Question
Which letter represents the lag phase in the population graph shown?
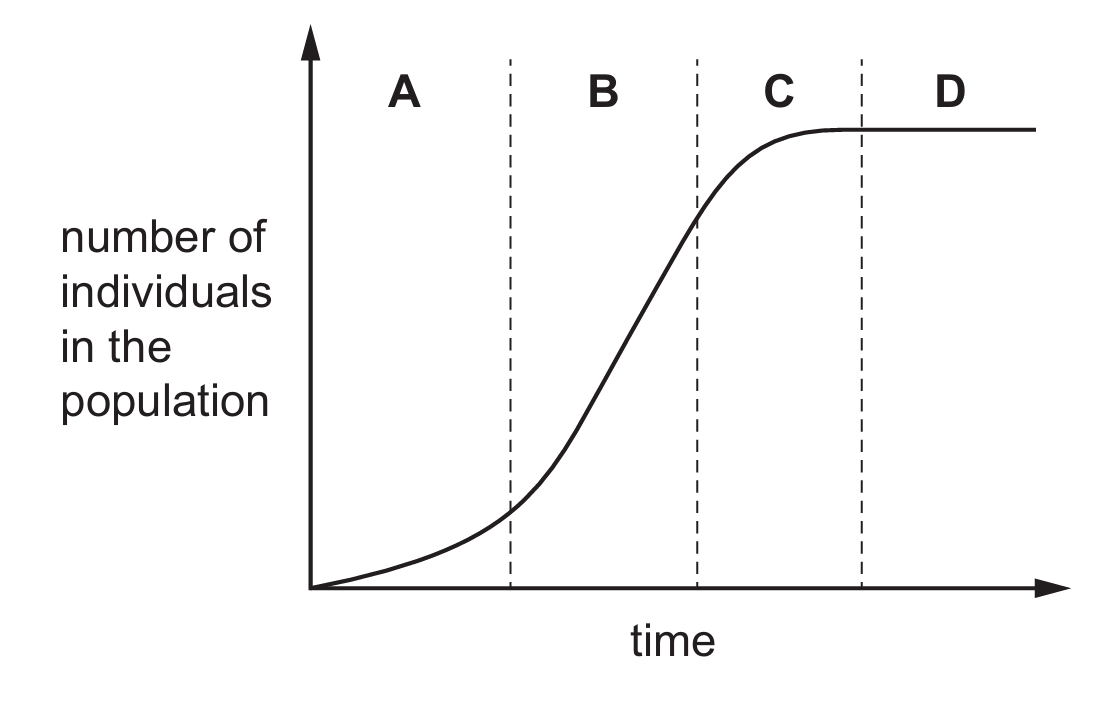
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
What are sources of genetic variation in populations?
(B) meiosis, random mating, asexual reproduction
(C) mitosis, mutation, random fertilisation
(D) mitosis, random fertilisation, asexual reproduction
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Genetic variation arises from processes that shuffle or change DNA. Meiosis contributes through crossing over and independent assortment, while mutations create entirely new alleles. Random mating ensures diverse combinations of these alleles within a population. In contrast, mitosis and asexual reproduction produce genetically identical clones, which limits rather than increases variation. Therefore, option (A) is the only set containing three genuine sources of diversity.
✅ Answer: (A)
Question
What is a way in which new alleles are formed?
(B) mutation
(C) natural selection
(D) sexual reproduction
▶️ Answer/Explanation
New alleles are created exclusively through mutation, which is a permanent change in the $DNA$ sequence of a gene. While sexual reproduction (D) increases genetic variation by shuffling existing alleles through recombination and independent assortment, it does not create “new” genetic information. Similarly, natural selection (C) and artificial selection (A) only act upon the variations that are already present in a population, favoring certain traits over others. Therefore, mutation is the primary source of all new genetic material and the ultimate driver of evolutionary novelty.
✅ Answer: (B)
