Question
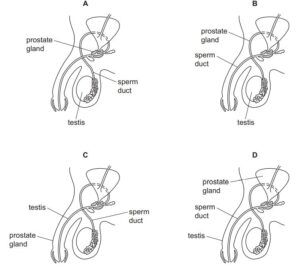
Which diagram of the male reproductive system is correctly labelled?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The male reproductive system is a complex network of organs and structures that work together to produce, store, and deliver sperm for fertilization of the female egg. It is responsible for the production of male gametes (sperm cells) and the secretion of hormones that play a role in the development of secondary sexual characteristics and the regulation of reproductive processes.
Here are the main components from the above diagram of the male reproductive system:
- Testis: The testes, also known as testicles, are the primary male reproductive organs. They are responsible for producing sperm cells and the male sex hormone testosterone. Sperm production occurs within structures called seminiferous tubules located within the testes.
- Prostate Gland: The prostate gland produces a milky fluid that is added to semen during ejaculation. This fluid helps neutralize the acidity of the female reproductive tract, enhancing the survival of sperm.
- Sperm duct: The “sperm duct” is a colloquial term for the vas deferens, which is a vital component of the male reproductive system. The vas deferens is a muscular tube that carries mature sperm from the epididymis, where they are stored and matured, to the ejaculatory ducts, and eventually to the urethra. During ejaculation, sperm are propelled through the vas deferens by rhythmic contractions of its muscular walls.
Question
Which method of birth control works by preventing an egg from being released?
condom
contraceptive pill
monitoring body temperature
vasectomy
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The method of birth control that works by preventing an egg from being released is the contraceptive pill. Contraceptive pills contain hormones that regulate a woman’s menstrual cycle and prevent ovulation (the release of an egg from the ovaries). This prevents the possibility of fertilization by sperm and subsequently prevents pregnancy. The other methods you mentioned—condoms, monitoring body temperature, and vasectomy—work through different mechanisms to prevent pregnancy. Condoms provide a barrier to block sperm from reaching the egg, monitoring body temperature (often used in fertility awareness methods) helps identify fertile periods to avoid intercourse, and vasectomy is a permanent surgical procedure that blocks the vas deferens to prevent the release of sperm during ejaculation.
Question
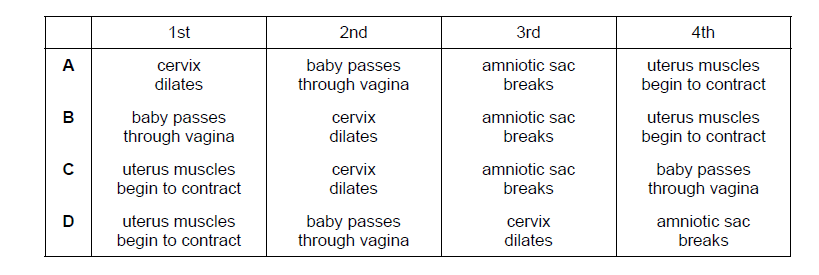
What is a possible order of events during labour and birth?
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Uterus Muscles Begin to Contract: Labor begins with the onset of uterine contractions. These contractions are coordinated muscle movements of the uterus that help push the baby downward and eventually out of the body.
Cervix Dilates: As the contractions become more frequent and intense, the cervix starts to dilate (open up) to allow the baby’s head to pass through the birth canal.
Amniotic Sac Breaks (Water Breaks):The amniotic sac, which contains the amniotic fluid that surrounds and protects the baby during pregnancy, may rupture. This is commonly known as the “water breaking.” It can happen before labor starts, during labor, or even after labor has begun.
Baby Passes Through Vagina: As the cervix continues to dilate, and with the force of contractions, the baby’s head descends further into the birth canal and eventually passes through the vagina during the pushing stage of labor.
Question
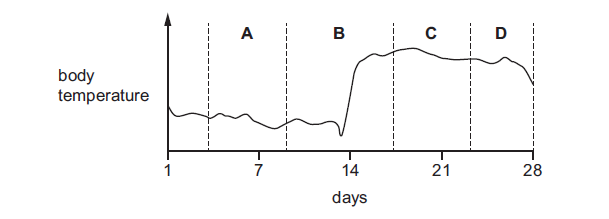
The diagram shows a woman’s body temperature during a menstrual cycle.
Monitoring body temperature is one natural method of birth control.
During which part of the menstrual cycle should sexual intercourse be avoided to try to prevent
pregnancy?
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Monitoring body temperature is a part of the fertility awareness method (FAM), which is a natural approach to birth control. It involves tracking various signs and changes in a woman’s body to identify fertile and infertile days in her menstrual cycle.
In a typical menstrual cycle, there are two main phases: the follicular phase and the luteal phase.
Follicular Phase: This phase begins on the first day of menstruation and typically lasts about 10-14 days. During this phase, the ovaries develop follicles (small fluid-filled sacs), one of which will mature and release an egg. Estrogen levels increase during this phase.
Luteal Phase: After ovulation (the release of the egg), the luteal phase begins and lasts about 10-16 days. During this phase, the ruptured follicle forms the corpus luteum, which produces progesterone. Progesterone helps prepare the uterine lining for possible pregnancy.
To use body temperature monitoring as a method of birth control, sexual intercourse is typically avoided during the fertile window. The fertile window is the period when a woman is most likely to conceive, and it includes the days leading up to and including ovulation. Ovulation usually occurs around the middle of the menstrual cycle. Monitoring body temperature as a method of birth control is often referred to as the “Basal Body Temperature” (BBT) method.
Question
Which cells in the human body are produced by the process of meiosis?
A blood cells
B muscle cells
C skin cells
D sperm cells
▶️Answer/Explanation
D. sperm cells
Sperm cells are produced through the process of meiosis. Meiosis is a specialized cell division that occurs in the testes (male reproductive organs) and results in the production of haploid sperm cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original diploid cell. This is essential for sexual reproduction, as it ensures that when the sperm fuses with an egg cell during fertilization, the resulting zygote has the correct diploid number of chromosomes.