Question
A short-toed animal was crossed with a long-toed animal of the same species. All the offspring
had short toes. One of these offspring was crossed with another long-toed animal of the same
species.
Which ratio of short-toed to long-toed animals should be expected?
A 1 : 1 B 2 : 1 C 3 : 1 D 4 : 1
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The short-toed trait is dominant and the long-toed trait is recessive. When a short-toed animal is crossed with a long-toed animal and all offspring have short toes, this indicates that the short-toed trait is expressed in the heterozygous offspring.
So, the genotype of the offspring from the first cross is likely: Ss (where S represents the allele for short toes and s represents the allele for long toes).
When an Ss individual (offspring from the first cross) is crossed with a long-toed animal (ss), the possible combinations are:
1. Ss x ss
Offspring genotypes: Ss and ss
Offspring phenotypes: Short-toed and long-toed
Therefore, the expected ratio of short-toed to long-toed animals in the second generation cross is 1 : 1, which corresponds to option A: 1 : 1.
Question
In fruit flies, the allele for grey body, G, is dominant over the allele for black body, g.
The result of a mating between two flies is shown.
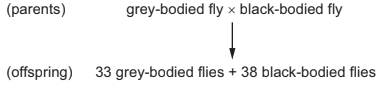
What were the genotypes of the parents?
A Gg × gg B Gg × Gg C GG × gg D GG × Gg
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
In fruit flies, the allele for grey body (G) is dominant over the allele for black body (g). This means that if an individual has at least one G allele (Gg or GG), it will have a grey body phenotype. The offspring include 33 grey-bodied flies and 38 black-bodied flies.
Given this information, we can deduce the genotypes of the parents:
– The offspring include both grey-bodied and black-bodied flies, which means that at least one parent must have the Gg genotype (heterozygous, carrying one dominant and one recessive allele).
– Since grey body (G) is dominant, a parent with the GG genotype would only produce grey-bodied offspring.
– The only possibility left is that one parent is Gg and the other is gg. This is because a Gg parent (heterozygous) can produce both grey-bodied and black-bodied offspring, while a gg parent (recessive) would only produce black-bodied offspring.
So, the correct answer is:
A. Gg × gg
Question
In cats, the allele for short hair is dominant to the allele for long hair. A short-haired cat gives birth
to five kittens. Two of them have long hair.
Which statement must be correct?
A Neither of the parents is heterozygous.
B One parent is homozygous.
C The female cat is heterozygous.
D The male cat is heterozygous.
▶️Answer/Explanation
The correct answer is C: The female cat is heterozygous.
Since the allele for short hair (S) is dominant to the allele for long hair (s), a short-haired cat can have either two copies of the dominant short hair allele (SS) or one copy of the dominant short hair allele and one copy of the recessive long hair allele (Ss).
Given that a short-haired cat (which can be either SS or Ss) gave birth to two long-haired kittens, we can deduce the following possibilities for the parents’ genotypes:
- Female parent: Ss (heterozygous)
- Male parent: ss (homozygous recessive)
The male parent must be homozygous recessive (ss) because it can only contribute a recessive allele for long hair (s) to the offspring. The female parent (Ss) can contribute either a dominant allele for short hair (S) or a recessive allele for long hair (s).
Therefore, the correct answer is C: The female cat is heterozygous.
Question
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disease that occurs when an individual is homozygous for a
recessive allele.
If parents are both heterozygous for this characteristic, what is the probability that their first child
will have cystic fibrosis?
A 0% B 25% C 50% D 100%
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the CFTR gene. Inheritance of cystic fibrosis follows an autosomal recessive pattern. This means that a person needs to inherit two copies of the mutated gene (one from each parent) to actually have the disease.
Let’s denote the normal allele as “N” and the mutated allele as “M.”
If both parents are heterozygous carriers for cystic fibrosis, their genotypes would be: NM (parent 1) and NM (parent 2).
When these parents have children, the possible combinations of alleles in their offspring are as follows:
1. NN (normal)
2. NM (carrier)
3. NM (carrier)
4. MM (affected)
So, out of these possibilities, there is a 1 out of 4 chance (or 25%) that their child will have cystic fibrosis (MM genotype).
The correct answer is: B) 25%
Question
Genetics is the study of
A development of organisms.
B mechanisms of inheritance.
C nuclear division.
D variation between species.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Genetics is the scientific study of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms. It focuses on understanding how traits are passed from one generation to another and how genetic information is stored, transmitted, and expressed in organisms. The correct answer from the options you provided is:
B mechanisms of inheritance.
This means that genetics involves investigating the processes by which genetic information is inherited from parents to offspring, how traits are determined by genes, and the underlying mechanisms that govern these processes. Genetics encompasses a wide range of topics, including DNA structure and function, gene expression, genetic mutations, genetic recombination, and the interactions between genes and the environment. By studying genetics, scientists aim to gain insights into the fundamental principles that drive biological diversity, evolution, and the development of organisms.
