Question
The diagram shows the position of some of the human endocrine glands.
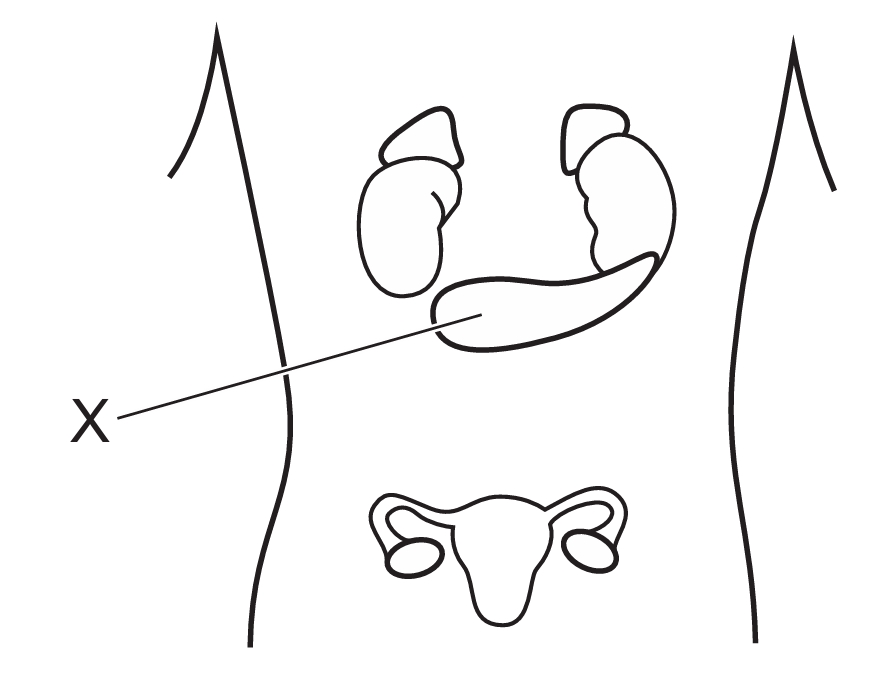
Which hormone is secreted by $X$?
(A) adrenaline
(B) insulin
(C) oestrogen
(D) testosterone
(B) insulin
(C) oestrogen
(D) testosterone
▶️ Answer/Explanation
The label $X$ points to the pancreas, a leaf-shaped gland located behind the stomach. The pancreas plays a vital role in regulating blood glucose levels by secreting the hormone insulin from its beta cells. While the diagram also shows the adrenal glands (above the kidneys) which secrete adrenaline, and the ovaries which secrete oestrogen, $X$ specifically identifies the pancreatic structure. Therefore, among the given options, insulin is the correct hormone produced by this specific gland.
✅ Answer: (B)
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
Which row shows the correct speed and duration for the type of control?

▶️ Answer/Explanation
Hormonal control involves chemicals (hormones) traveling through the bloodstream to target organs, making the speed of action slow compared to electrical impulses. However, these effects often last for a long duration because the chemicals remain in the blood until broken down. In contrast, nervous control is characterized by rapid electrical signals (fast) that have immediate, localized, and fleeting effects (short). Therefore, row B correctly identifies the characteristics of hormonal control.
✅ Answer: (B)
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
Which hormones increase the blood glucose concentration in humans?
(A) adrenaline and glucagon
(B) adrenaline and insulin
(C) glucagon only
(D) insulin only
(B) adrenaline and insulin
(C) glucagon only
(D) insulin only
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Blood glucose levels are regulated by several hormones with opposing effects. Glucagon, secreted by the pancreas, increases glucose levels by stimulating the liver to convert stored glycogen into glucose. Adrenaline (epinephrine) also increases blood glucose during “fight or flight” situations to provide immediate energy to muscles. Conversely, insulin works to decrease blood glucose by promoting its uptake into cells. Since both adrenaline and glucagon act to raise concentration, option (A) is correct.
✅ Answer: (A)
✅ Answer: (A)
