Question
Scientists developed genetically modified (GM) maize.
Fig. 3.1 shows the mass of GM maize grown in one country from \(2000\) to \(2015\).
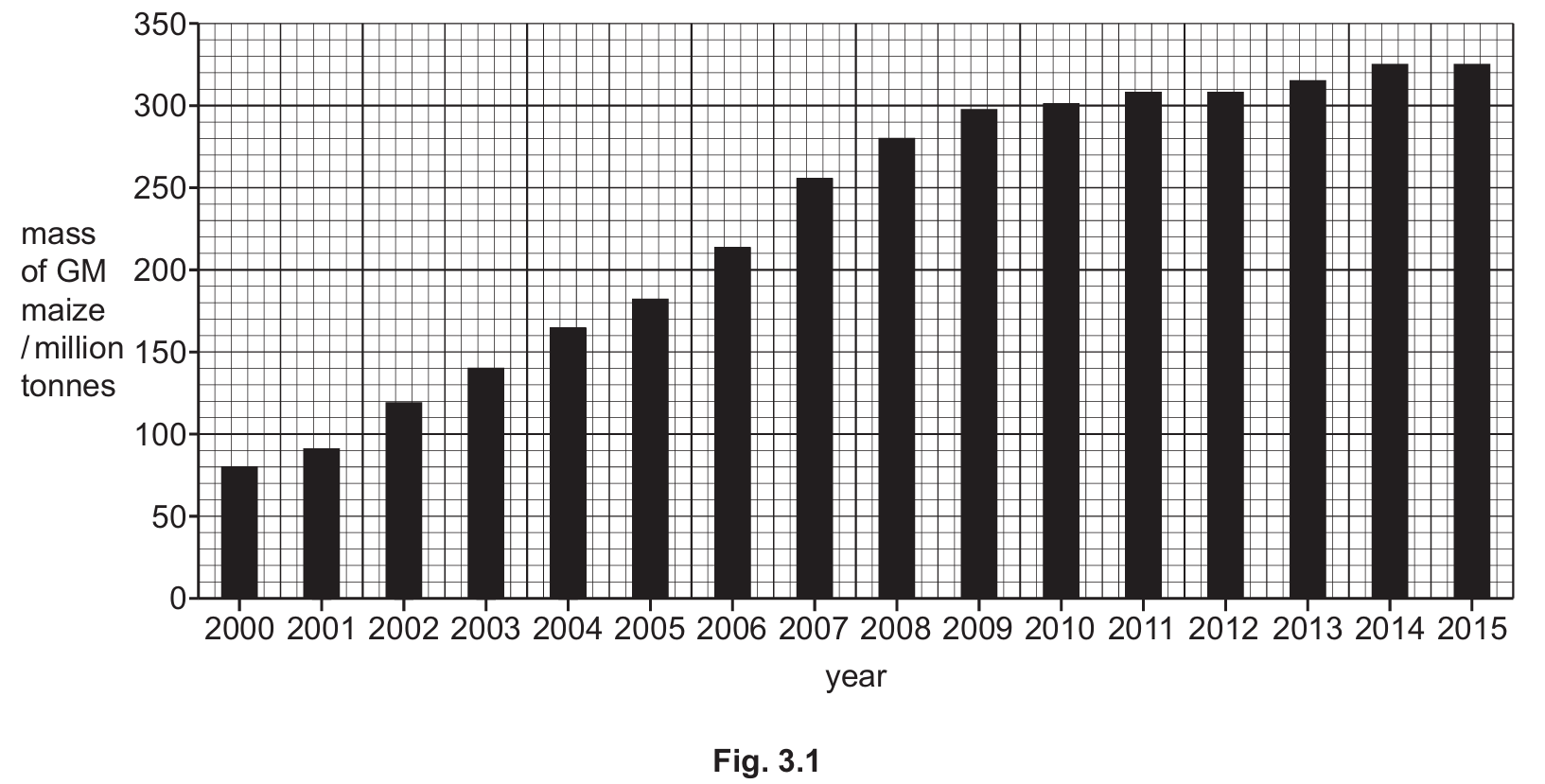
(a) Calculate the percentage increase in the mass of GM maize grown between \(2000\) and \(2015\).
Give your answer to two significant figures.
Space for working.
(b) To develop GM maize, a gene for producing a natural insecticide was taken from a bacterium and transferred into maize plant cells.
(i) Genes are found at specific positions on a biological molecule.
State the name of this biological molecule.
(ii) Scientists who develop GM crop plants breed them for many generations before allowing farmers to grow the crop plants.
Suggest why scientists breed the GM crop plants for many generations.
(iii) Human proteins can also be made using bacteria that have been genetically modified.
Describe how a gene can be transferred from one organism to another using genetic modification.
(c) Some people are worried that GM crops could pollinate wild plants.
(i) Suggest how pollination between GM crops and wild plants could be prevented.
(ii) State two advantages of GM crops other than insect resistance.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) 310 %
To calculate the percentage increase, you must read the values from the graph:
- Mass in \(2000 \approx 80\) million tonnes.
- Mass in \(2015 \approx 328\) (accept approx. \(330\)) million tonnes.
The formula for percentage increase is: \[ \frac{\text{Final Value} – \text{Initial Value}}{\text{Initial Value}} \times 100 \] Substituting the values: \[ \frac{328 – 80}{80} \times 100 = \frac{248}{80} \times 100 = 310\% \] The question asks for two significant figures; however, \(310\) is accepted in the mark scheme (the zero is often treated as a placeholder in integers, or the calculation results exactly in \(310\)).
(b)(i) DNA
Genes are specific sections or lengths of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) that code for proteins.
(b)(ii)
Scientists breed plants for multiple generations to ensure stability and viability. Key reasons include:
- To check that the gene is expressed (i.e., the plant actually produces the insecticide/toxin).
- To ensure the crop has a high enough yield and good quality.
- To ensure the gene does not cause unexpected or unwanted side effects.
- To confirm the crop can grow successfully in the intended environment.
- To produce a large enough quantity of seed to sell to farmers.
(b)(iii)
This describes the standard process of genetic engineering using a bacterial plasmid:
- Isolation: The specific gene (e.g., for the human protein) is isolated and cut from the donor organism’s DNA using restriction enzymes.
- Plasmid preparation: A bacterial plasmid (a circular ring of DNA) is cut using the same restriction enzyme.
- Sticky ends: Cutting both the donor DNA and the plasmid with the same enzyme creates complementary sticky ends.
- Insertion: The human gene is inserted into the bacterial plasmid.
- Ligation: The enzyme DNA ligase joins the gene and the plasmid together to form a recombinant plasmid.
- Transformation: The recombinant plasmid is inserted back into bacteria.
- Replication: The bacteria are placed in a fermenter to reproduce/multiply, producing the specific protein.
(c)(i)
To prevent the transfer of pollen (gene flow) to wild relatives:
- Grow the GM crops in enclosed environments like glasshouses.
- Cover the flowers to prevent pollinators (insects/wind) from accessing them.
- Remove the male parts of the flower (stamens/anthers) so no pollen is produced.
- Plant a buffer zone of a different species around the GM crop.
(c)(ii)
Advantages of GM crops (excluding insect resistance mentioned in the question):
- Herbicide resistance: Allows farmers to spray weeds without killing the crop.
- Environmental resistance: Ability to survive drought, heat, salinity (salt), or cold.
- Nutritional enhancement: Adding vitamins (e.g., Golden Rice with Vitamin A) or other nutrients.
- Improved characteristics: Better flavour, longer shelf life, or higher yield.
