Question
(iii) The list contains statements that describe selective breeding of barley plants to increase yield.
- A Humans select barley plants with a high yield.
- B New barley plants are grown.
- C Offspring with a high yield are selected and bred together.
- D Pollination and fertilisation occurs.
- E Seeds form.
- F The process is repeated over many generations.
Arrange the statements in the correct order to describe the process of selective breeding in barley plants. Two have been done for you.

▶️ Answer/Explanation
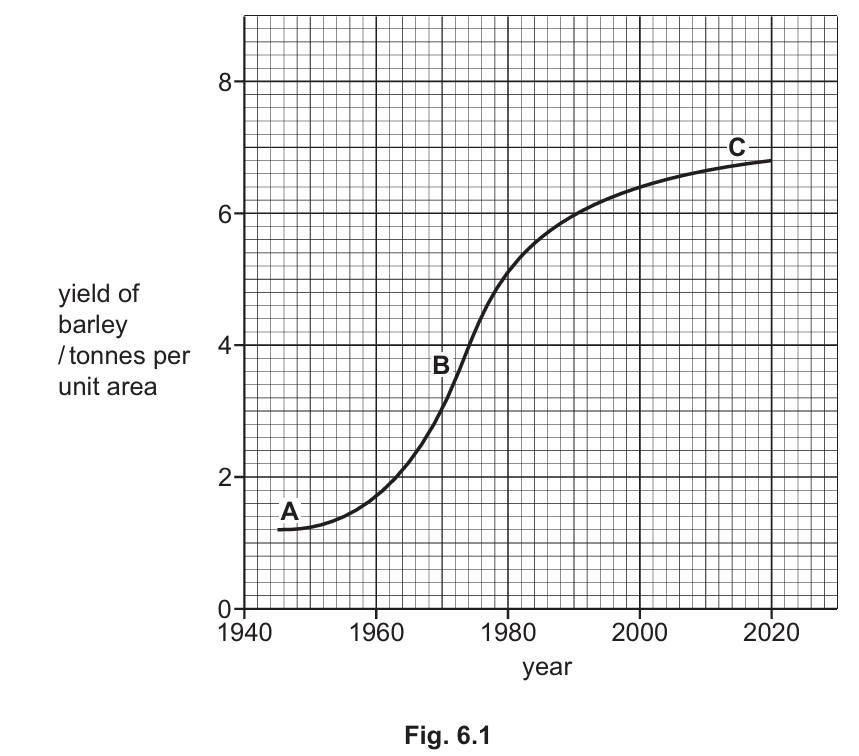
(a)(i)
Period: B
Explanation: This section of the graph has the steepest curve (gradient), indicating the fastest rate of yield increase over time.
(a)(ii)
Answer: \(6400 \text{ kg}\)
Calculation: Reading from the graph at the year 2000, the yield is \(6.4\) tonnes. Since \(1 \text{ tonne} = 1000 \text{ kg}\): $$6.4 \times 1000 = 6400 \text{ kg}$$
(a)(iii)
Order: A, D, E, B, C, F
The logical sequence of selective breeding is: 1. Humans select high yield plants (A). 2. These plants are bred/crossed via pollination/fertilisation (D). 3. Seeds result from this cross (E). 4. These seeds are grown into new plants (B). 5. The best offspring are selected (C). 6. The process is repeated (F).
(a)(iv)
Any three from the following:
- Use fertilisers (to provide minerals/ions).
- Use insecticides / pesticides (to kill pests).
- Use herbicides (to kill weeds).
- Use Genetically Modified (GM) seeds.
- Use irrigation / improved drainage / watering systems.
- Deter animals that eat barley.
(b)(i)
Monoculture: Growing only one type of plant / single crop species in a specific area (at the same time).
(b)(ii)
Advantage (any one):
- Allows large area of land to be used efficiently.
- Increases overall yield.
- Allows specialized machinery to be used (easier harvesting).
- Allows farmers to specialise.
Disadvantage (any one):
- Increases population of insect pests (due to abundant food supply).
- Increases risk of disease spread (rapid transmission between identical plants).
- Risks total crop failure.
- Reduces biodiversity.
- Depletes specific soil nutrients.
Graph Analysis (Part a): In biological graphs, the rate of a process is determined by the gradient (slope) of the line. Section B is the steepest part of the sigmoid curve, representing the period where agricultural technology (like the “Green Revolution”) likely had the most impact on yield. For part (ii), accurate graph reading is required. The y-axis is in “tonnes per unit area”. The line intersects the year 2000 exactly at the \(6.4\) mark. The question demands the answer in kilograms, necessitating the conversion \(6.4 \times 1000\).
Selective Breeding (Part a-iii): This question tests the understanding of artificial selection as a step-by-step process. It mirrors natural selection but is directed by human choice. The key is recognizing that “Pollination” (D) and “Seeds forming” (E) must happen before “New plants are grown” (B), and that selection of offspring (C) happens after the new generation has grown.
Food Supply & Monoculture (Part b): This relates directly to the impact of humans on ecosystems. While monoculture is economically efficient (high yield, standardized machinery), it is ecologically fragile. A single pest species can wipe out the entire crop because there are no physical barriers or genetic variations to stop it. Furthermore, growing the same crop repeatedly exhausts specific soil ions (like nitrates), requiring heavy fertiliser use.
