Question
(a) Microplastics are pieces of plastic with a diameter less than \(0.5\, \text{cm}\).
Fig. 6.1 shows the mass of microplastics in the oceans between 2000 and 2040. The data between 2000 and 2020 is an estimate. The data after 2020 is a prediction. 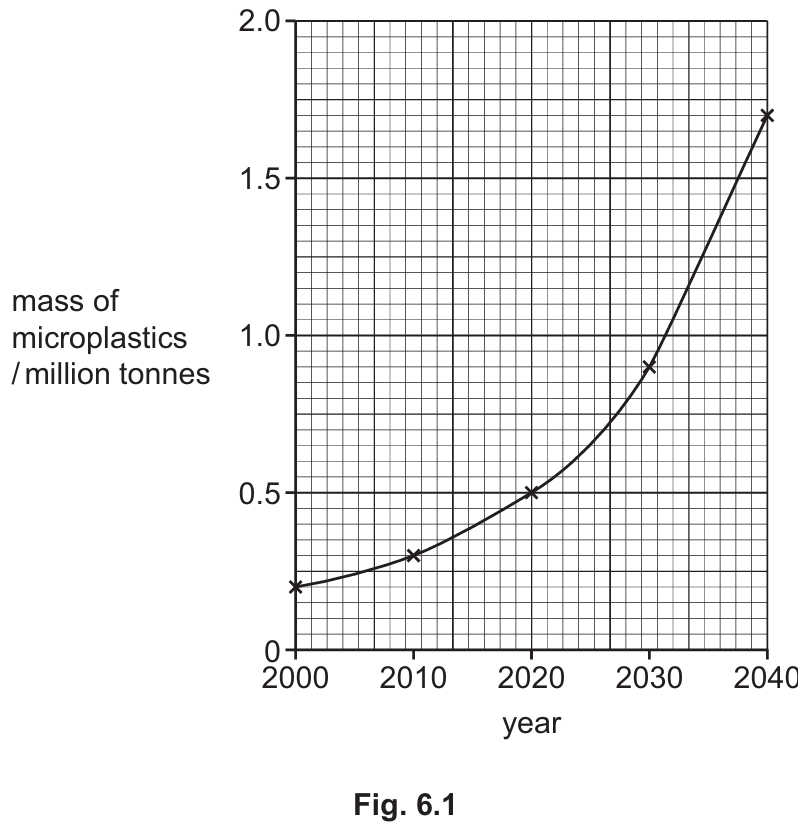
Shearwater birds feed on fish in the ocean.

Suggest how microplastics can end up in consumers such as shearwater birds.
Describe three ways the population of shearwater birds can be conserved.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)(i)
The value is an estimate because it is impossible to count every piece of microplastic in the entire ocean. The ocean is too large, deep, and largely inaccessible to survey completely. Additionally, some microplastics may have been eaten by marine organisms or settled on the ocean floor where they cannot be collected. Scientists rely on samples taken from specific areas and extrapolate the data, rather than measuring the whole.
(a)(ii)
To calculate the percentage increase:
1. Identify the initial mass in 2000: \(0.2\) million tonnes.
2. Identify the final mass in 2040: \(1.7\) million tonnes.
3. Calculate the difference: \(1.7 – 0.2 = 1.5\).
4. Calculate the percentage increase: \(\frac{1.5}{0.2} \times 100 = 750\%\).
(b)(i)
A producer is an organism that makes its own organic nutrients (like glucose). It does this using energy from sunlight through the process of photosynthesis.
(b)(ii)
Microplastics are non-biodegradable, meaning they do not break down. They are first absorbed or ingested by producers like phytoplankton. These phytoplankton are then eaten by fish (primary/secondary consumers). Finally, the shearwater birds eat the fish. The microplastics are passed along the food chain and can accumulate in the bodies of the top consumers (bioaccumulation).
(b)(iii)
Ways to conserve the population include:
• Monitoring the species numbers to track population health.
• Protecting their habitats or nesting sites to ensure they have a safe place to reproduce.
• Implementing captive breeding programmes to increase numbers before releasing them back into the wild.
• Creating laws to ban hunting or poaching of the birds.
• Education and awareness campaigns to reduce human impact.
(b)(iv)
A decrease in population size reduces the genetic variation within the species. This leads to a higher chance of inbreeding, which increases the likelihood of harmful recessive alleles being expressed (genetic diseases). With less genetic variation, the population is less able to adapt to environmental changes (like new diseases or climate change), significantly increasing the risk of extinction. It also becomes more difficult for individuals to find mates.
