Question
Bacteria and animals are found in many habitats on land and in the sea.
(a) State two ways in which the structure of a bacterial cell differs from the structure of an
animal cell.

(b) Some bacteria were grown in the laboratory. Fig. 6.1 shows the change in numbers of
bacteria when grown in a closed flask containing nutrients and oxygen.
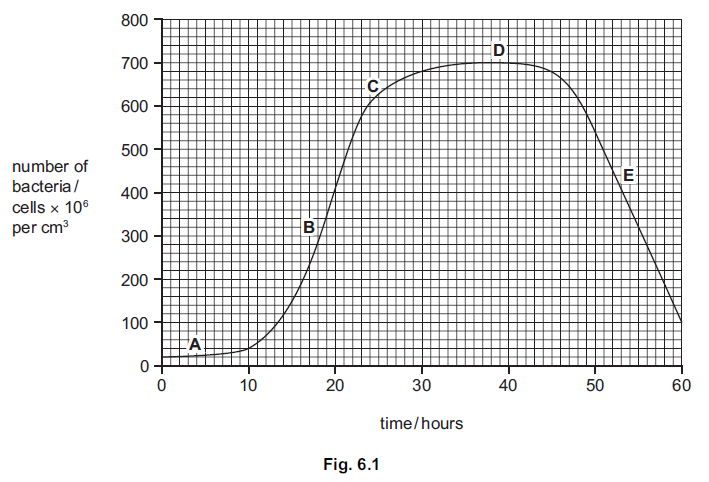
(i) Name the phases of growth, A and B.

(ii) Explain why the numbers of bacteria do not change in phase D and decrease in
phase E.

(c) Fig. 6.2 shows the vent crab, Bythograea thermydron, which lives at great depths in the
sea where there is no light.
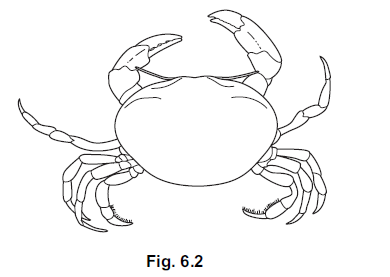
(i) State one feature, visible in Fig. 6.2, that show that B. thermydron is an arthropod.
![]()
(ii) Although most species of crabs are red, brown or green, B. thermydron is white.
Suggest and explain how white crabs evolved at great depths in the sea.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Question
A biologist made a slide of some epidermal cells from a scale leaf of an onion bulb.
Fig. 4.1 is a drawing that the biologist made of one of the cells.
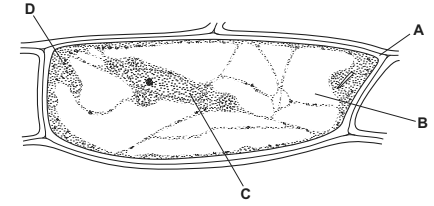
Fig. 4.1
(a) Table 4.1 shows the functions of the structures within a plant cell.
Complete the table by:
naming the part of the cell that carries out each function
using the letters from Fig. 4.1 to identify the part of the cell named.
Table 4.1
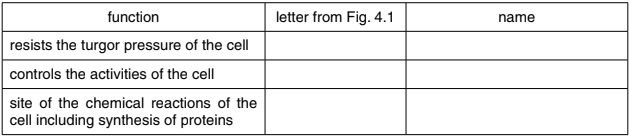
(b) The biologist added a few drops of concentrated salt solution to the cells on the slide and took a photograph of the cells, as shown in Fig. 4.2.
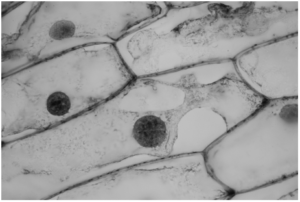
(i) With reference to Fig. 4.2, describe the effect on the plant cells of adding a concentrated salt solution.
(ii) Use the term water potential to explain the effect you have described.
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
(a) 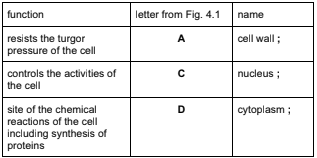
(b) (i) cytoplasm/ vacuole, decreases in, size/ volume ;
(some) cell membrane/ cytoplasm, pulls away /AW, from cell wall ;
plasmolysis / cells are plasmolysed ;
cells, are flaccid/ not turgid/ lose turgor ;
cell walls no longer, pushed outward/withstand pressure ;
(ii) salt solution has a lower water potential than the cell ; ora
water moves out of the cells, by osmosis ;
down a water potential gradient/ from a high(er) water potential to a low(er) water potential ;
through a partially permeable membrane ;
