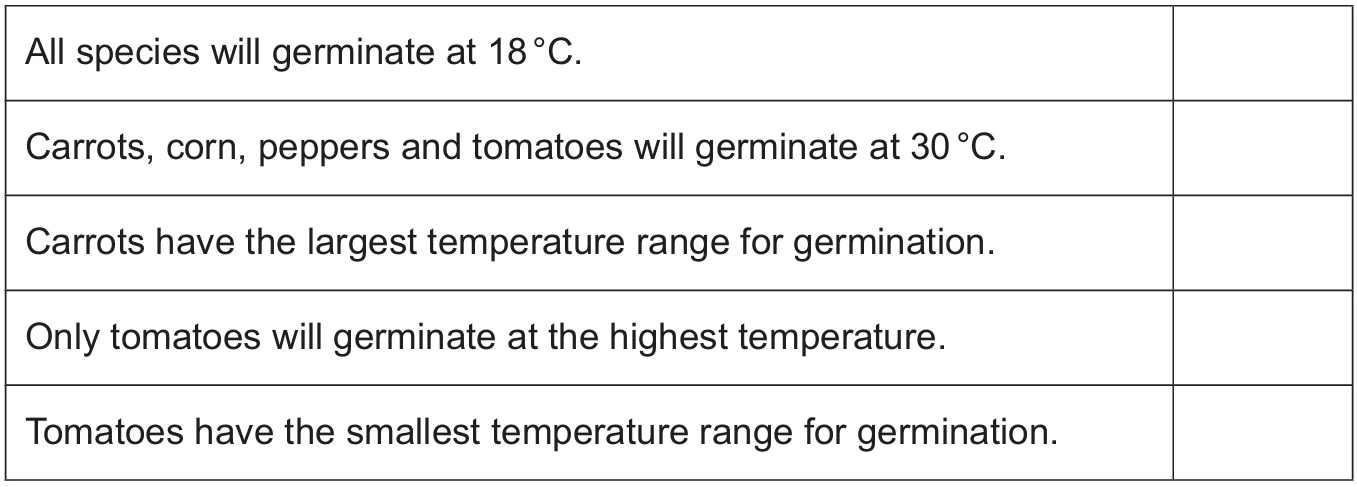
Question
(a) Seeds of different crop plants germinate at different temperatures.
Table 2.1 shows the temperatures at which each crop plant germinates.

The list shows five conclusions. Tick (✓) two conclusions for the data shown in Table 2.1.
(b) A student investigated the conditions needed for carrot seed germination.
The seeds were kept at \(10^\circ\text{C}\), which is a suitable temperature for germination.
Test-tubes A and C contained only carbon dioxide gas.
Test-tubes B and D contained only oxygen gas.
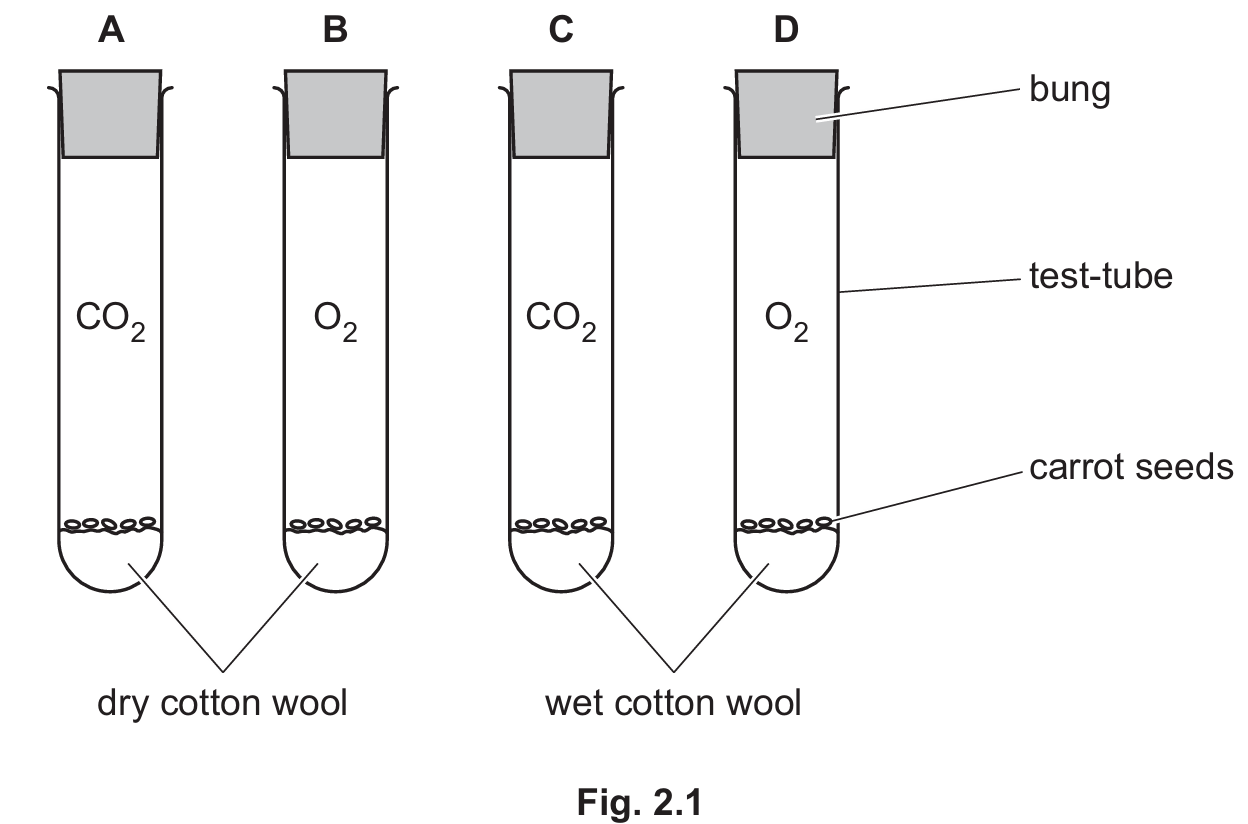
(i) Using the information in Fig. 2.1, state the letter of the test-tube containing carrot seeds that will germinate and explain why these seeds will germinate.
The investigation was repeated at \(25^\circ\text{C}\).
Predict the results you would expect at \(25^\circ\text{C}\).
This tropic response is called …………… .
The plant root grows into the soil towards …………… .
This tropic response is called ………….. .
Root hairs develop, which increase the uptake of ……….. and water.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
The correct conclusions are:
- ✅ Carrots have the largest temperature range for germination. (Range: \(29 – 7 = 22^\circ\text{C}\))
- ✅ Tomatoes have the smallest temperature range for germination. (Range: \(35 – 21 = 14^\circ\text{C}\))
(b)(i)
Test-tube: D
Explanation: Germination requires three key factors: water, oxygen, and a suitable temperature. Test-tube D contains wet cotton wool (providing water) and oxygen, making it the only setup with all necessary conditions. Tubes A and C lack oxygen (containing carbon dioxide instead), and Tube B lacks water (dry cotton wool).
(b)(ii)
Prediction: The seeds would germinate faster (or earlier/more quickly).
Reason: A temperature of \(25^\circ\text{C}\) is closer to the optimum temperature for the enzymes involved in germination compared to \(10^\circ\text{C}\). Higher kinetic energy leads to a faster rate of metabolic reactions.
(c)
The plant shoot grows towards the direction of light.
This tropic response is called phototropism.
The plant root grows into the soil towards gravity.
This tropic response is called gravitropism (or geotropism).
Root hairs develop, which increase the uptake of ions / minerals / mineral ions and water.
