Question
(a) Complete the sentences about the control of blood glucose concentration.
Blood glucose concentration increases after a person eats a meal containing carbohydrates.
This causes the …………………. to release insulin. Insulin causes the ………………. to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into ……………….. .
The control of blood glucose concentration is an example of …………………. .
(c) A scientist investigated the effect of an injection of glucose solution on blood glucose concentration in healthy people. The injection was given at \(0\) minutes.
Fig. 3.1 shows the results.
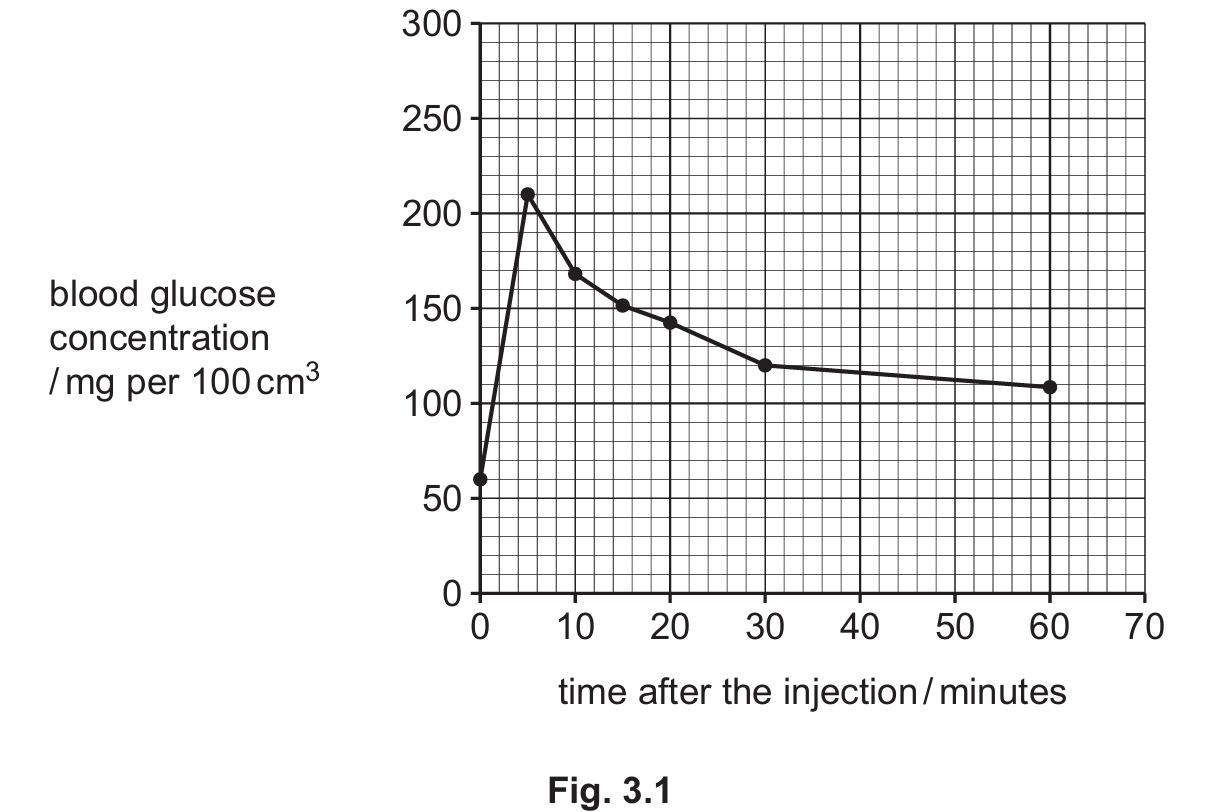
Calculate the percentage change in the blood glucose concentration from \(5\) minutes after the injection to \(30\) minutes after the injection.
Give your answer to two significant figures.
Suggest how this is an advantage for the “fight or flight” response.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
This causes the pancreas to release insulin. Insulin causes the liver to remove glucose from the blood and convert it into glycogen.
The control of blood glucose concentration is an example of negative feedback (or homeostasis).
(b)
Treatment includes (any two):
- Insulin injections or use of an insulin pump.
- Monitoring blood glucose levels regularly.
- Controlled diet (counting carbohydrates/matching food intake to activity).
(c)
\(-43\%\) (decrease of \(43\%\)).
(See explanation below for calculation steps).
(d)
(Any three points):
- Adrenaline causes the breakdown (conversion) of glycogen (stored carbohydrate) into glucose.
- This results in increasing blood glucose concentration.
- This glucose is used in respiration to release energy.
- The released energy is used for muscle contraction (to fight or run away).
Part (a): Homeostatic Control
When blood glucose rises, the body aims to bring it back to a “set point.” This is the definition of homeostasis, specifically achieved via negative feedback (a mechanism that reverses a change). The pancreas detects high glucose and secretes insulin. Insulin signals the liver (and muscle cells) to absorb glucose and store it as the insoluble polysaccharide glycogen.
Part (b): Type 1 Diabetes
In Type 1 diabetes, the immune system destroys the cells in the pancreas that make insulin. Therefore, the primary treatment is replacing that missing hormone via insulin injections. Monitoring is crucial to ensure the dose matches the carbohydrate intake.
Part (c): Percentage Change Calculation
To find the percentage change, we extract the data from the graph (Fig 3.1):
1. Value at \(5\) minutes (Start): \(\approx 210~mg/100~cm^3\)
2. Value at \(30\) minutes (End): \(\approx 120~mg/100~cm^3\)
3. Formula: \(\text{Percentage Change} = \frac{\text{Final Value} – \text{Initial Value}}{\text{Initial Value}} \times 100\)
4. Calculation: $$ \frac{120 – 210}{210} \times 100 = \frac{-90}{210} \times 100 \approx -42.857\% $$ 5. Rounding: The question asks for two significant figures. $$ -42.857 \rightarrow -43\% $$ The negative sign indicates a decrease.
Part (d): Adrenaline and Survival
The “fight or flight” response requires immediate physical exertion. Muscles need ATP (energy) to contract rapidly. By breaking down stored glycogen back into glucose, adrenaline floods the blood with fuel. This fuel is delivered to muscles for respiration, providing the necessary energy to escape danger or fight.
