Question
A student investigated the effect of high temperature on the production of nitrate ions in soil.
Two samples of soil were taken. One sample was heated to $100$ °C.
All the nitrate ions were completely removed from both soil samples.
Ammonium ions were then added to both soil samples.
After two weeks, both soil samples were tested for the presence of nitrate ions.
The results are shown.
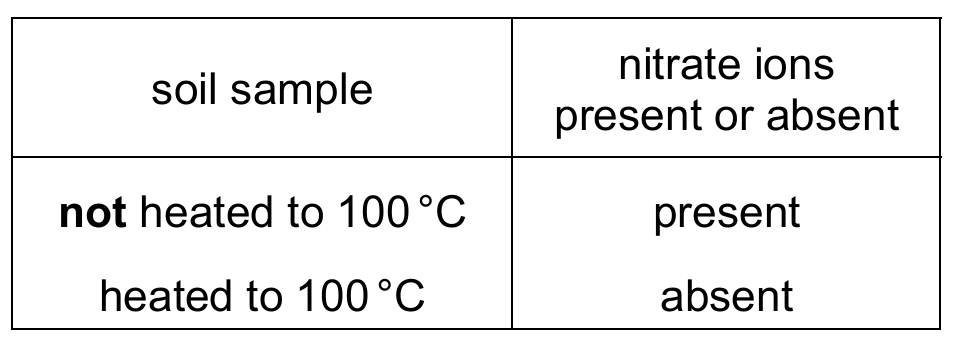
Which statement explains the results?
(B) Heating the soil increased the activity of denitrifying bacteria.
(C) Heating the soil killed nitrifying bacteria.
(D) Heating the soil killed nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (C)
Question
The graph shows the change in the percentage of bacteria resistant to antibiotic $X$.
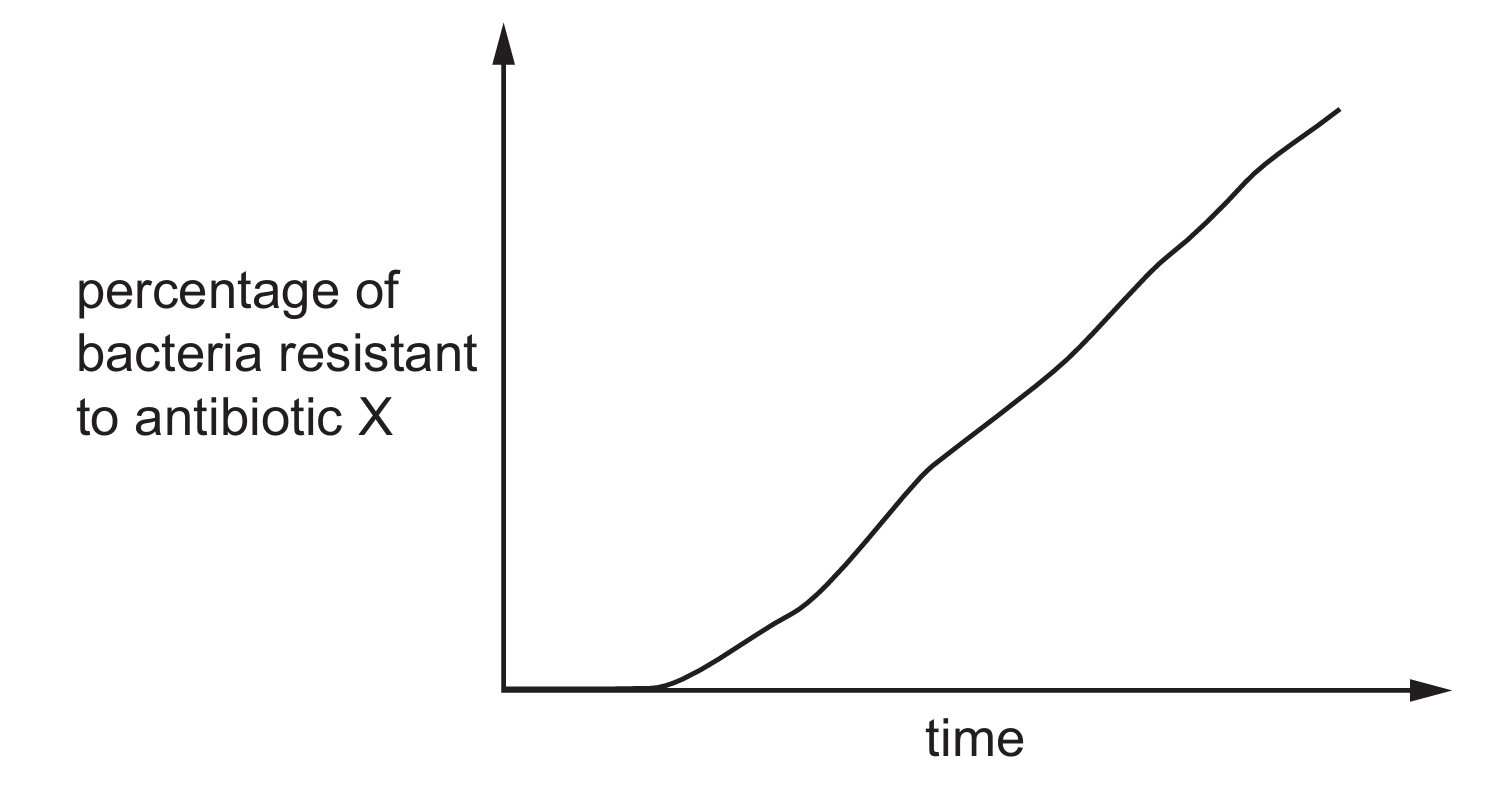
What causes the change shown in the graph?
(B) natural selection
(C) meiosis
(D) random fertilisation
▶️ Answer/Explanation
✅ Answer: (B)
Question
What is the reason why antibiotics should be used only when essential?
(B) It increases the natural selection of antibiotic resistant bacteria.
(C) It reduces the artificial selection of antibiotic resistant bacteria.
(D) It reduces the natural selection of antibiotic resistant bacteria.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Antibiotics act as a selective pressure in a population of bacteria. When antibiotics are used, they kill susceptible bacteria, while those with rare mutations for resistance survive and reproduce. Overusing antibiotics provides more opportunities for this natural selection process to occur, leading to a rise in resistant strains. By using antibiotics only when essential, we limit the exposure of bacteria to the drug, thereby reducing the rate at which natural selection for resistance occurs. This helps preserve the effectiveness of treatments for future infections.
✅ Answer: (D)
