Question
The flowers of pea plants, Pisum sativum, are produced for sexual reproduction. The
flowers are naturally self-pollinating, but they can be cross-pollinated by insects.
(a) Explain the difference between self-pollination and cross-pollination.

(b) Explain the disadvantages for plants, such as P. sativum, of reproducing sexually.

Pea seeds develop inside pea pods after fertilization. They contain starch. A gene controls
the production of an enzyme involved in the synthesis of starch grains.
The allele, R, codes for an enzyme that produces normal starch grains.
This results in seeds that are round.
The allele, r, does not code for the enzyme. The starch grains are not formed normally. This
results in seeds that are wrinkled.
Figure shows round and wrinkled pea seeds.

Pure bred plants are homozygous for the gene concerned. A plant breeder had some pure
bred pea plants that had grown from round seeds and some pure bred plants that had
grown from wrinkled seeds.
(c) State the genotypes of the pure bred plants that had grown from round and from
wrinkled seeds.

These pure bred plants were cross-pollinated (cross 1) and the seeds collected.
All the seeds were round. These round seeds were germinated, grown into adult plants
(offspring 1) and self-pollinated (cross 2).
The pods on the offspring 1 plants contained both round and wrinkled seeds.
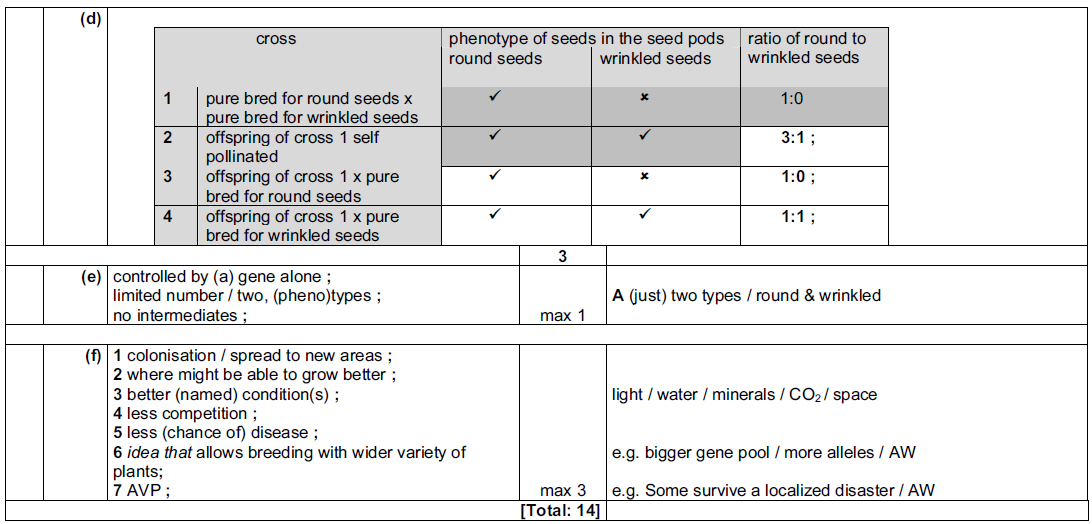
Further crosses (3 and 4) were carried out as shown in Table 6.1.
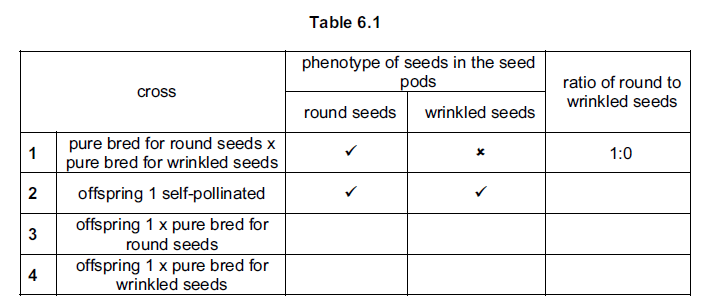
(d) Complete Table 6.1 by indicating
• the type of seeds present in the pods with a tick (✔) or a cross (✖)
• the ratio of round to wrinkled seeds.
You may use the space below and on page 22 for any rough working. [3]
(e) Seed shape in peas is an example of discontinuous variation.
Suggest one reason why seed shape is an example of discontinuous variation.

Plants have methods to disperse their seeds over a wide area.
(f) Explain the advantages of having seeds that are dispersed over a wide area.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
Figure shows a diagram showing the events from pollination to fertilization in a species of flowering
plant.
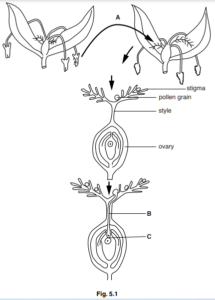
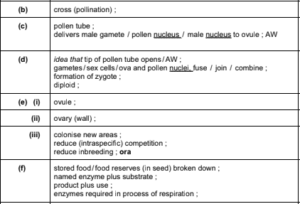
(a) Name the likely method of pollination for the flowers shown at A in Fig. 5.1. Give an explanation
for your choice.
method of pollination …………………………………………………………………………………………………..
explanation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(b) In Fig. 5.1 pollen is transferred from one plant to another.
State the name for this type of pollination.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) Name structure B shown in Fig. 5.1 and state its function.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) Fertilization occurs at C as shown in Fig. 5.1.
Describe what happens at fertilization in flowering plants.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(e) Seed formation occurs after fertiliation. Seeds are formed inside the fruits and then dispersed.
(i) Name the part of the flower that develops into the seed.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(ii) Name the part of the flower that develops into the fruit.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(iii) State an advantage of seed dispersal.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
(f) Seed germination occurs when conditions are suitable.
Explain the role of enzymes in seed germination.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Answer/Explanation
Ans: