Question
Woodlice are small organisms that live in damp places.
In an experiment, three live woodlice are put into a glass container. The diagram shows what happens after 30 minutes.
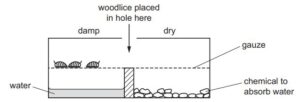
Which characteristic of living organisms is shown by this experiment?
growth
nutrition
respiration
sensitivity
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Woodlice, also known as pill bugs or roly-polies, are small crustaceans that belong to the group of isopods. They are commonly found in damp environments such as gardens, forests, and under decaying logs or rocks. They are equipped with sensory organs or receptors, known as hygroreceptors, that allow them to detect and respond to changes in their environment. They require a moist environment to thrive, as their bodies are prone to desiccation (drying out).
Over the course of 30 minutes, the woodlice begin to exhibit sensitivity towards the damp surface present in the container. The damp surface within the container provides a more suitable habitat for woodlice compared to the drier areas.
The diagram shows four animal cells, as seen under a light microscope.
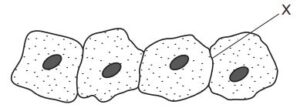
What will be present at X?
one cell membrane
one cell wall
two cell membranes
two cell walls
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
In the diagram, if two animal cells are observed under a light microscope and they are in close contact, there is a structure known as a cell junction. Specifically, at the point of contact between the two cells, there are two cell membranes. The cell membrane, also called the plasma membrane, is a thin, flexible barrier that surrounds the cell and separates its internal contents from the external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer embedded with various proteins that regulate the movement of substances into and out of the cell.
When two animal cells come into contact, they can form specialized junctions between their cell membranes. There are three types of cell junctions commonly found in animal tissues: tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap junctions. These cell membranes may be visually distinguishable as separate lipid bilayers or appear fused together depending on the type of junction present.
The diagram shows a root hair cell.
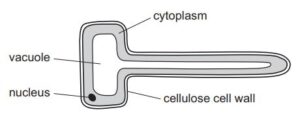
How is this cell modified for the absorption of water?
It has a cellulose cell wall.
It has a thin layer of cytoplasm.
It has a large surface area.
It has a large vacuole.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The root hair cell is specialized for the absorption of water and minerals from the soil. It possesses several structural modifications that enhance its ability to absorb water effectively. One of the key modifications is the presence of numerous root hair projections on its surface, which significantly increases the cell’s surface area.
The large surface area of the root hair cell allows for more contact with the soil particles and a greater surface area for water absorption. This is important because water moves into the cell through osmosis, which is the process of water moving from an area of higher concentration (in this case, the soil) to an area of lower concentration (inside the cell). By having a larger surface area, the root hair cell can absorb water more efficiently and maximize the absorption of water and dissolved minerals from the surrounding soil.
Question
The diagram shows two cells.
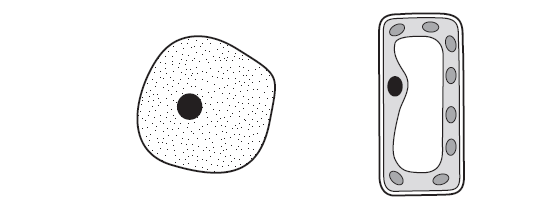
Which process can be carried out by only one of these cells?
A controlling the chemical reactions in the cell
B controlling the movement of substances into the cell
C making starch inside the cell
D using glucose inside the cell
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The process that can be carried out by only one of the cells shown in the diagram is C) making starch inside the cell.
Starch synthesis, or the production of starch, is primarily carried out by plant cells, particularly in the chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, a process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy in the form of glucose. Plants then utilize this glucose to produce other organic compounds, including starch, which serves as a storage form of energy.
Animal cells do not possess chloroplasts and are unable to carry out photosynthesis or synthesize starch. Instead, animal cells obtain energy by breaking down glucose through cellular respiration to produce ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells.
Question
The diagram shows a palisade mesophyll cell from a green leaf.
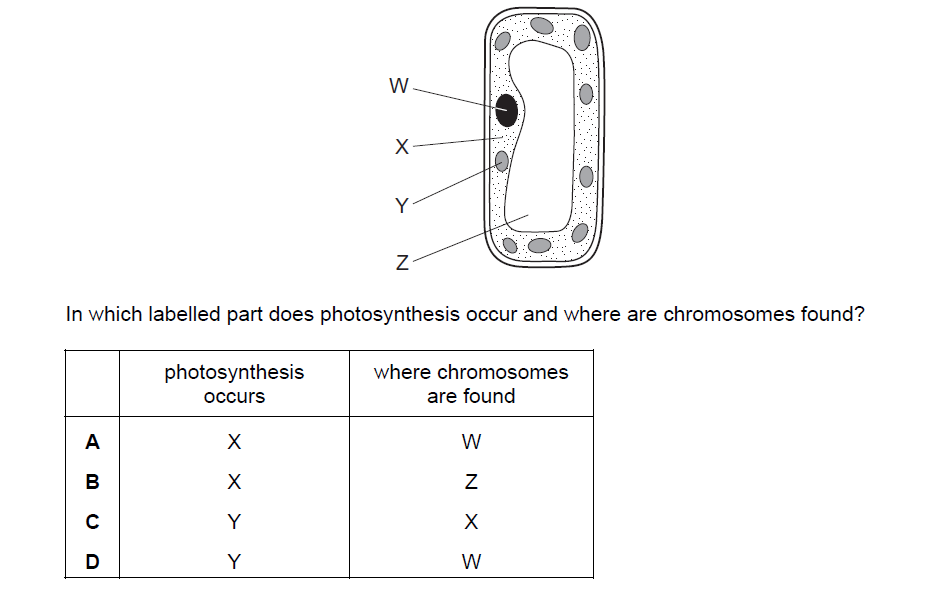
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
In the diagram, the part labeled “Y” is where photosynthesis occurs, and the part labeled “W” is where chromosomes are found.
1. Part Y: Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the cells of the palisade mesophyll layer in leaves. The palisade mesophyll cells are located in the upper part of the leaf and contain numerous chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are responsible for capturing sunlight and converting it into chemical energy through the process of photosynthesis. This energy is then used to produce glucose, which serves as a source of energy for the plant.
2. Part W: Chromosomes are found in the nucleus of cells. The nucleus is the control center of the cell and contains genetic material in the form of DNA organized into structures called chromosomes. Chromosomes carry the genetic information that determines the characteristics and traits of an organism. In the diagram, the part labeled “W” likely represents the nucleus of the palisade mesophyll cell, where the chromosomes are located.
It’s important to note that while the palisade mesophyll cells are involved in photosynthesis, chromosomes are present in all cells of an organism and are not directly related to photosynthesis itself.
