Question
Fig. 4.1 is a diagram of the human female reproductive system.
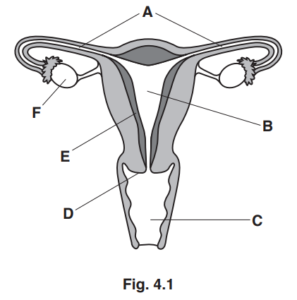
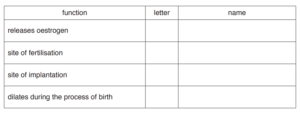
(a) Complete Table 4.1 to show the letter and the name of each of the structures that perform
these functions.
(b) Fertilization is the fusion of the nuclei of a male gamete and a female gamete resulting in a
zygote.
State the number of chromosomes present in a human:
female gamete
zygote
(c) Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted infection (STI).
Fig. 4.2 shows the number of reported cases of chlamydia in females in each age group in
one country
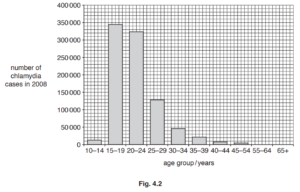
Describe the results shown by the data in Fig. 4.2.
(d) Chlamydia is caused by a bacterium.
(i) Suggest a treatment for chlamydia. [1]
(ii) State the name of one other STI [1]
(iii) Complete the sentences about the spread of STIs.
STIs are transmitted through the transfer of ……………………………………….. during sexual
contact. One way individuals can avoid the spread of STIs is to use a type of
……………………………………….. contraception. One example of this type of contraception
is ……………………………………….. . [3]
[Total: 14]
Answer/Explanation
Ans
4 (a) 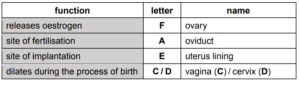
4 (b) 23 ;
46 / 23 pairs ;
4 (c) 1 cases increases then decrease ;
2 large increase between 10–14 and 15–19 ;
3 most cases in the 15–19 age group ;
4 from 15–19 number of cases decrease / from 20–24 number of cases steep
decrease ;
5 no cases above 55 years old / in 55–64 age group / 65+ age group ;
6 data quote with number of cases and age group ;
4 (d) (i) antibiotics ;
4 (d) (ii) HIV ;
4 (d) (iii) (named) bodily fluids / sexual fluid ;
barrier ;
condom / femidom ;
Question
(a) Fig. 5.1 shows the female reproductive system.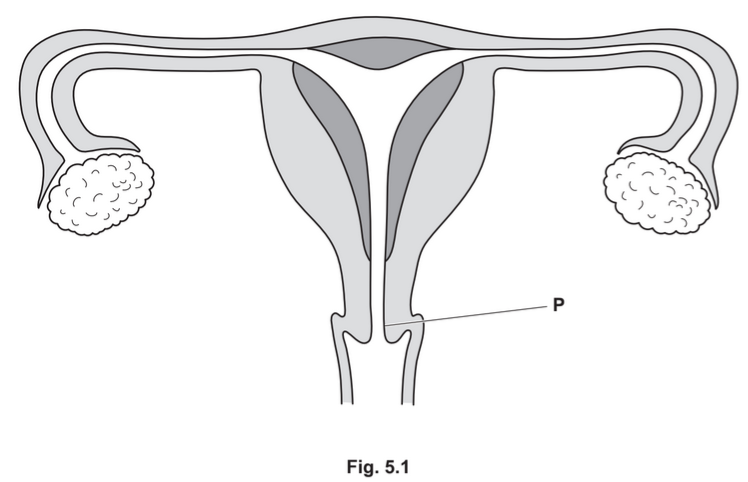
Label Fig. 5.1 using the letters listed to show the position of the organs that are identified by
their functions.
The first one (P) has been completed for you.
P site of secretion of mucus
Q site of fertilisation
R site of implantation
S site of oestrogen secretion
T site where sperm are deposited during sexual intercourse
(b) Fig. 5.2 shows a section through an egg cell at the time of ovulation.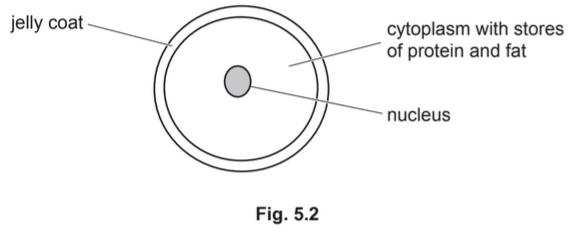
(i) Explain why the egg cell contains stores of protein and fat.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(ii) Describe the function of the jelly coat.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
(c) Fertilisation results in the formation of a zygote.
Describe how an embryo is formed from a zygote.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
(a) Fig. 2.1 is a photomicrograph showing the fertilization of one human egg cell.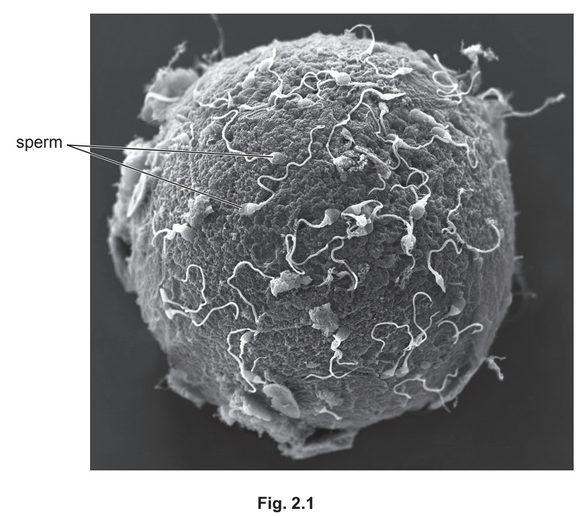
Describe and explain the adaptations of the cells shown in Fig. 2.1 that enable fertilisation
and early development of the embryo to occur.
(b) People can use artificial insemination (AI) or in vitro fertilisation (IVF) to increase their chance
of becoming pregnant.
(i) Outline the process of artificial insemination.
(ii) Outline how the process of in vitro fertilisation (IVF) differs from artificial insemination (AI).
(iii) Describe the social implications of fertility treatments.
Answer/Explanation
Ans
(a) sperm (max. four from):
- presence of acrosome (containing enzymes) ;
- idea of enzymes, digest/breakdown, egg members/jelly coat ;
- many mitochondria ;
- for respiration / to release energy (for swimming);
- flagellum/streamlined shape ;
- for, swimming / movement / locomotion ;
egg : - energy/(named) nutrient, stores;
- energy/(named) nutrients for, development of embryo/ mitosis/ cell division ;
- jelly coat ;
- (hardens) to prevent other sperm from entering (after fertilisation) ;
both; - haploid(nuclei)/half the normal number of chromosomes or 23 chromosomes in, sperm/egg ;
- gametes are haploid so, correct number of chromosomes in / 46 chromosomes in / diploid, zygote ;
(b) (i) any three from:
sample of , semen/sperm, collected / donates ;
sperm, washed/concentrated ;
(semen/sperm) inserted into vagina / uterus / near cervix ;
ref. to (sperm insertion) at the time of fertility ;
ref. to fertility drugs;
(ii) any four from:
- treatments are expensive ;
- idea that there are questions over who will fund treatments ;
- risk of multiple, births/children / pregnancies;
- poor success rates;
- ref to emotional stress / ref to not knowing heritage ;
- ethical/religious/cultural, issues, with fertility treatment process ;
- allows people who have lost their partners to have children ;
- allows people undergoing cancer treatment to have children ;
- lower chance of genetic diseases if embryos screened ;
- allows infertile people to have children ;
- allows older people to have children ;
- spare embryos can be used for, medical research/ treatments / stem cells ;
- AVP ;
Question
Fig. 4.1 shows a section through the human female reproductive system.
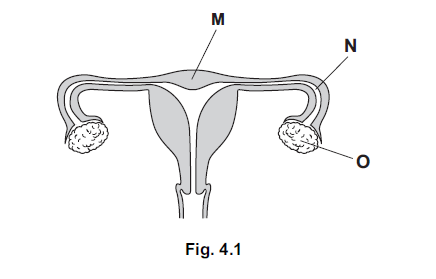
(a) (i) State one function of each of the parts labelled M and N.

(ii) State two functions of the part labelled O.

(b) When an adult female is not pregnant her menstrual cycle lasts about four weeks.
Describe the changes to the uterus and ovaries during one menstrual cycle.

(c) Fertilisation may occur after sexual intercourse.
Describe the process of fertilisation.

(d) Secondary sexual characteristics in females develop at puberty.
(i) State the hormone that controls this development.
![]()
(ii) Describe two secondary sexual characteristics controlled by this hormone.

Answer/Explanation
Ans:

Question
(a) Table 3.1 contains six statements about different methods of birth control.
Only three of the statements are correct.
Read each statement carefully and decide if it is correct.
Place a tick (✓) in the box next to each correct statement.
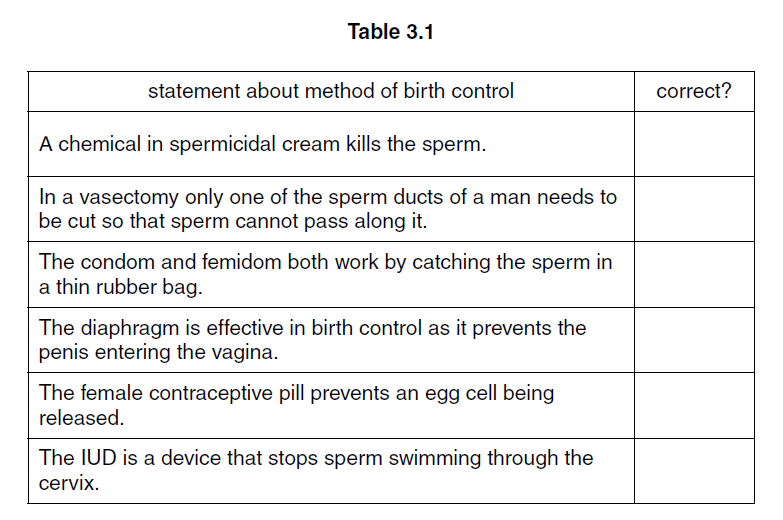
[3]
(b) State which method of birth control is effective at preventing the spread of the human
immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
Explain why it is effective.
Method ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Explanation ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
[3]
(c) The rhythm method is another type of birth control.
It is less reliable than other methods.
(i) Outline how the rhythm method works.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [2]
(ii) Suggest a reason why the rhythm method is used, even though it is not very reliable.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. [1]
Answer/Explanation
Ans:


