Question
(a) Fig. 7.1 shows a food chain for some organisms living in a large lake.
giant water lily $\rightarrow$ water lily beetle $\rightarrow$ frog $\rightarrow$ heron
Fig. 7.1
Table 7.1 shows some information about the organisms in the food chain in Fig. 7.1.
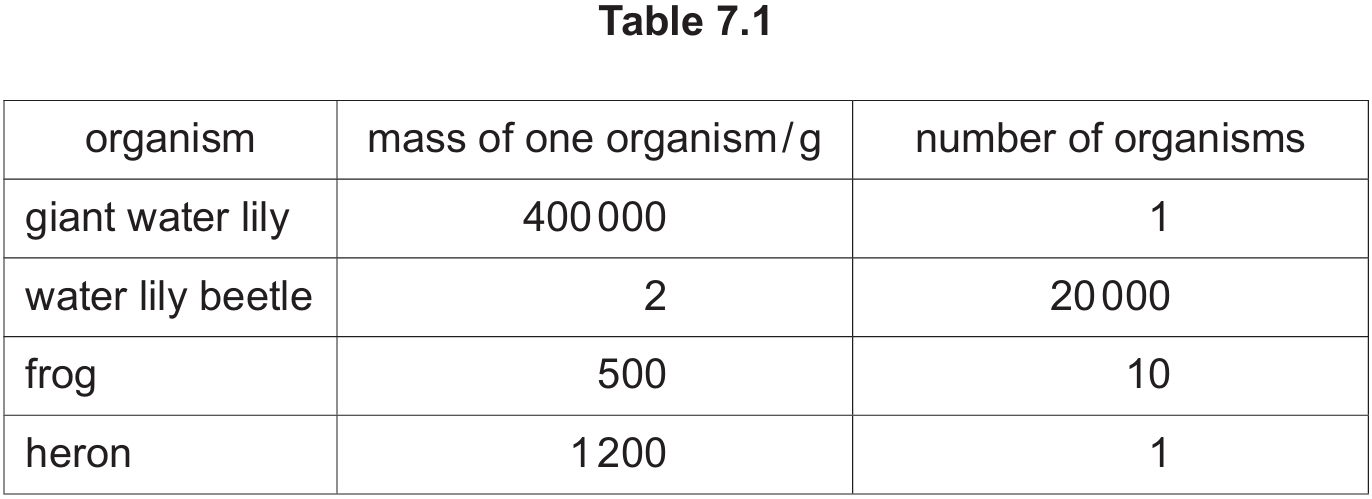
Fig. 7.2 shows pyramids based on the information in Fig. 7.1 and Table 7.1.
For the food chain in Fig. 7.1, state the letter in Fig. 7.2 which shows:
a pyramid of numbers …………..
a pyramid of biomass ……………
(b) Fig. 7.3 is a food web for a different large lake.
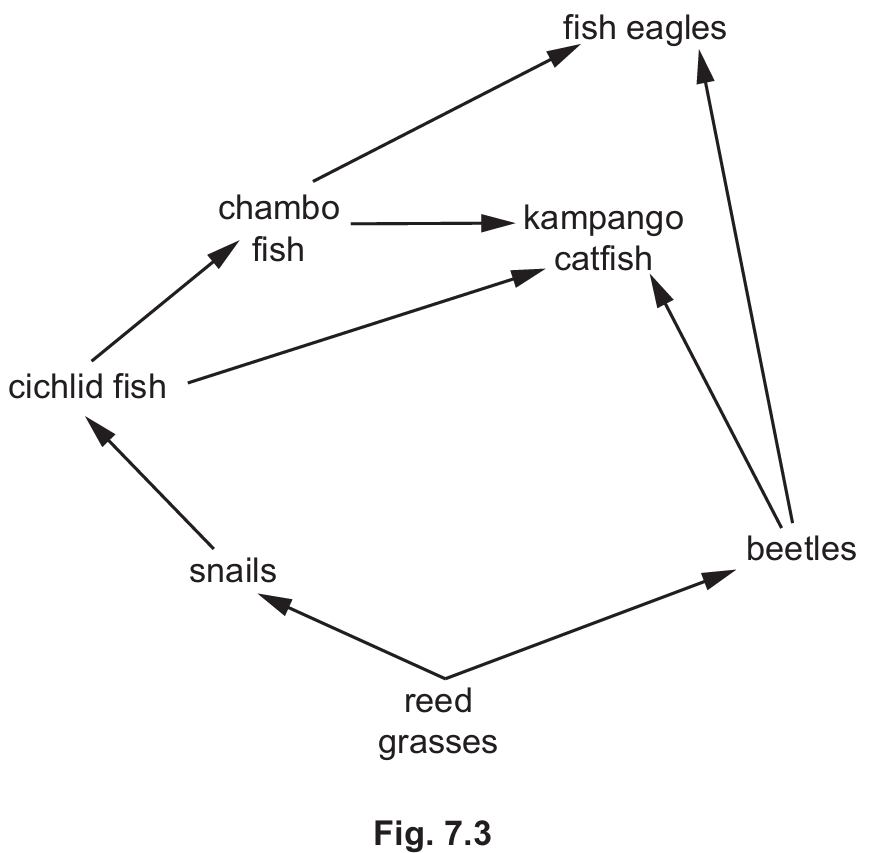
(i) State one organism, shown in Fig. 7.3, that receives energy from the chambo fish.
(ii) State the number of trophic levels in the food web shown in Fig. 7.3.
(iii) Using the food web shown in Fig. 7.3, state the name of an organism:
feeding at the second trophic level ……………………….
feeding at more than one trophic level. ……………………….
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
Pyramid of numbers: B
Pyramid of biomass: D
Explanation:
A pyramid of numbers represents the number of organisms at each trophic level. In this chain, there is 1 producer (giant water lily), which supports 20,000 beetles, followed by 10 frogs and 1 heron. This creates a shape with a very narrow base, a wide second level, and a narrowing top, matching diagram B.
A pyramid of biomass represents the mass of living material at each level. The producer has the largest biomass ($400,000 \text{ g}$), followed by the beetles ($20,000 \times 2 = 40,000 \text{ g}$), frogs ($10 \times 100 = 1,000 \text{ g}$), and heron ($150 \text{ g}$). This creates a traditional pyramid shape that gets consistently narrower towards the top, matching diagram D.
(b)
(i) Kampango catfish or fish eagle (or crocodile).
These organisms have arrows pointing to them from the chambo fish, indicating energy transfer.
(ii) 5
Note: The longest food chain shown determines the number of trophic levels. For example: Reed grasses ($1$) $\rightarrow$ Snails ($2$) $\rightarrow$ Cichlid ($3$) $\rightarrow$ Chambo ($4$) $\rightarrow$ Fish eagle ($5$).
(iii)
Feeding at the second trophic level: Snails (or beetles).
These are primary consumers feeding directly on producers (reed grasses/plankton).
Feeding at more than one trophic level: Kampango catfish or fish eagle.
For instance, the fish eagle may eat chambo fish (trophic level 4 or 5 depending on the chain) or cichlids (trophic level 3 or 4).
(c)
Possible reasons for the decrease include:
1. Overharvesting (overfishing) by humans.
2. Habitat destruction or pollution.
3. Introduction of foreign species or an increase in natural predators.
(d)
Endangered species can be conserved by:
* Monitoring and protecting species and habitats.
* Education programs.
* Captive breeding programmes.
* Creating seed banks (for plants).
(e)
A sustainable resource is defined as one which is produced as rapidly as it is removed from the environment so that it does not run out.
