Question
(a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the human gas exchange system.
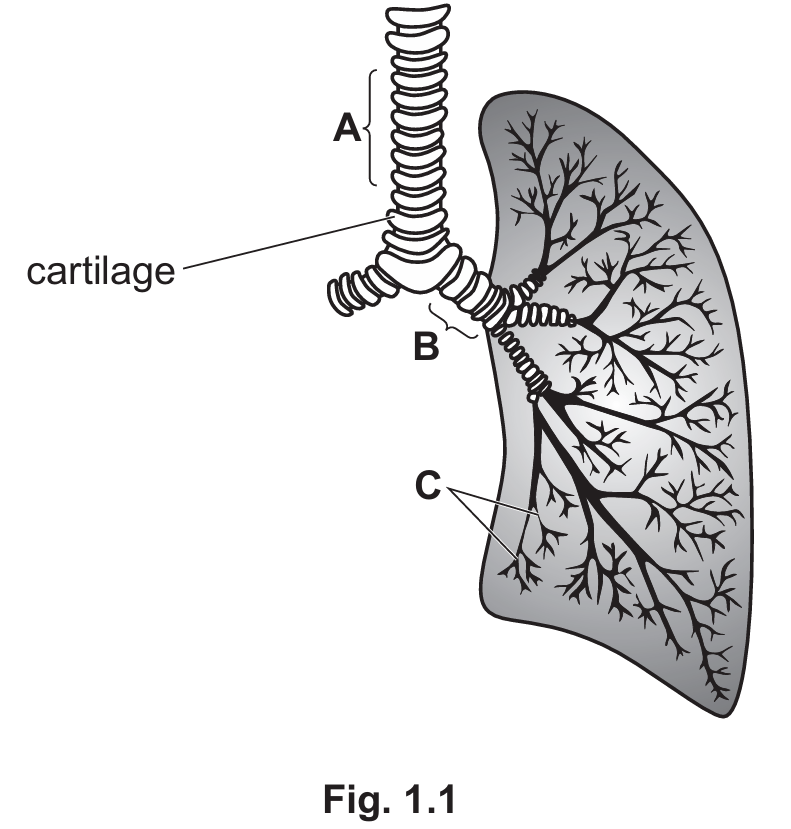
(i) Identify structures A, B and C shown in Fig. 1.1.
(ii) State the function of the cartilage shown in Fig. 1.1.
(iii) Explain how inspiration occurs.
(b) Cystic fibrosis is a condition that affects the lungs. People with cystic fibrosis have mucus in the airways of their lungs that is thicker and stickier than usual.
(i) Two types of cells that line the airways protect the body against pathogens and particles.
State the names of these two types of cell and describe how they protect the body.
(ii) Suggest how having thicker and stickier mucus in the airways affects the ability of a person to do exercise.
(c) Cystic fibrosis is an inherited condition in humans caused by a recessive allele of a gene.
There are two alleles for this gene:
- the allele for no cystic fibrosis is represented by the letter F
- the allele for cystic fibrosis is represented by the letter f
Two heterozygous parents wanted to have a child.
Complete the genetic diagram to predict the probability of these parents having a child with cystic fibrosis.
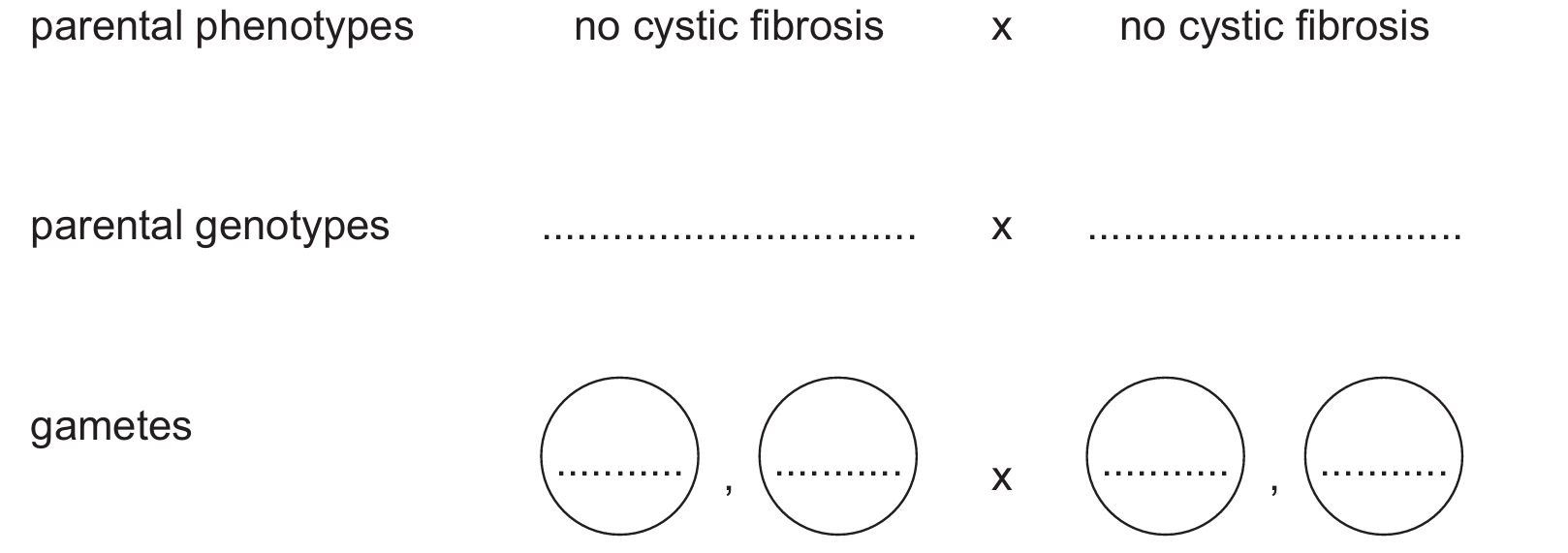
offspring genotypes: ………….. ………….. ………….. …………..
offspring phenotypes: ………….. ………….. ………….. …………..
probability of having a child with cystic fibrosis: ………………
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i) Identification of structures:
A: Trachea
B: Bronchus (or Bronchi)
C: Bronchiole(s)
Explanation: The trachea (windpipe) is the main tube with cartilage rings (A) leading from the mouth/nose. It splits into two bronchi (B) which enter the lungs, and further subdivides into smaller tubes called bronchioles (C).
(a)(ii) Function of cartilage:
The function is to keep the airway open or prevent the collapse of the airway.
Explanation: The C-shaped rings of cartilage provide structural support so that the trachea does not collapse inward when the pressure drops during inspiration.
(a)(iii) Mechanism of inspiration:
During inspiration (breathing in):
- The diaphragm contracts and flattens (moves downwards).
- The external intercostal muscles contract (while internal intercostal muscles relax), causing the ribs to move up and out.
- This action increases the volume of the thorax (chest cavity).
- Consequently, the pressure decreases inside the thorax/lungs.
- Air flows into the lungs to equalise the pressure difference.
(b)(i) Protection of airways:
Two common cell types are:
- Goblet cells: They secrete mucus. This sticky mucus traps dust, particles, and pathogens (bacteria/viruses).
- Ciliated cells: They have hair-like structures called cilia. These beat/move to sweep the mucus (containing trapped pathogens) up and out of the airways towards the throat to be swallowed.
Note: Lymphocytes (produce antibodies) and Phagocytes (engulf pathogens) are also acceptable answers.
(b)(ii) Effect on exercise:
Thicker mucus creates a blockage or narrowing of the airways. This leads to:
- Reduced surface area for gas exchange or reduced rate of diffusion.
- Less oxygen ($O_2$) reaches the blood and muscle cells (and less $CO_2$ is removed).
- Muscle cells perform less aerobic respiration and must rely more on anaerobic respiration.
- This results in less energy/ATP being released/produced for muscle contraction, causing fatigue more quickly.
(c) Genetic Diagram:
Since both parents are heterozygous, they carry one dominant and one recessive allele.
Parental genotypes: $Ff$ x $Ff$
Gametes: ($F$), ($f$) x ($F$), ($f$)
Offspring genotypes: $FF$, $Ff$, $Ff$, $ff$
Offspring phenotypes: No cystic fibrosis, No cystic fibrosis, No cystic fibrosis, Cystic fibrosis
Probability: $0.25$ or $25\%$ or $1:3$ or $\frac{1}{4}$
Explanation: The cross yields one homozygous dominant ($FF$), two heterozygous carriers ($Ff$), and one homozygous recessive ($ff$). Since cystic fibrosis is recessive, only the $ff$ genotype presents the condition.
