Question
Fig. 6.1 shows the body temperature of a student over a 32 hour period.
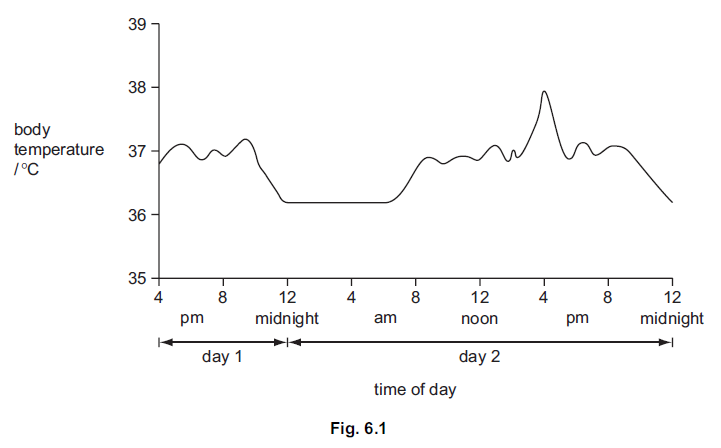
(a) Between 2.30pm and 4.15pm on day 2 the student was involved in gymnastics training.
Explain why the body temperature increased during the training.

(b) The student had a normal body temperature of 36.8 °C. If the body temperature rises
above normal, homeostasis takes place.
(i) Define homeostasis.

(ii) Explain how sweating can help to change body temperature.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) Define the term homeostasis.
(b) Fig. 2.1 shows a section through the skin.
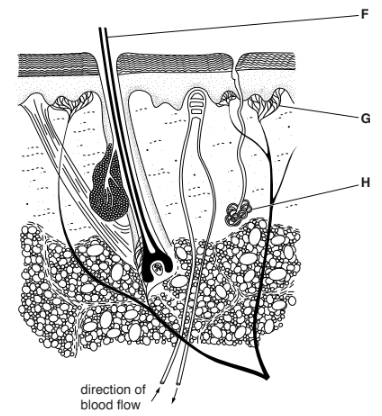
Fig. 2.1
(i) Name the structures F, G and H, shown on Fig. 2.1.
Fig. 2.2 shows the same section through the skin.
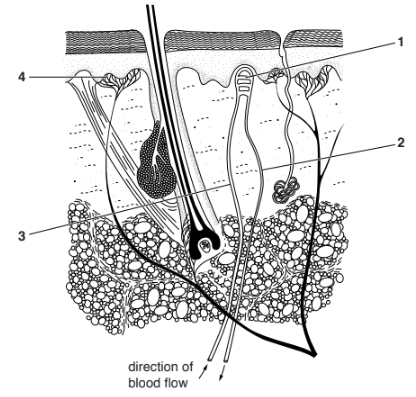
Fig. 2.2
(ii) Using Fig. 2.2, state which numbered part of the skin, 1 – 4, has the highest temperature on a cold day.
(c) When the body temperature rises above 37 °C, two changes occur in the skin to help the temperature return to normal:
• vasodilation
• increased sweating.
Fig. 2.3 shows a simplified diagram of the skin.
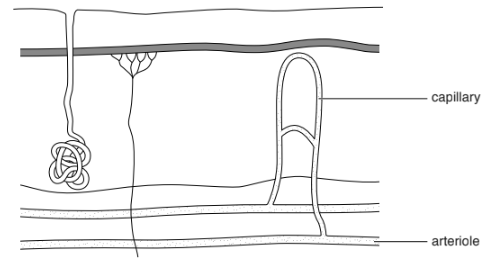
Fig. 2.3
(i) Describe what happens in vasodilation, and explain how this helps to lower body temperature.
Use Fig. 2.3 to help with your explanation.
(ii) Explain how increased sweating helps to lower the body temperature.
(iii) State two methods, other than reduced sweating, that the body uses to stop the body temperature falling below normal on a cold day.
(d) Name the part of the body which coordinates the changes in the skin to keep the body temperature at 37 °C.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) constant/maintenance/AW ;
internal environment/AW ;
(b) (i) F: hair ;
G: (temperature) receptors /AW ;
H: sweat gland ;
(ii) 3 ;
(c) (i) arterioles dilate;
more blood flows, to the (skin) surface / through the
(surface)capillaries ;
(more) heat is taken to the surface / blood carries heat ;
heat (energy ) is lost (from the skin) ;
(ii) 1. sweat/water on skin surface ;
2. water is evaporated ;
3. (body) heat/ energy used (in evaporation) ;
4. heat, from body / carried by blood ;
5. blood temperature decreases ;
6. correct reference to heat loss by conduction / convection / radiation ;
(iii) shivering or description ;
vasoconstriction/AW ;
hairs stand on end ;
increased rate of respiration ;
(d) brain ;
hypothalamus ;
