Question
Fig. 3.1 shows the human female reproductive system.
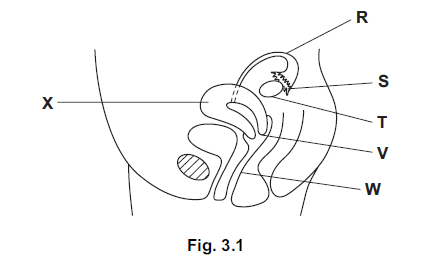
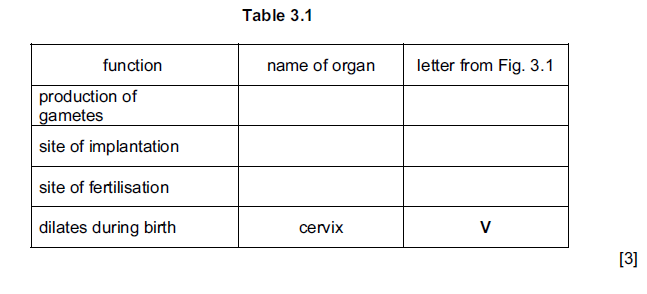
(a) Table 3.1 shows four functions of the female reproductive system.
Complete the table by:
• naming the part of the system that carries out each of the functions;
• using the letters from Fig. 3.1 to identify the part of the system named.
One row has been completed for you.
The hormone FSH is important in regulating the menstrual cycle.
(b) (i) State the target organ of FSH.
![]()
(ii) State one effect of FSH.

(c) The drug clomiphene is given to women who have difficulty in having children. The
drug increases the secretion of FSH.
As part of treatment for infertility, a woman was given clomiphene for five days. The
concentration of oestrogen in her blood was measured every day for 27 days.
The results are shown in Fig. 3.2.
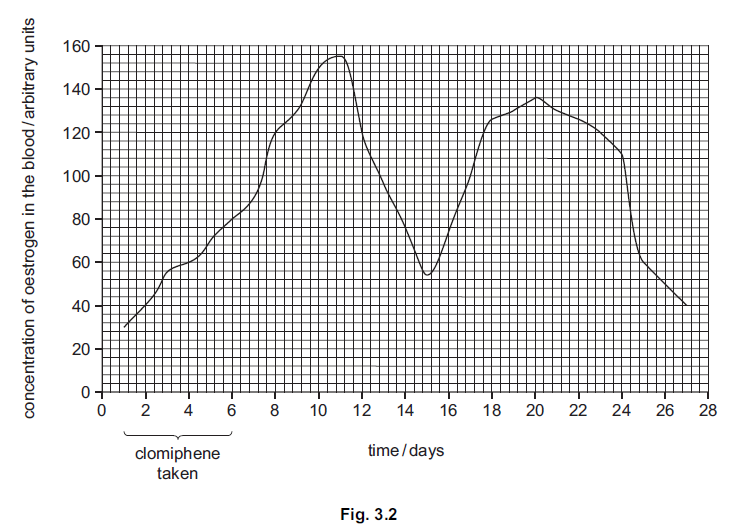
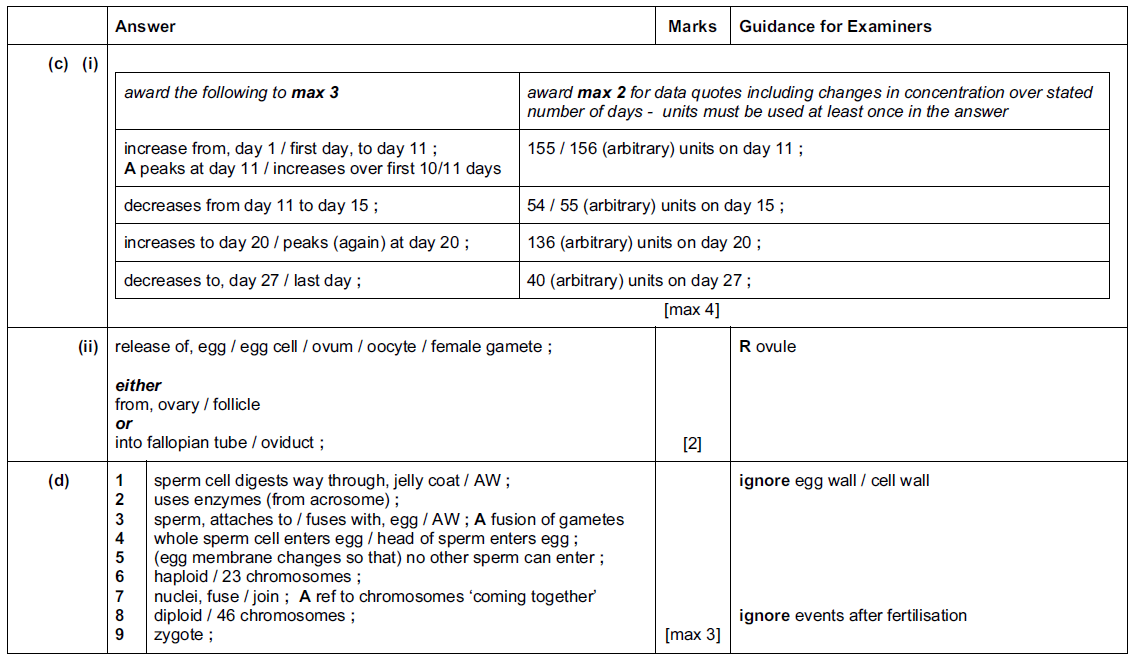
(i) Describe the changes in oestrogen in the blood over the 27 days.
You will gain credit if you use results from Fig. 3.2 in your answer.

(ii) Doctors thought that ovulation occurred around day 15.
Explain what is meant by the term ovulation.

(d) The treatment was not successful on the first occasion.
As an alternative to this treatment, women may be offered in vitro fertilisation (IVF)
treatment.
In IVF treatment, an egg is fertilised outside the body and the resulting embryo is
placed into the uterus.
Describe what happens when an egg is fertilised by a sperm.

(e) Some embryos produced by IVF do not develop because there are problems with their
chromosomes, such as having the wrong number.
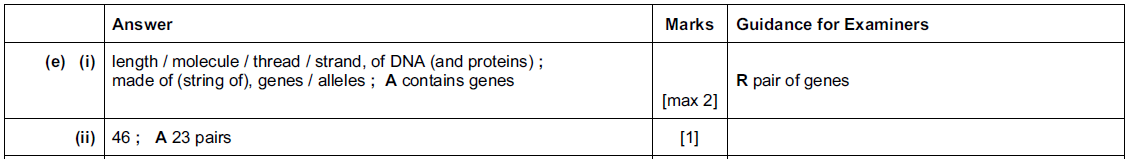
(i) Define the term chromosome.

(ii) State the correct number of chromosomes that should be in a cell of a human
embryo.
![]()
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question:
The blood of a fetus does not mix with the blood of its mother, but substances are exchanged
across the placenta.
(a) Table 3.1 shows five substances that cross the placenta, their direction of movement and the
reason for the movement.
Complete Table 3.1. The second row has been completed for you.

b) During pregnancy, women are often given dietary advice.
Explain why pregnant women require more iron and vitamin D in their diet.
iron …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
vitamin D …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(c) Mothers may be encouraged to breast-feed their newborn babies. The first milk that a mother
secretes is called colostrum and contains antibodies.
(i) Name the cells that produce antibodies.
(ii) Explain why it is important for newborn babies to have antibodies.
(iii) Some mothers bottle-feed their newborn babies with formula milk rather than breast-feed.
Describe four advantages of breast-feeding, other than providing antibodies.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a)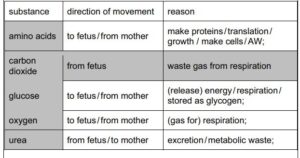
(b) iron:
for red blood cells/haemoglobin/to transport oxygen/prevent anemia;
vitamin D:
absorption of calcium;
growth/formation/ strengthening, of bones/teeth;
preventing rickets;
(c) i. lymphocytes/white blood cells/leucocytes;
ii. provides (passive) immunity;
iii. bonding/AW, with mother;
it’s free/‘cheap’;
sterile/no risk of infection;
body temperature;
no preparation/easily available;
provides, best/complete/most suitable/balanced/AW, nutrients /food;
composition/quantity, of breast milk changes to match development;
easier to digest/reduced risk of colic;
reduce risk of allergies;
contraceptive effect;
AVP;
