles and the relaxation of circular muscles in the iris.
Part (c):
R (Cornea): This is the transparent frontal part of the eye that refracts (bends) light as it enters.
P (Retina): The inner lining at the back of the eye containing photoreceptors (rods and cones).
Q (Optic Nerve): Transmits electrical impulses generated by the receptor cells to the brain for processing. The point where this nerve exits the eye lacks receptors, creating the blind spot.
