Question
(a) Fig. 3.1 shows one stage involved in plant reproduction after pollination.
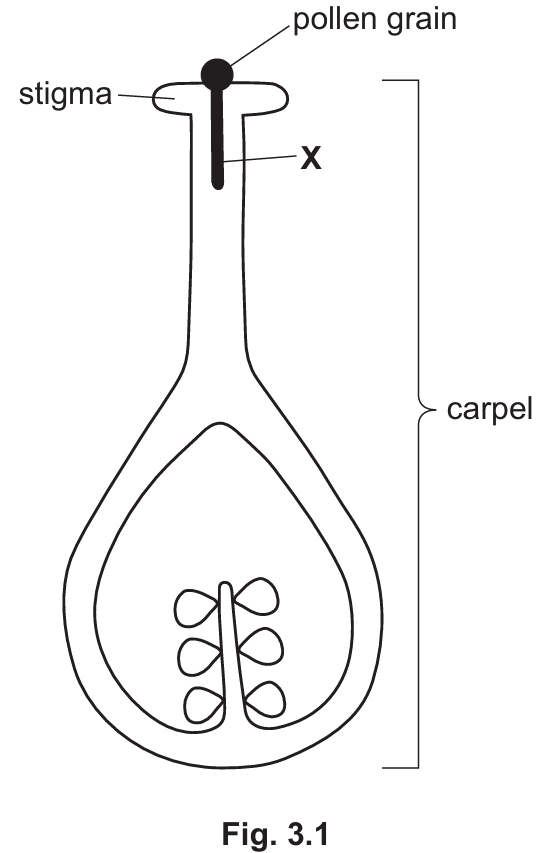
(i) State the name of the part labelled X in Fig. 3.1.
(b) A species of plant can use self-pollination and cross-pollination.
(i) Suggest reasons for this species of plant to use self-pollination rather than cross-pollination.
State two other sources of genetic variation in populations.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i)
The part labelled X is the pollen tube.
(a) (ii)
Following the stage shown, the pollen tube grows down through the style to enter the ovary (specifically the ovule). The male nucleus travels down this tube. Fertilisation occurs when the male nucleus fuses with the female nucleus (inside the ovule).
(b) (i)
Reasons for self-pollination include:
- There may be a lack of pollinators (e.g., insects or wind).
- The plant might be physically isolated from others of the same species.
- It allows the plant to use less pollen and energy compared to cross-pollination strategies.
- It ensures an increased chance of fertilisation and offspring production.
- If the plant is well-adapted to its environment, maintaining the same genetic makeup can be beneficial.
(b) (ii)
The effects of exclusive self-pollination include:
- There is less or no genetic variation within the population.
- The population is less likely to survive or adapt to environmental changes.
- There is less resilience against disease, meaning a disease could spread more quickly and wipe out the population.
- There is an increased risk of extinction.
- There is a higher likelihood of genetic diseases being expressed.
(c)
Two other sources of genetic variation are:
- Mutation (random changes in DNA base sequence).
- Random mating or random pollination.
- Random fertilisation (which specific sperm fuses with the egg).
(d)
Mitosis is a type of nuclear division that results in the production of genetically identical cells. During this process, the replicated chromosomes separate such that the chromosome number is maintained (diploid to diploid). Its roles in organisms include growth, repair of damaged tissues, replacement of cells, and asexual reproduction.
(e)
The unspecialised cells that divide by mitosis are called stem cells.
Part (a): Pollination Mechanics
Once a pollen grain lands on the stigma, it must transport the male gametes to the ovules located at the base of the carpel. It does this by growing a structure called a pollen tube. This tube digests its way through the style, delivering the male nucleus directly to the egg cell for fusion (fertilisation).
Part (b): Evolutionary Trade-offs
Self-pollination is a “safety net.” If a plant cannot find a partner (isolation) or insects are scarce, self-pollination ensures it can still reproduce. However, it results in clones (or near-clones). Genetic variation is crucial for a population’s long-term survival because it increases the probability that some individuals will possess traits allowing them to survive new threats, like a new pest or climate change. Without variation, the entire population is vulnerable.
Part (c): Sources of Variation
While meiosis shuffles existing genes (via crossing over and independent assortment), mutations create entirely new alleles. Furthermore, the randomness of sexual reproduction—which two individuals mate and which specific gametes fuse—adds massive variety to the offspring.
Part (d) & (e): Mitosis & Stem Cells
Mitosis is the process of cell cloning. It is essential when an organism needs to get bigger (growth) or fix a cut (repair), as the new cells must be exact copies of the old ones to function correctly. Stem cells are unique because they retain the ability to divide by mitosis and then differentiate into specialised cells (like nerve or muscle cells) as needed.
