Question
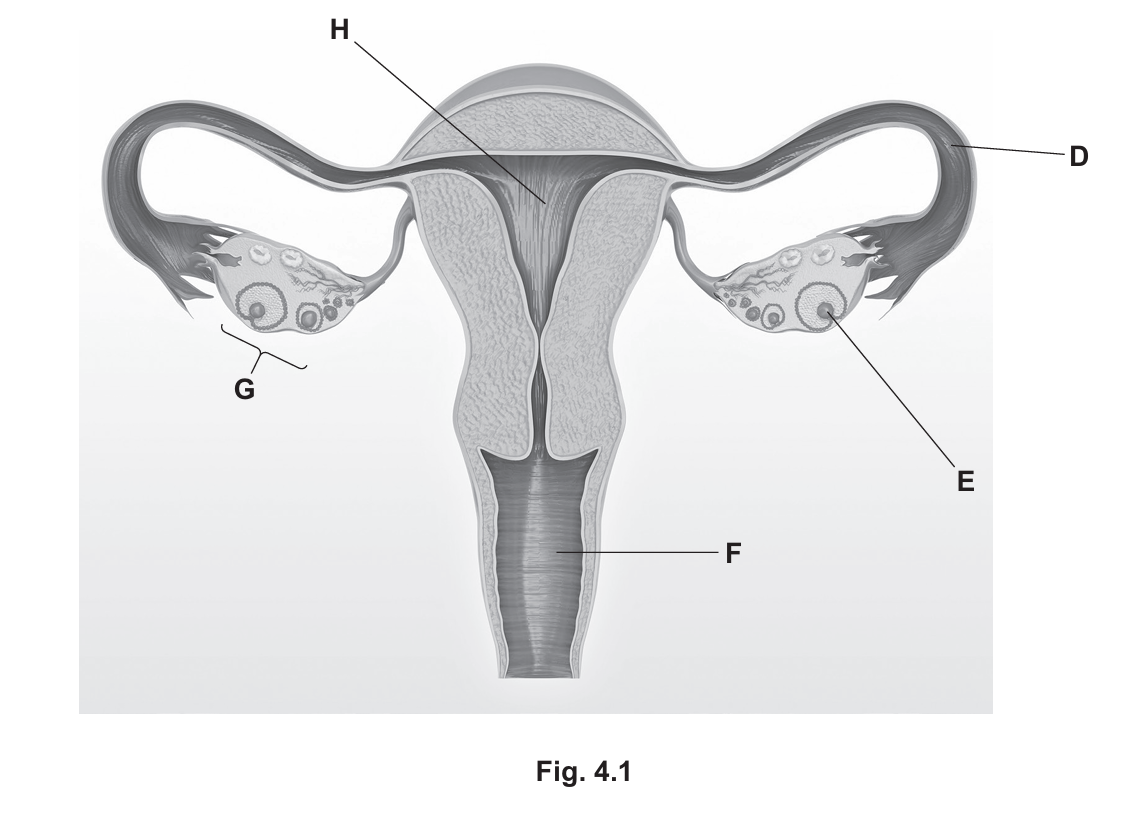
(i) State the letter in Fig. 4.1 that identifies:
- the vagina …………..
- an oviduct …………..
- an egg cell …………..
(iii) State the name of the organ shown in Fig. 4.1 that produces a female reproductive hormone and state one function of the hormone.
(b) Complete the sentences about the endocrine system using words from the list.
Each word may be used once, more than once or not at all.
homeostasis insulin internal
muscles neurones phagocytosis testosterone tissues
The endocrine system contains organs called ……………….. . These organs produce hormones.
Some hormones help to maintain a constant ……………… environment. This is called …………….. .
The pancreas produces a hormone called ………………… that helps to control blood ……………….. concentration.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Identification of parts:
• The vagina: F
• An oviduct: D
• An egg cell: E
Explanation: Looking at the diagram, D points to the fallopian tube (oviduct) connecting the ovary to the uterus. E points specifically to the ovum (egg) developing inside a follicle within the ovary. F points to the muscular canal (vagina) leading to the uterus. (For reference: G is the ovary, H is the uterus lining/endometrium).
(a)(ii) Site of fertilisation:
The letter X should be drawn with a label line ending in or on the oviduct (part D).
Explanation: Fertilisation, the fusion of the male and female gametes, normally takes place in the oviducts (fallopian tubes) shortly after ovulation, before the egg reaches the uterus.
(a)(iii) Hormone production:
• Organ: Ovary
• Function: Development of secondary sexual characteristics (e.g., breast development, widening of hips) OR regulation of the menstrual cycle OR repair/thickening of the uterus lining.
Explanation: The ovaries (G) are the primary female reproductive organs. They produce hormones such as oestrogen and progesterone. Oestrogen is responsible for the development of secondary sexual characteristics during puberty and repairing the uterus lining.
(b) Endocrine system fill-in-the-blanks:
The endocrine system contains organs called glands. These organs produce hormones.
Some hormones help to maintain a constant internal environment. This is called homeostasis.
The pancreas produces a hormone called insulin that helps to control blood glucose concentration.
Explanation:
- Glands: Endocrine glands secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream.
- Homeostasis: This is the maintenance of a stable internal environment (like temperature, water levels, and pH) despite external changes.
- Insulin & Glucose: The pancreas detects high blood glucose levels (e.g., after a meal) and secretes insulin. Insulin signals cells (liver and muscle) to absorb glucose, thereby lowering blood glucose levels to a normal range.
