Question
- The genotype of a male was ee.
- The genotype of a female was Ee.
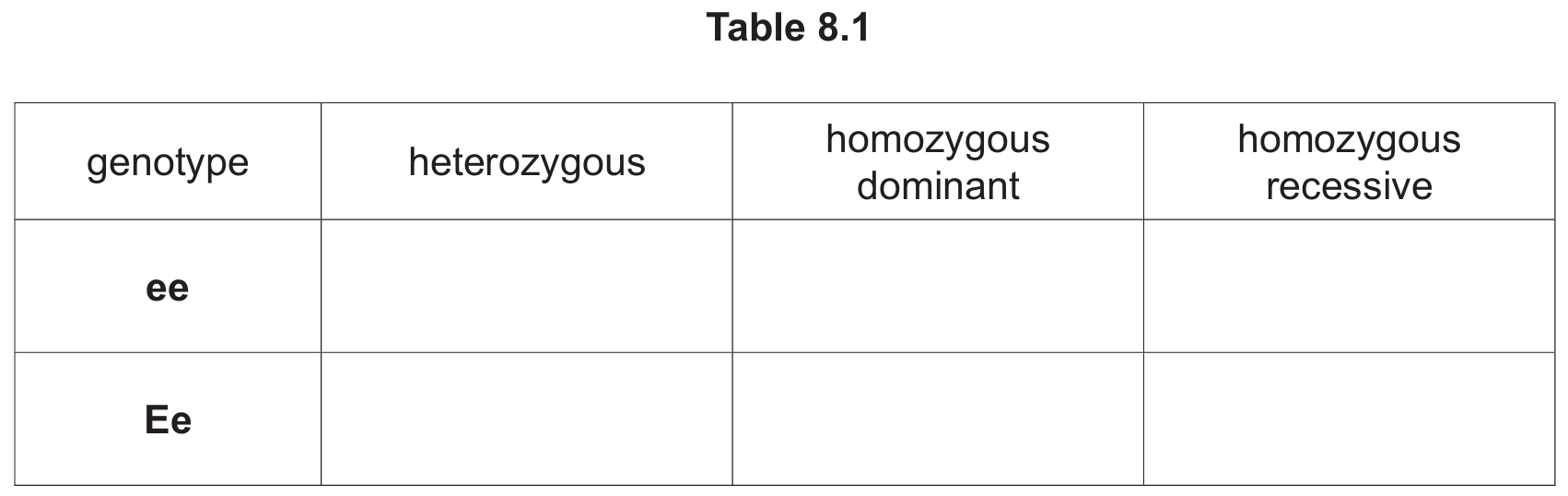
(i) Table 8.1 shows some terms used to describe these genotypes. Place ticks (\(\checkmark\)) in the boxes in Table 8.1 to show the correct descriptions for these genotypes.
(ii) A male with the genotype ee had a child with a female with the genotype Ee. Complete the Punnett square to show the:
- gametes of the male and the female
- possible genotypes of the offspring from this cross
- ratio of long eyelashes to short eyelashes in the offspring from this cross.
| male | |||
| ……………….. | ……………….. | ||
| female | ……………….. | ……………….. | ……………….. |
| ……………….. | ……………….. | ……………….. | |
▶️ Answer/Explanation
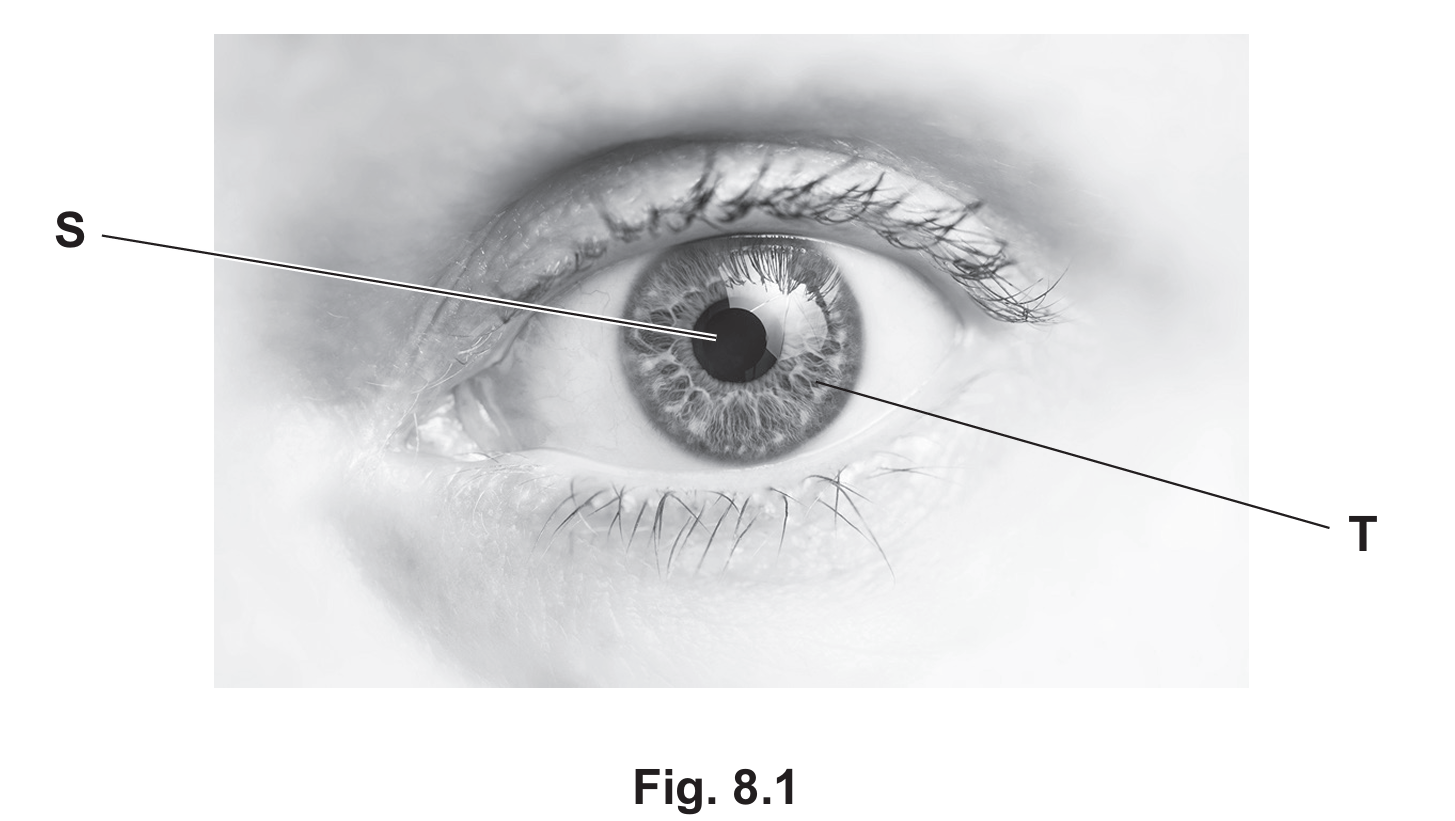
(a)(i)
pupil
Explanation: Structure S indicates the dark circular opening in the center of the iris, which is the pupil.
(a)(ii)
controls how much light enters the pupil / eye
Explanation: Structure T is the iris. Its primary function is to regulate the size of the pupil (via the pupil reflex) to control the intensity of light reaching the retina.
(b)(i)
length of DNA; that codes for a protein
Explanation: A gene is defined as a specific segment or length of a DNA molecule that contains the instructions (genetic code) to synthesize a specific protein.
(b)(ii)
two categories / two phenotypes / no intermediates / controlled by one gene
Explanation: Discontinuous variation refers to characteristics that fall into distinct categories with no gradation in between (you have it or you don’t). Eyelash length is described here as having only two options (short or long), which is characteristic of discontinuous variation controlled by a single gene (monogenic inheritance).
(c)(i)
The correct ticks are:
• ee: Tick in homozygous recessive.
• Ee: Tick in heterozygous.
Explanation:
– Homozygous means having two identical alleles (e.g., ee). Since ‘e’ is recessive, ee is homozygous recessive.
– Heterozygous means having two different alleles (e.g., Ee).
(c)(ii)
Punnett Square Completion:
| Male (ee) | ||
| Female (Ee) | e | e |
| E | Ee | Ee |
| e | ee | ee |
Ratio: 1:1 (or 1 long : 1 short)
Explanation:
The male produces only gametes containing the e allele. The female produces gametes with E (50%) and e (50%).
The resulting offspring genotypes are:
– Ee (Long eyelashes): 2 out of 4 (50%)
– ee (Short eyelashes): 2 out of 4 (50%)
Therefore, the phenotypic ratio is 1:1.
