Question
(a) The list shows some statements about variation. Place ticks (✓) in the boxes to show which statements are correct.

(b) Fava bean plants need a good water supply to produce beans. A drought is a period of low rainfall. Farmers want fava bean plants that can tolerate drought.
(i) Complete the steps a farmer should use to produce fava bean plants which can tolerate drought.
Step 1: Choose plants with the highest drought tolerance.
Step 2: …………………………………..
Step 3: ……………………………………..
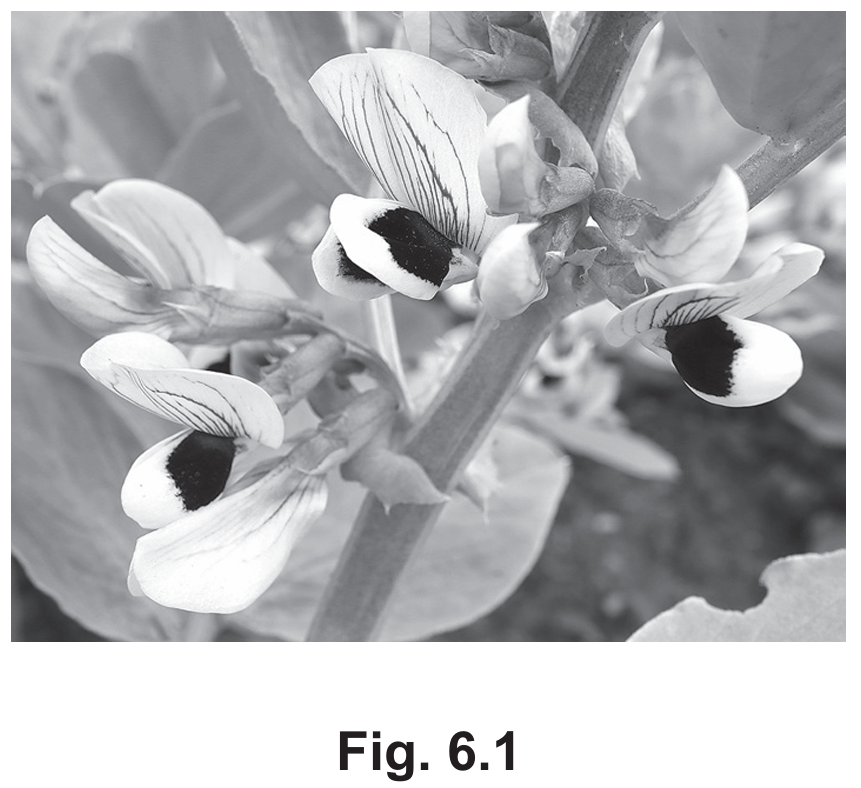

(i) State the genus of the plant shown in Fig. 6.1.
(ii) The flower petals of this fava bean plant have coloured spots.
The allele for black spots is dominant and is represented by the letter B.
The allele for yellow spots is recessive and is represented by the letter b.
A plant with flowers with black spots was crossed with a plant with flowers with yellow spots.
The Punnett square shows the alleles in the gametes of the plant with flowers with black spots.
Complete the Punnett square and calculate the phenotypic ratio of the offspring plants.

phenotypic ratio of the offspring plants
……………………. flowers with black spots : ……………………. flowers with yellow spots
▶️ Answer/Explanation
6 (a)
The correct statements are: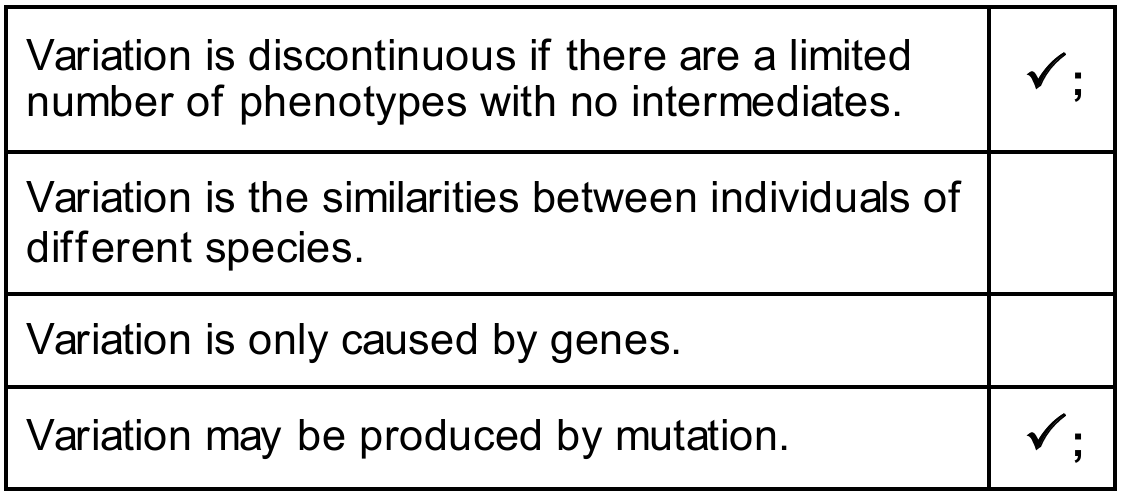
Explanation: Discontinuous variation (such as blood groups) is usually caused by genes only and results in distinct phenotypes with no intermediates. Mutation is a random genetic change and is a source of genetic variation in populations.
(b) (i)
Step 2: Breed (cross) the selected plants (with the highest drought tolerance) together.
Step 3: Select the offspring with the highest drought tolerance and repeat the process for many generations.
Explanation: This describes the process of selective breeding where humans select individuals with desirable features (drought tolerance) and cross them to pass alleles to the next generation.
(b) (ii)
Selective breeding (or artificial selection).
(c) (i)
Vicia
Explanation: According to the binomial system, the scientific name of an organism is made up of two parts showing the genus and species. The first name is the genus and is always capitalized.
(c) (ii)
Punnett Square Calculation:
The plant with yellow spots is recessive (bb), producing only gametes with b. The plant with black spots is heterozygous (Bb) as implied by the gametes in the table header (B and b).

Phenotypic ratio:
The offspring genotypes are 2 Bb (Black spots) and 2 bb (Yellow spots).
Ratio = 1 : 1.
Answer: 1 flowers with black spots : 1 flowers with yellow spots.
