Question
What is an example of a non-renewable resource?
A biofuels
B fish
C fossil fuels
D trees
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The correct answer is C: fossil fuels.
Fossil fuels are considered non-renewable resources because they are finite and take millions of years to form through natural processes. Once they are depleted, they cannot be replenished within a human-relevant time frame. Examples of fossil fuels include coal, oil, and natural gas. In contrast, options A, B, and D are not considered non-renewable resources. Biofuels can be produced from renewable resources like plants, fish can be managed sustainably through proper fisheries management, and trees can be replanted and regrown, making them potentially renewable resources if managed responsibly.
Question
What process uses the principal source of energy input to biological systems?
A ingestion
B decomposition
C photosynthesis
D respiration
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The process that uses the principal source of energy input to biological systems is:
C) Photosynthesis
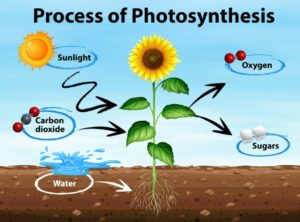
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants, algae, and certain bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose (sugar). This process is essential for producing food and oxygen, which are the foundation of many biological systems.
Question
Which diagram shows the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
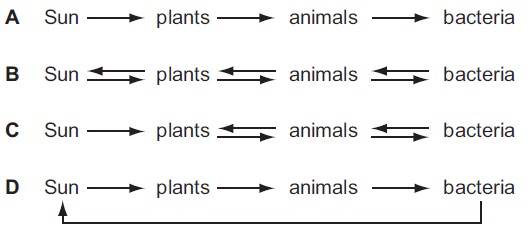
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The flow of energy in an ecosystem is represented through a trophic (feeding) structure, which illustrates how energy is transferred between different organisms within the ecosystem. The correct answer is A.
Sun (Source of Energy): The sun is the primary source of energy for most ecosystems. It provides the energy needed for photosynthesis to occur in plants, which is the foundation of the energy flow.
Plants (Primary Producers): Plants, through photosynthesis, convert solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and other organic compounds. This process stores energy in the chemical bonds of these compounds.
Animals (Consumers): Animals are categorized into different trophic levels based on their feeding habits.
- Herbivores (Primary Consumers): These animals, such as rabbits, deer, or cows, consume plants for energy by eating leaves, stems, or fruits.
- Carnivores (Secondary and Tertiary Consumers): Carnivores are further divided into secondary consumers (e.g., foxes, hawks) and tertiary consumers (e.g., lions, eagles). They obtain energy by consuming herbivores or other carnivores.
- Top Carnivores (Tertiary Consumers): These are predators at the top of the food chain and have few or no natural predators themselves.
Bacteria (Decomposers): Bacteria play a crucial role in the ecosystem by decomposing dead organisms and organic waste. They break down complex organic matter into simpler compounds, releasing nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon back into the environment. These nutrients are then taken up by plants and used to restart the cycle.
Energy Flow:
- The sun’s energy is captured by plants through photosynthesis.
- Plants use this energy to produce organic compounds (like glucose) and grow.
- Herbivores consume plants and extract energy from the plant material.
- Carnivores consume herbivores, transferring the energy stored in herbivore tissue.
- Top carnivores might consume other carnivores, completing the energy transfer.
- When plants, animals, and animals’ waste products die, bacteria and other decomposers break down the organic matter, releasing nutrients and energy back into the ecosystem.
Question
Which statement explains why the energy flow in a food chain is in one direction?
A Decomposers recycle nutrients for plants.
B Energy is not recycled.
C Plants convert light energy to chemical energy.
D The number of organisms decreases at each level in the food chain.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B Energy is not recycled.
The statement that explains why the energy flow in a food chain is in one direction is option B. Energy is not recycled within an ecosystem; it flows through the food chain in a linear manner. Energy enters the ecosystem primarily from the sun, is captured by plants through photosynthesis, and then gets transferred to herbivores, then to carnivores, and so on. At each trophic level, some of the energy is used for the organism’s life processes and lost as heat, and only a portion is passed on to the next trophic level. This results in a unidirectional flow of energy.
Question
What is shown in the diagram?
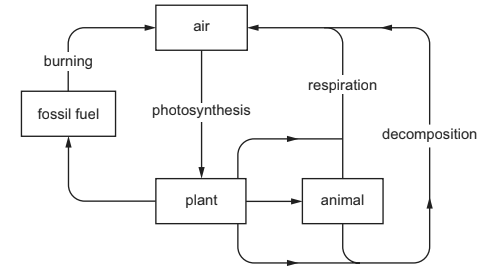
A a food web
B non-cyclical energy flow
C the carbon cycle
D the water cycle
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
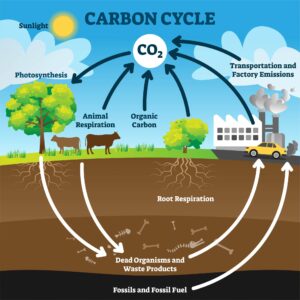
The carbon cycle is a natural process that involves the movement of carbon in various forms between the Earth’s atmosphere, oceans, land, and living organisms. Carbon exists in different reservoirs, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) in the atmosphere, dissolved carbon in the oceans, organic matter in plants and animals, and carbon-rich compounds in rocks and fossil fuels.
The cycle operates through processes like photosynthesis, respiration, decomposition, and combustion. During photosynthesis, plants and algae absorb CO2 from the air and convert it into organic compounds, releasing oxygen in the process. Animals then consume these plants or other animals, incorporating carbon into their own bodies.
Respiration, which occurs in all living organisms, releases carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2 when organic matter is broken down to release energy. Decomposition of dead organic matter by bacteria and fungi also returns carbon to the atmosphere and soil.
Additionally, the carbon cycle involves the transfer of carbon through geological processes. Over long periods, carbon-rich organic matter can be buried and transformed into fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas. Human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have significantly disrupted the carbon cycle by releasing excess CO2 into the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change.