Question
▶️ Answer/Explanation
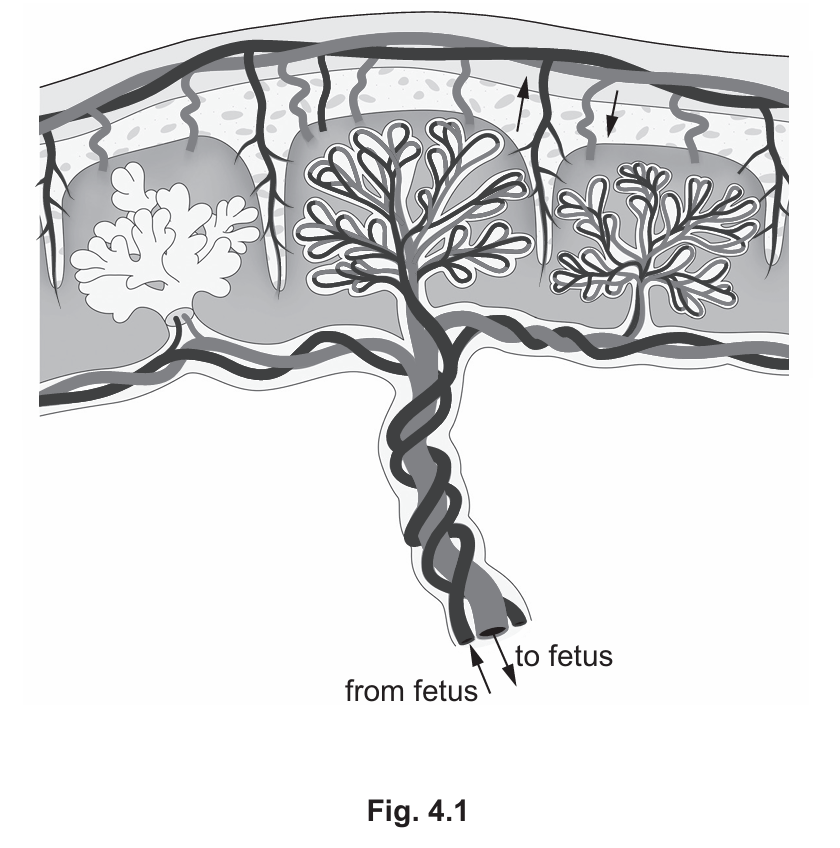
(a)(i)
The functions of the placenta and umbilical cord include:
- Separation of blood: It keeps maternal and fetal blood separate to prevent immune rejection and damage from high maternal blood pressure.
- Exchange of substances: It facilitates the transfer of nutrients (e.g., glucose, amino acids) and oxygen from the mother to the fetus, and the transfer of metabolic wastes (e.g., carbon dioxide, urea) from the fetus to the mother.
- Passive Immunity: It allows the transfer of antibodies from mother to fetus.
- Protection: The placenta acts as a barrier to certain toxins and pathogens.
- Hormone Secretion: The placenta secretes hormones like progesterone and oestrogen to maintain the pregnancy.
(a)(ii)
The amniotic sac and fluid perform the following functions:
- Protection: It cushions the fetus, protecting it against mechanical damage or shocks.
- Temperature Regulation: It maintains a constant temperature suitable for development.
- Development: It allows the fetus to move freely, which is essential for proper muscle and bone development.
- Barrier: It helps protect the fetus from infection.
- Lung Development: It allows for lung development (fetal breathing movements).
(b)(i)
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is another STI that can be passed from mother to fetus.
(b)(ii)
Ways to control the spread of STIs include:
- Barrier methods: Using condoms or femidoms during sexual intercourse.
- Abstinence: Refraining from sexual activity.
- Education: Increasing awareness about safe sex practices.
- Screening/Testing: Regular testing and tracing sexual partners of infected individuals.
- Vaccination: Using vaccines (e.g., for Hepatitis B or HPV).
- Medication: Using antibiotics to treat bacterial infections (preventing further spread).
Explanation:
Part (a): The placenta is a vital temporary organ. It provides a large surface area for the diffusion of materials between the maternal and fetal blood supplies without the blood actually mixing. Mixing would be dangerous because the mother’s immune system might attack the fetal cells (which contain foreign antigens from the father), and her higher blood pressure could damage delicate fetal vessels. The umbilical cord connects the fetus to the placenta; the umbilical artery carries deoxygenated, waste-laden blood away from the fetus, while the umbilical vein returns oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood to the fetus. The amniotic fluid creates a weightless environment where the fetus can exercise its muscles against the fluid resistance, crucial for orthopedic development.
Part (b): Syphilis is bacterial, whereas HIV is viral; both can cross the placental barrier or be transmitted during birth. Controlling STIs relies heavily on breaking the chain of transmission. Barrier methods physically prevent the exchange of bodily fluids which carry the pathogens. Contact tracing ensures that asymptomatic partners are treated so they do not unknowingly infect others.
