Question
What is meant by the term tropism?
A absorption of light by chlorophyll
B growth of parts of a plant towards or away from a stimulus
C growth of seed into a small plant
D level at which an organism feeds in a food chain
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is:
B growth of parts of a plant towards or away from a stimulus
Tropism refers to the growth or movement of an organism (usually a plant) in response to a specific external stimulus, such as light, gravity, or touch. The growth can be either towards or away from the stimulus. For example, phototropism is the growth of a plant towards a light source, and gravitropism is the growth of plant roots towards gravity and shoots away from it.
Question
The diagram shows seedlings in two experiments on the tropic response of seedlings to gravity
and light.
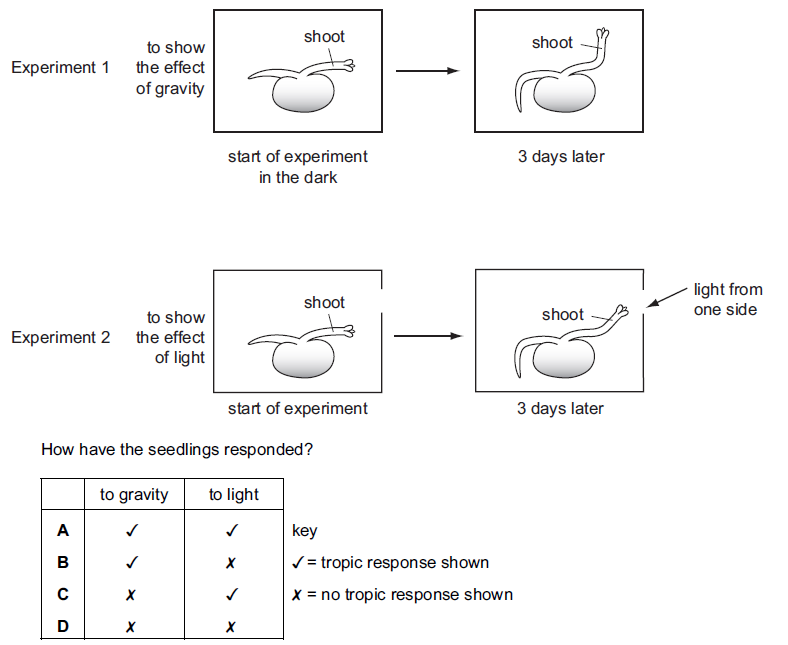
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Both seedlings responded to light as well as gravity. Seedlings’ responses to these external stimuli are known as tropic responses. Tropic responses are directional growth movements in response to specific stimuli, such as light (phototropism) or gravity (gravitropism).
In the experiments:
Experiment 1: Tropic Response to Gravity In this experiment, seedlings are placed in a controlled environment where the direction of gravity is observed over time. Seedlings typically display positive gravitropism, which means their roots grow in the direction of gravity (downward), while their shoots grow in the opposite direction (upward).
Experiment 2: Tropic Response to Light In this experiment, seedlings are placed in a controlled environment with light sources from one side. Seedlings exhibit positive phototropism, meaning they grow toward a light source. This phenomenon is commonly seen in plants as they adjust their growth patterns to maximize their exposure to light for photosynthesis.
Question
Which response is a result of geotropism?
A flowers being produced
B growing bigger leaves
C roots growing downwards
D seeds germinating
 Answer/Explanation
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
C roots growing downwards
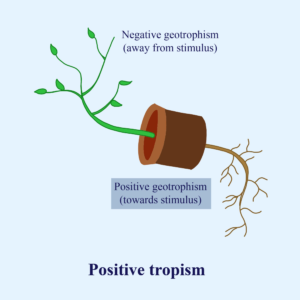
Geotropism, also known as gravitropism, is a plant’s growth response to gravity. In the case of roots, they exhibit positive geotropism, meaning they grow in the direction of gravity, which is downward. This helps anchor the plant in the soil and allows roots to access water and nutrients more effectively.
Question
The diagram shows an experiment to investigate the response of a plant stem to gravity.

What is a suitable control for this experiment?
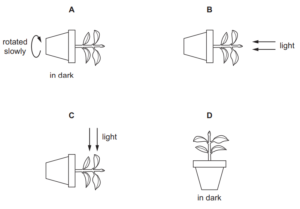
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The response of a plant stem to gravity over a period of two days is a dynamic process known as gravitropism. Gravitropism, also referred to as geotropism, is a plant’s natural ability to sense and respond to the direction of gravity. This response helps the plant to orient its growth in a way that maximizes its access to light and nutrients. If you were to place a potted plant on its side, you would likely see the following progression:
1. The shoots or stems of a plant exhibit negative gravitropism. This means they grow against the direction of gravity, moving upwards. This response allows the above-ground parts of the plant to position themselves optimally for sunlight exposure and photosynthesis.
2. In response to darkness and the lack of light cues, the stems might undergo rapid elongation. This elongation is a growth strategy to reach any available light source as quickly as possible.
3. If the stem was initially placed horizontally, you might observe curvature in the stem as it bends upwards against gravity. This curvature is a result of differential growth rates on the upper and lower sides of the stem. Plant A would be a suitable control for this experiment. Over a two-day period, If you were to place a potted plant on its side, you would likely see the above progression.
Question
The diagram shows seedlings in two experiments on the tropic response of seedlings to gravity
and light.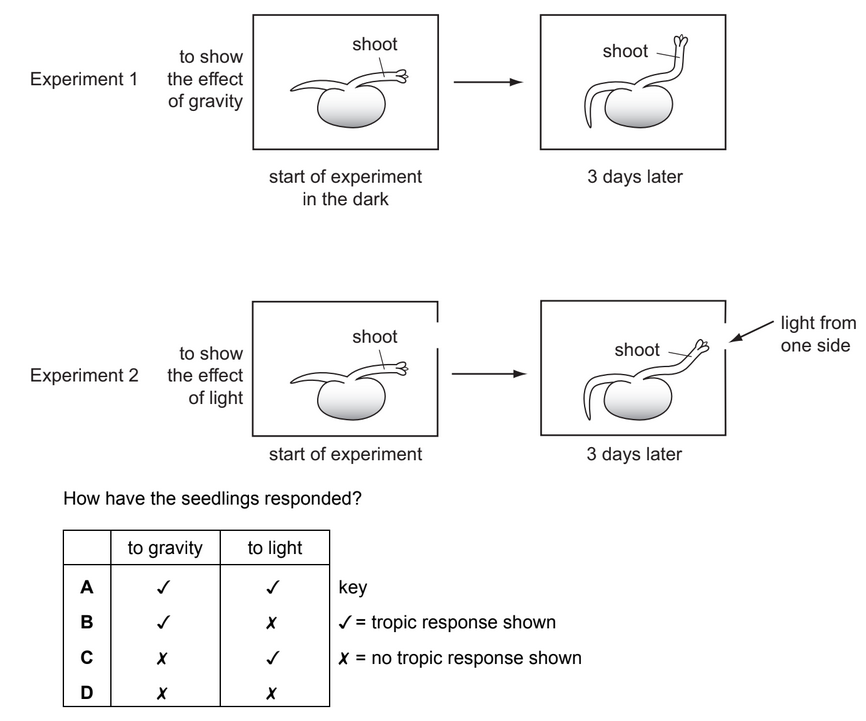
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Both seedlings responded to light as well as gravity. Seedlings’ responses to these external stimuli are known as tropic responses. Tropic responses are directional growth movements in response to specific stimuli, such as light (phototropism) or gravity (gravitropism).
In the experiments:
Experiment 1: Tropic Response to Gravity In this experiment, seedlings are placed in a controlled environment where the direction of gravity is observed over time. Seedlings typically display positive gravitropism, which means their roots grow in the direction of gravity (downward), while their shoots grow in the opposite direction (upward).
Experiment 2: Tropic Response to Light In this experiment, seedlings are placed in a controlled environment with light sources from one side. Seedlings exhibit positive phototropism, meaning they grow toward a light source. This phenomenon is commonly seen in plants as they adjust their growth patterns to maximize their exposure to light for photosynthesis.
