Question
What is the principal source of energy input into food chains?
glucose
heat
soil
sunlight
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
The principal source of energy input into food chains is sunlight. Sunlight is the ultimate source of energy for almost all ecosystems on Earth. It provides the energy necessary for photosynthesis, a process in which plants and other photosynthetic organisms convert sunlight into chemical energy stored in the form of glucose and other organic molecules. This energy then flows through food chains as organisms consume each other, with energy being transferred from one trophic level to another. So, sunlight is the primary driver of energy flow in most ecosystems, and it serves as the foundation for all food chains and food webs.
Question
The food web shows the feeding relationships in a woodland.

If all the chaffinches in the food web die, which effect would this have?
A The amount of damage to trees will increase.
B The food supply for grey squirrels will increase.
C The number of wood pigeons will increase.
D The population of caterpillars will decrease.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
The amount of damage to trees will increase.
Chaffinches are insectivorous birds that feed on insects, including caterpillars. If the chaffinch population were to die off, there would be fewer birds feeding on caterpillars and insects. This could lead to an increase in the population of caterpillars and other insects, which could in turn lead to more damage to trees. Caterpillars are known to feed on tree leaves, and a higher caterpillar population could result in increased defoliation and damage to the trees in the woodland ecosystem.
Question
The diagram shows an aquatic food web.
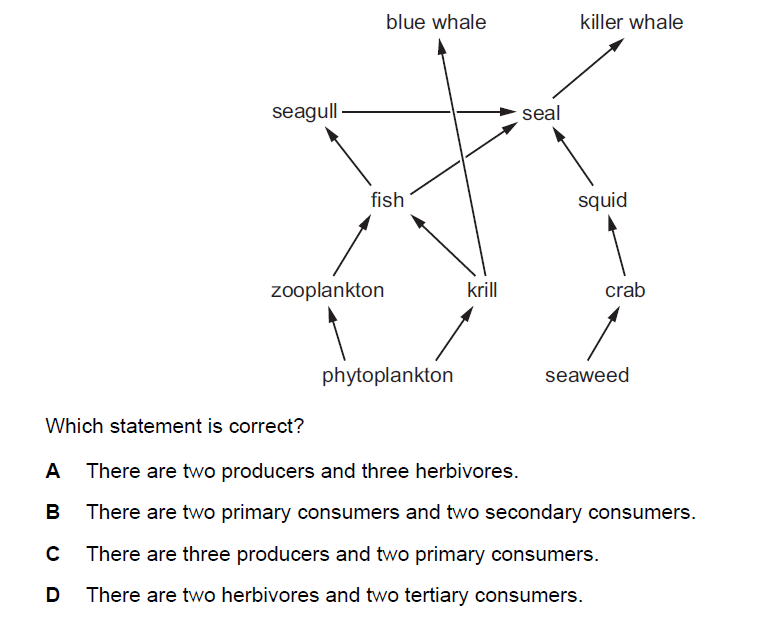
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
In an aquatic food web, producers are organisms that can synthesize their own food using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. They form the base of the food web by converting solar energy into organic matter. Herbivores, on the other hand, are animals that feed directly on producers, consuming plants or other photosynthetic organisms.
Here are two examples of aquatic producers and three examples of herbivores, along with explanations:
Producers:
Phytoplankton: These are microscopic algae that float in the upper layers of water bodies. They use photosynthesis to convert sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients into energy-rich organic compounds. Phytoplankton are a crucial source of food and oxygen production in aquatic ecosystems.
Seagrasses: Seagrasses are flowering plants that grow underwater in coastal areas. They have adapted to survive in saltwater environments and play a significant role as producers in coastal food webs. Seagrasses also provide habitat for various aquatic species.
Herbivores:
Zooplankton: Zooplankton encompass a wide variety of tiny animals that float in aquatic environments. While some zooplankton are herbivores that feed on phytoplankton, others are omnivores or even carnivores, consuming a mix of plant matter and other organisms.
Krill: Krill are small, shrimp-like crustaceans that primarily feed on phytoplankton. They play a crucial role in marine food webs, transferring energy from phytoplankton to higher trophic levels, including larger fish, whales, and other predators.
Crabs: While many crab species are indeed omnivorous or carnivorous, there are certain crab species that exhibit herbivorous feeding behaviors. For instance, the “herbivorous crabs” primarily consume algae and aquatic plants. These crabs use specialized mouthparts to scrape algae off surfaces and feed on plant material.
Question
Which diagram shows energy passing along a food chain?

▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Energy passing along a food chain refers to the transfer of energy from one organism to another through the consumption of food. Food chains are representations of how energy flows in an ecosystem, illustrating the sequence of organisms where each one serves as a source of food for the next. The energy originates from the Sun and is captured by primary producers, such as plants or algae, through the process of photosynthesis.
Here’s how the energy passes along a typical terrestrial food chain:
Producers (Autotrophs): These are the plants, algae, and other organisms capable of photosynthesis. They capture sunlight and convert it into chemical energy in the form of carbohydrates (like glucose).
Primary Consumers (Herbivores): These are the organisms that feed directly on the primary producers. They obtain energy by consuming plants or plant parts. Examples include animals like deer, rabbits, and grasshoppers.
Secondary Consumers (Carnivores or Omnivores): These are organisms that consume primary consumers. They get their energy by consuming herbivores. Carnivores exclusively eat other animals, while omnivores consume both plants and animals. Examples of carnivores include lions, wolves, and snakes, while humans are examples of omnivores.
Tertiary Consumers and Beyond: Depending on the complexity of the ecosystem, there can be additional levels of consumers, including tertiary consumers, quaternary consumers, and so on. Each level represents organisms that feed on organisms from the level below.
Question
Which organisms remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere?
A consumers
B decomposers
C herbivores
D producers
▶️Answer/Explanation
D producers
Producers are organisms, mainly plants and certain types of bacteria, that have the ability to perform photosynthesis. During photosynthesis, they use sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water to produce glucose (sugar) and oxygen. In this process, carbon dioxide is taken in from the atmosphere and converted into organic compounds, effectively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and helping to regulate the Earth’s carbon cycle.
