Question

The captive breeding programme started with 12 wild horses.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
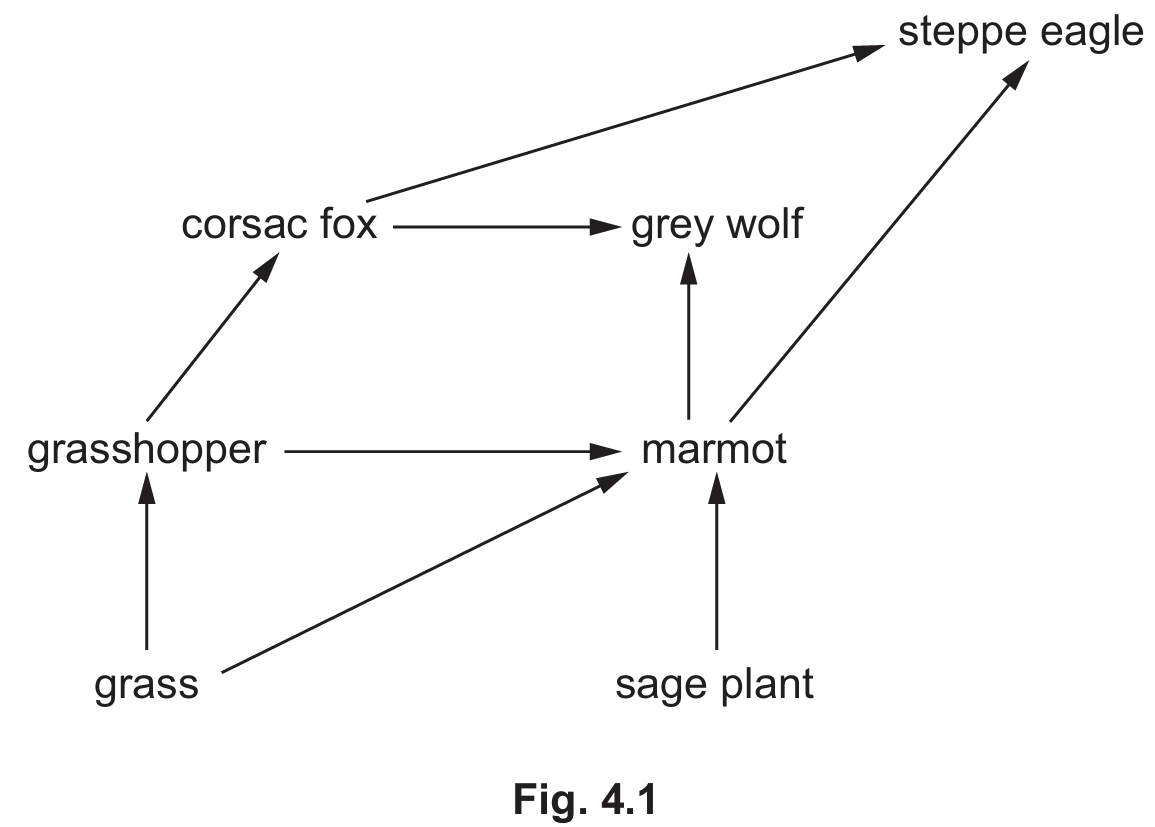
(a)(i)
Grasshopper OR marmot.
(a)(ii)
Grass $\rightarrow$ grasshopper $\rightarrow$ corsac fox $\rightarrow$ steppe eagle
OR
Grass $\rightarrow$ grasshopper $\rightarrow$ marmot $\rightarrow$ steppe eagle
(a)(iii)
Any two from:
• Energy is lost between each trophic level.
• Named example of energy loss (e.g., respiration, heat loss, movement, excretion/egestion, inedible parts).
• If less energy is available, then less biomass can be supported at the higher level.
(b)(i)
Any three from:
• Little genetic variation (small gene pool).
• Increased risk of genetic/inherited disease.
• Inbreeding (breeding between closely related individuals).
• Decreased heterozygosity / greater chance of being homozygous recessive.
• Less likely to adapt to changes in the environment.
• Increased susceptibility to transmissible disease.
(b)(ii)
Any four from:
• Protection of habitat (reserves/parks).
• Legislation protecting species / banning hunting (poaching).
• Monitoring / tracking populations.
• Education / awareness campaigns for local people.
• Provision of food / nutrients / veterinary care.
• Removal of predators.
• Removal of invasive species.
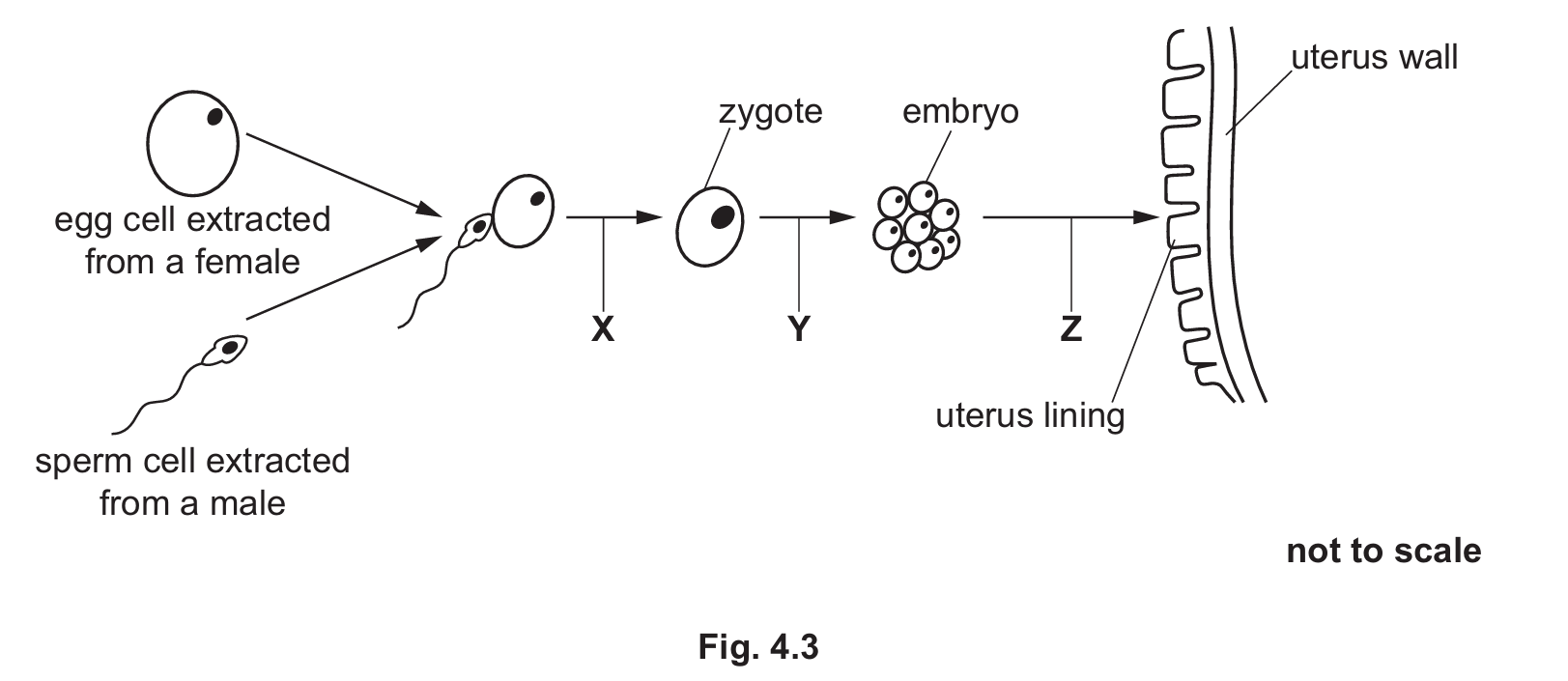
(c)
X: Fertilisation
Y: Mitosis / Cell division
Z: Implantation
Explanation:
Part (a): Food Webs and Energy Flow
Primary consumers are herbivores that feed directly on producers. In Fig. 4.1, the arrows originate from the grass and sage plant (producers) and point to the grasshopper and marmot. To construct a four-level food chain ending in the steppe eagle, we follow the arrows: Grass (1) is eaten by the grasshopper (2), which is eaten by the corsac fox (3), which is finally eaten by the steppe eagle (4). Populations decrease up trophic levels because energy transfer is inefficient (approx. 10% is passed on). Energy is lost as heat from respiration, movement, and waste, meaning there is insufficient energy to support a large population of predators.
Part (b): Conservation and Genetics
Starting a breeding programme with only 12 individuals creates a “bottleneck,” resulting in very low genetic diversity. This forces inbreeding, increasing the likelihood that harmful recessive alleles will pair up (homozygous recessive), causing genetic diseases. A lack of variation also reduces the population’s ability to adapt to new threats, such as a new pathogen or climate change. To maintain the population in the wild, active management is required, such as legal protection against poachers, monitoring their health and numbers, and ensuring their habitat remains intact.
Part (c): IVF and Development
The diagram illustrates the early stages of development often used in assisted reproduction.
• Process X shows a sperm cell fusing with an egg cell, which is the definition of fertilisation.
• Process Y shows the single-celled zygote dividing into a ball of cells (embryo) without growing in size; this type of cell division is mitosis.
• Process Z shows the embryo embedding itself into the lining of the uterus (endometrium), known as implantation.
