Question
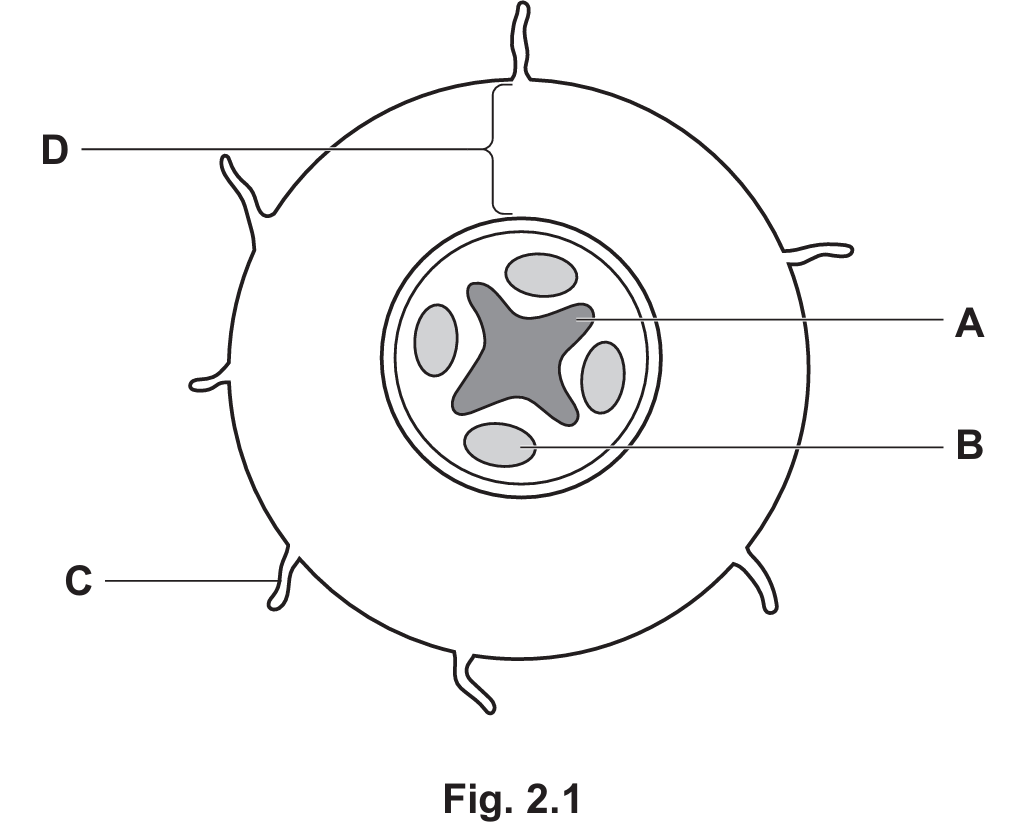
(a) (i) State the letter in Fig. 2.1 that shows:
- a tissue that transports amino acids ……………
- xylem tissue. …………..
(b) State two functions of xylem.
(ii) State the process by which water enters structure C in Fig. 2.1.
(iii) State the feature of C in Fig. 2.1 that increases the uptake of water.
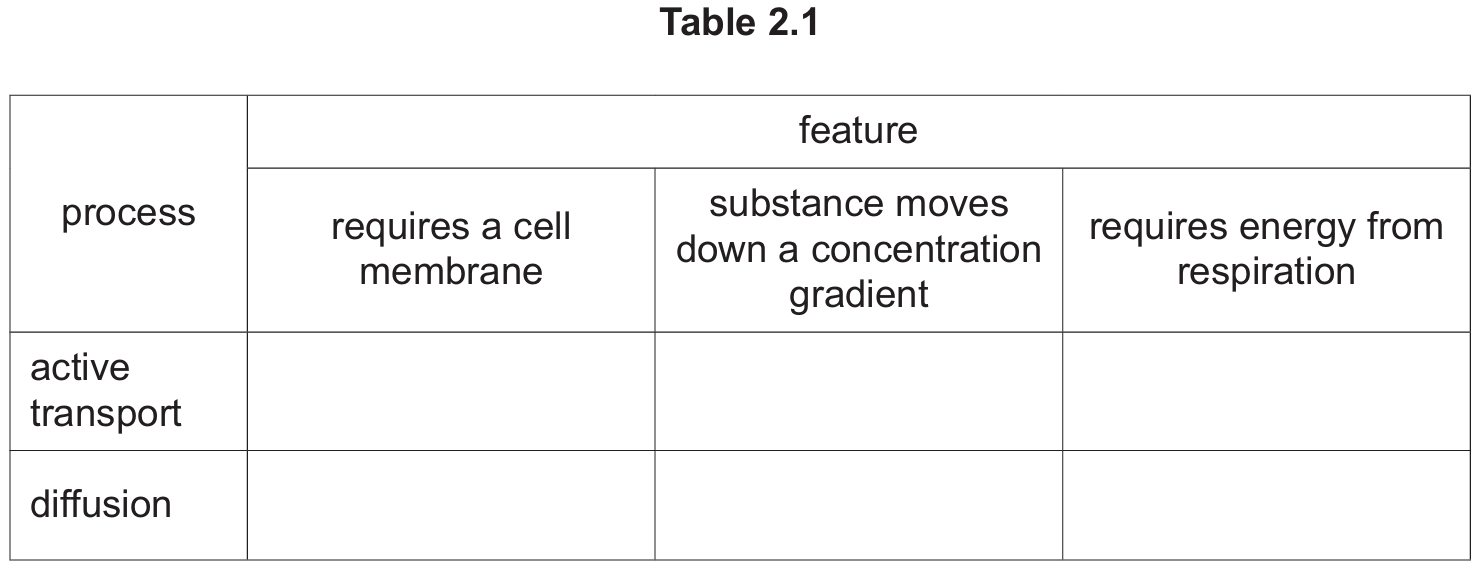
(d) Table 2.1 shows some features of processes that can be used to move substances.
Place ticks (\(\checkmark\)) in the boxes to show the correct features for each process.
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a) (i)
Tissue that transports amino acids: B (Phloem)
Xylem tissue: A
Explanation: In the root of a dicotyledonous plant, the vascular tissues are centrally located. The xylem (A) typically forms a central star shape or cross, and the phloem (B) is located between the arms of the xylem star. Phloem is responsible for the transport of sucrose and amino acids.
(a) (ii)
Name of cells in D: Cortex cells
Explanation: The cortex is the tissue located between the epidermis and the central vascular cylinder. Water passes through root cortex cells on its way to the xylem.
(b)
1. Transport of water and mineral ions
2. Support
Explanation: Xylem vessels have thick walls strengthened with lignin (even though details of lignification are not required for Core, the support function is key). This allows them to withstand pressure and support the plant while transporting water.
(c) (i)
Structure C: Root hair cell
(c) (ii)
Process: Osmosis
(c) (iii)
Feature: Large surface area
Explanation: Root hair cells are adapted for absorption. Their long, hair-like extensions provide a large surface area to maximize the rate of absorption of water and mineral ions from the soil.
(d)
Completed Table 2.1:

Explanation:
Active Transport requires energy (from respiration) to move particles against a concentration gradient, using protein carriers in the cell membrane.
Diffusion is the net movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to lower concentration due to random movement. It does not require energy.
(e)
Structure: Mitochondria
Explanation: Aerobic respiration is the chemical reaction in cells that uses oxygen to break down nutrient molecules to release energy. This process occurs in the mitochondria.
